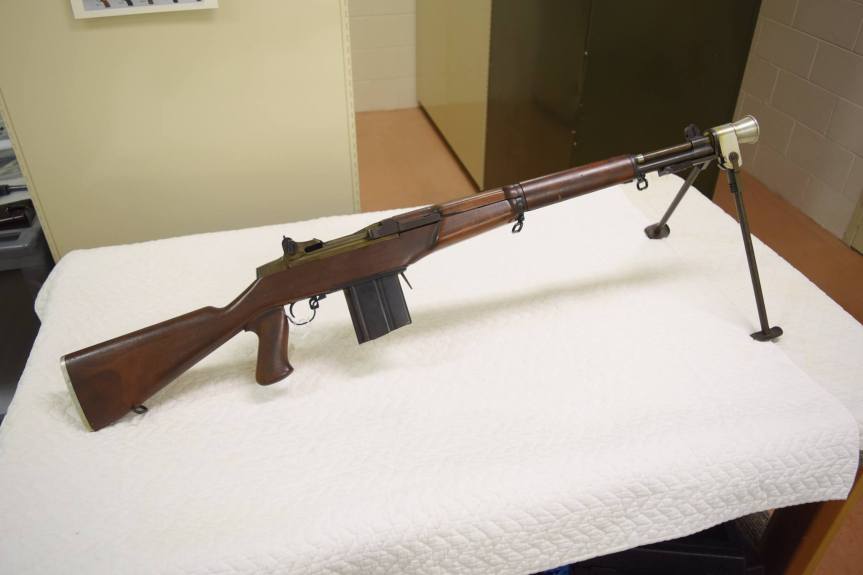
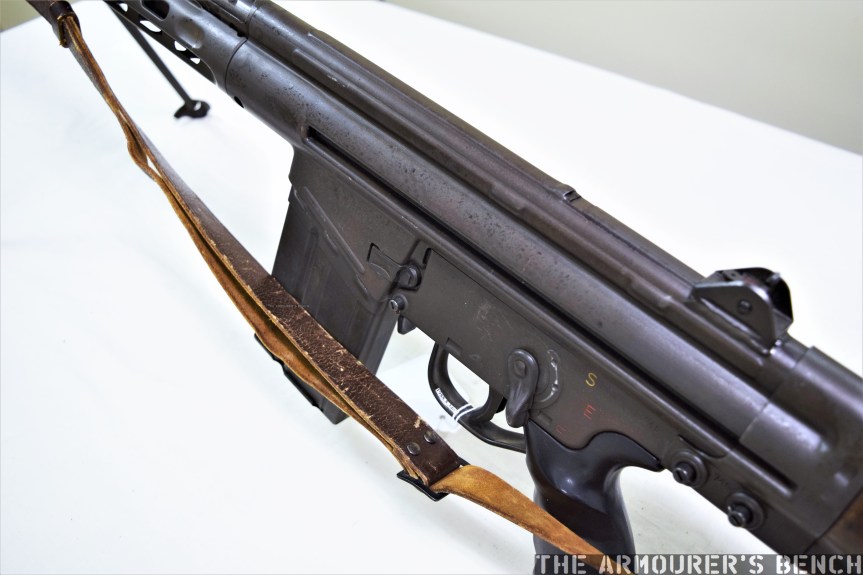
The Type 64 is an integrally suppressed submachine gun designed in China in the early 1960s, taking several design elements from other Combloc small arms. The guns were manufactured at one of China’s State Factories (with the factory’s ‘66’ in a triangle marking in the left side of the receiver – this indicates the factory number, although available sources differ on which it refers to, either 66, 626 or 366).

Designed concurrently with the Type 64 suppressed pistol during the 1960s, the Type 64 SMG was developed for Communist China’s special forces for use in clandestine operations. Chambered in the standard 7.62×25 ComBloc pistol round, the Type 64 functioned best with Type 64 subsonic ammunition, a special subsonic spitzer projectile variation of the standard 7.62mm pistol round. It did not chamber the low power 7.65x17mm round used by the Type 64/67 pistols.

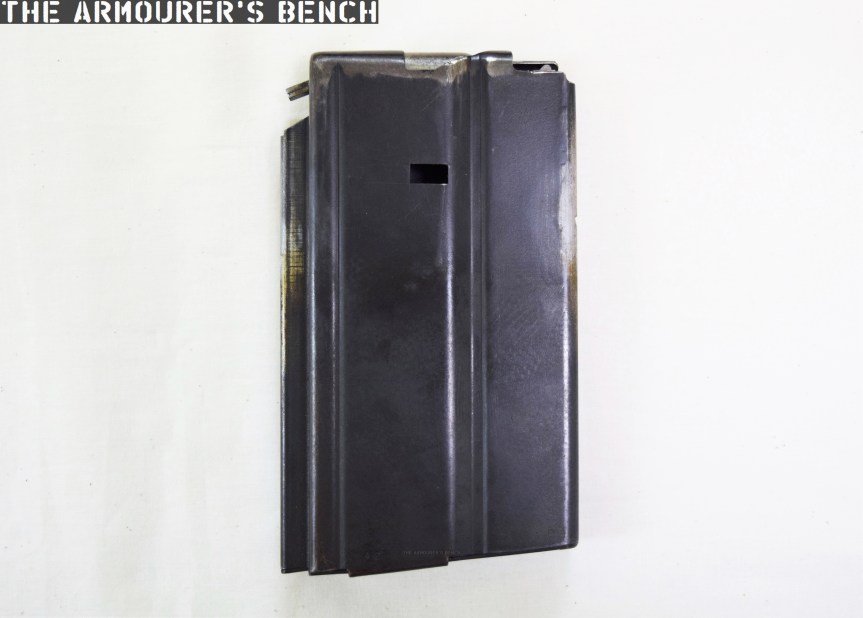
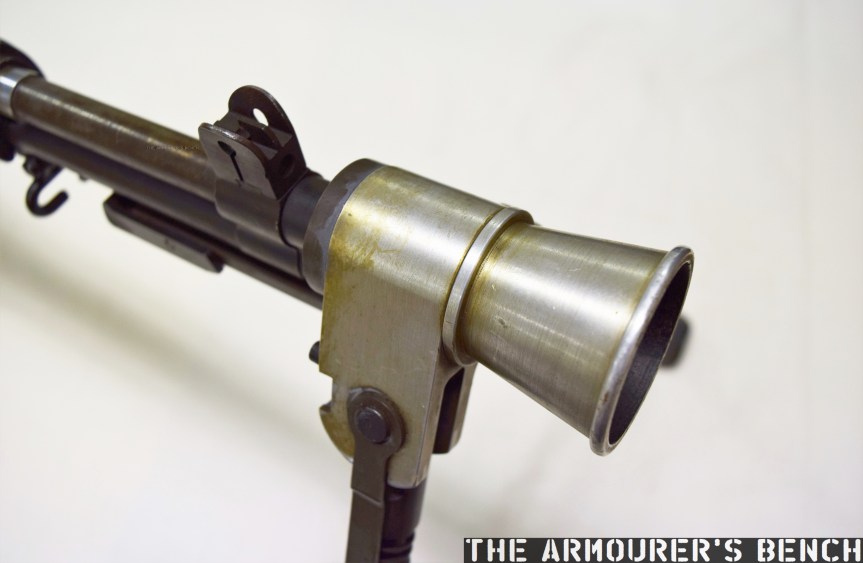
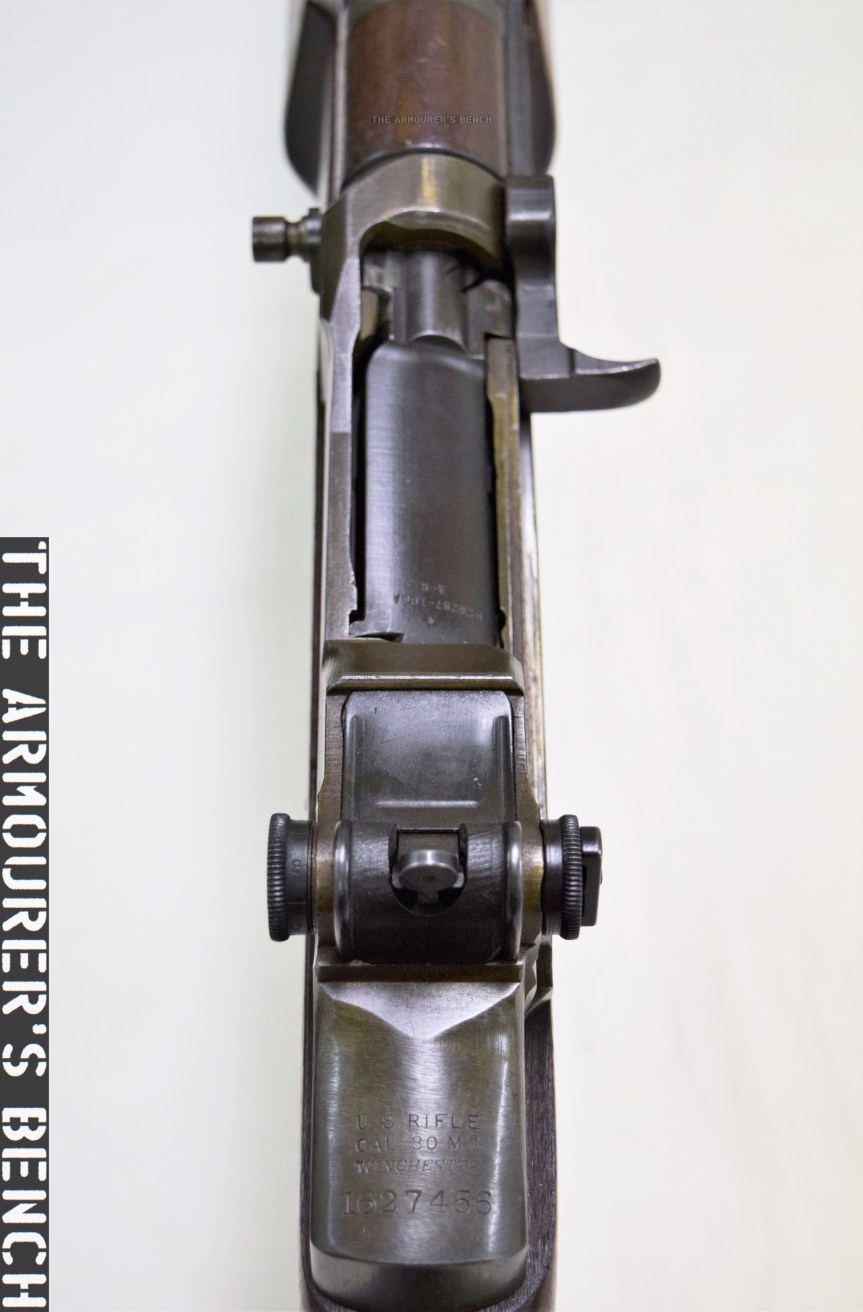
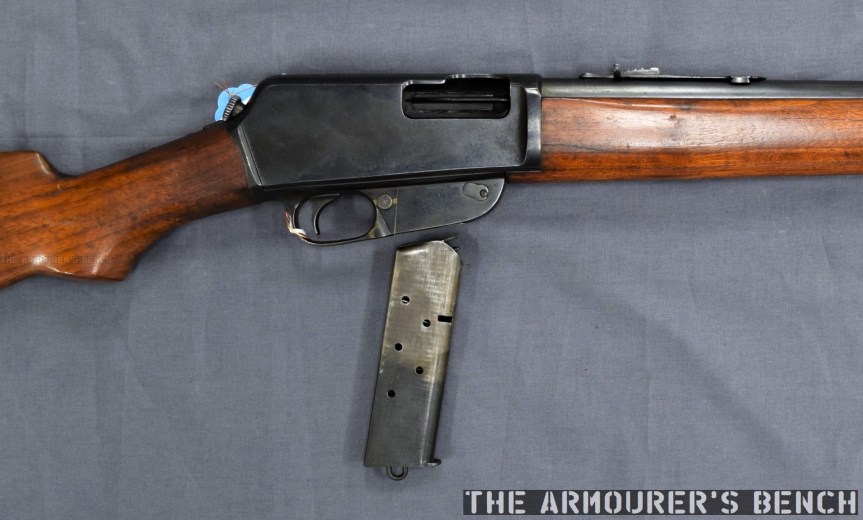
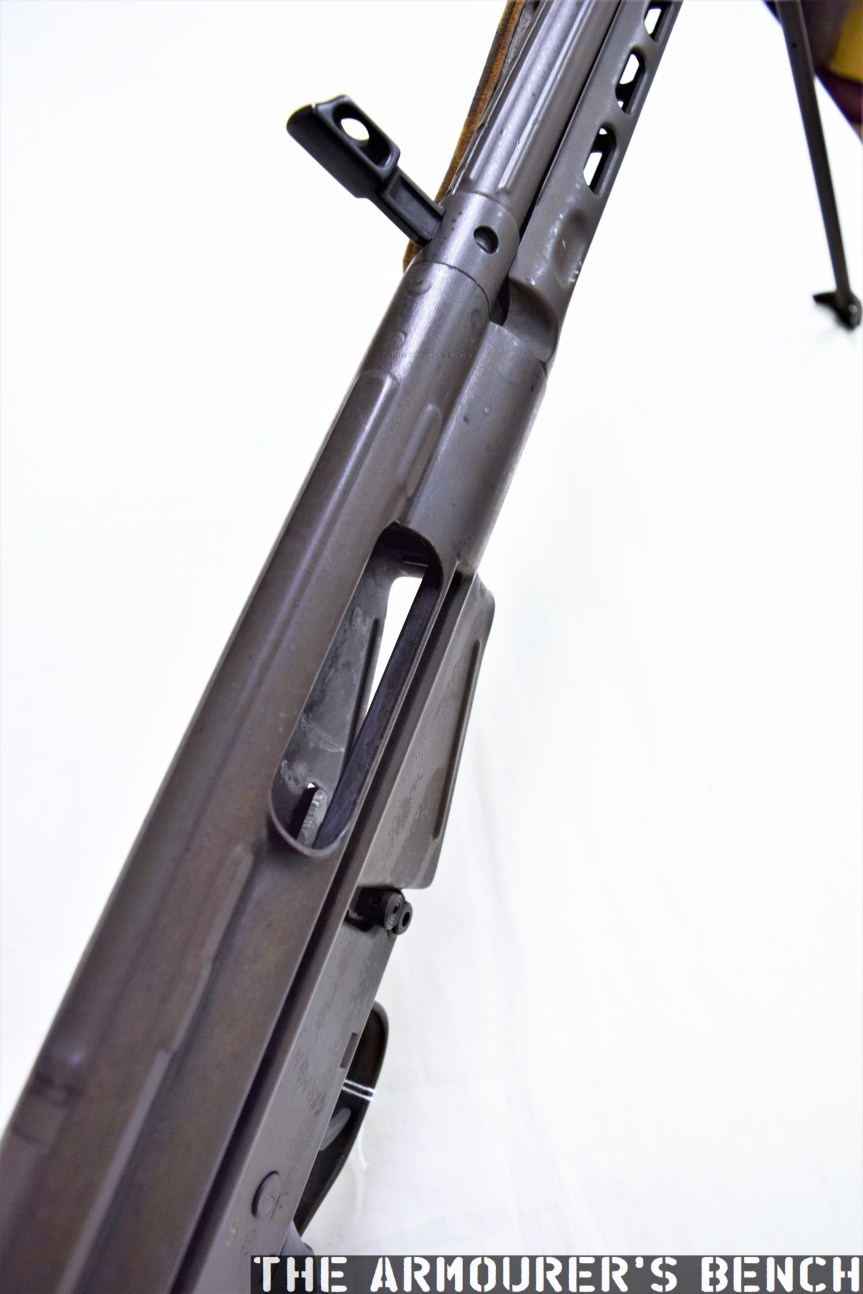
The Type 64 fed from 20 or 30 round double stack magazines which were reportedly developed from or at least influenced by the Soviet PPS-43’s double stack, double feed magazines. The weapon used a conventional blowback action and fired from an open bolt. Its maximum effective range was approximately 200 metres with two position flip up sights ranging out at 100 and 200 metres.
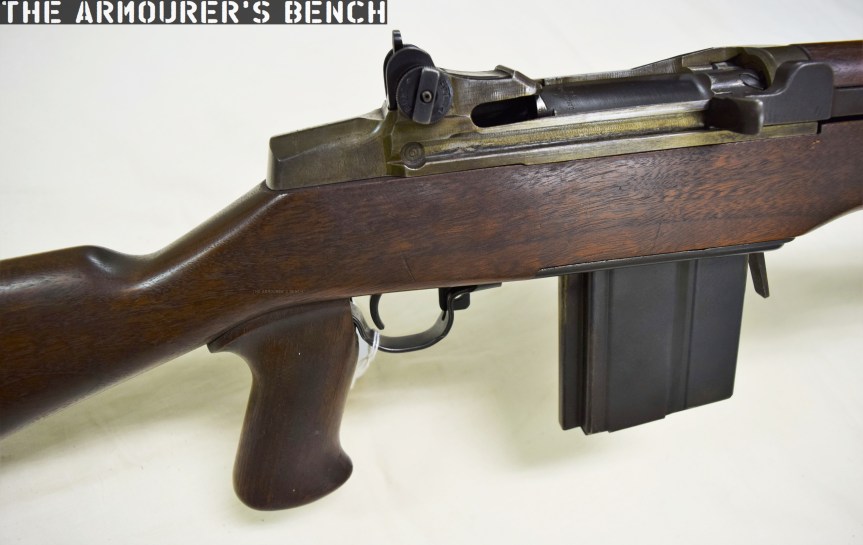
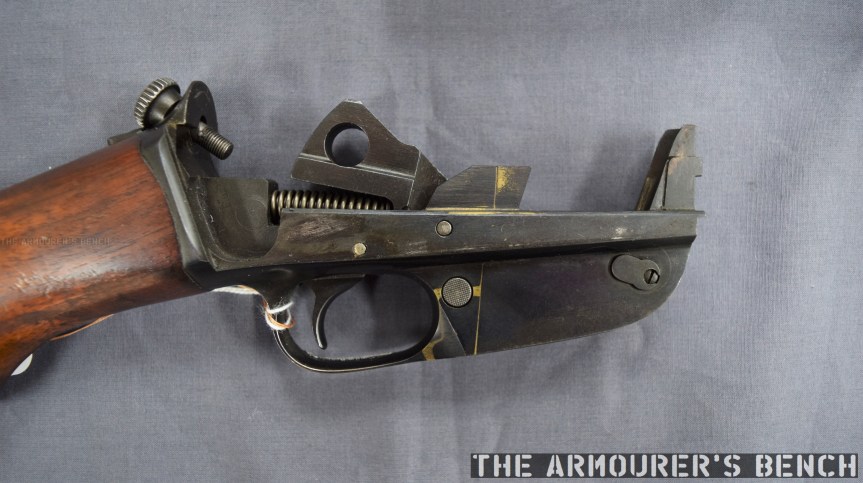
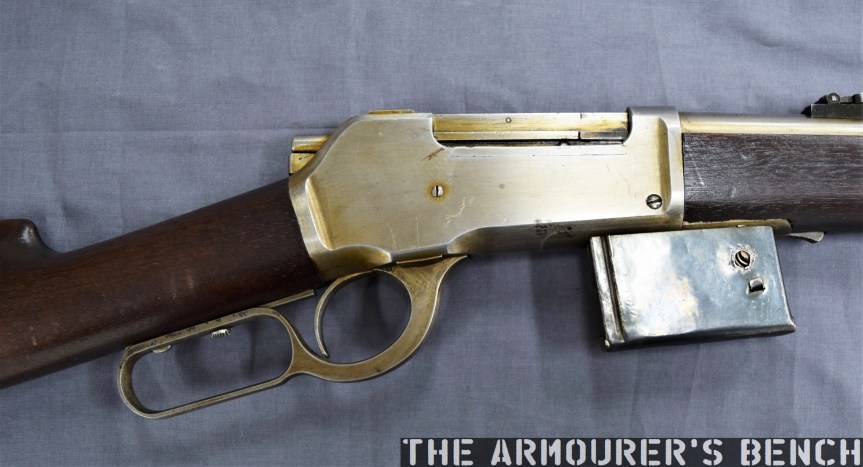
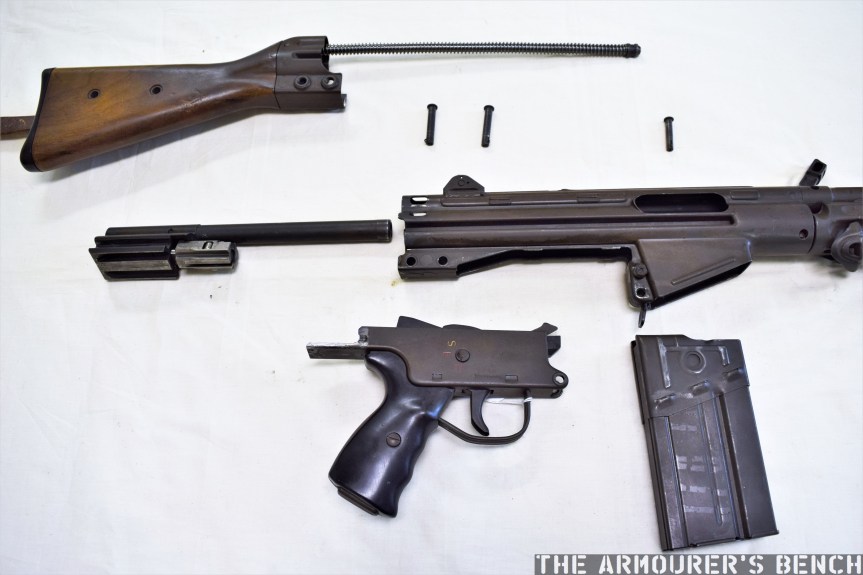
The Type 64 had a milled receiver with lightening cuts and weighed in at 7.6lb or 3.5kg unloaded. It took its bolt from the Russian PPS-43 submachine gun and a trigger group inspired by the ZB vz.26 light machine gun’s, which was well liked by the Chinese military.

The Type 64 shared a number of external similarities with the standard Type 56 AK-clone including its pistol grip, safety lever and under-folding stock (which is similar but slightly different to the Type 56-I’s under-folding stock).

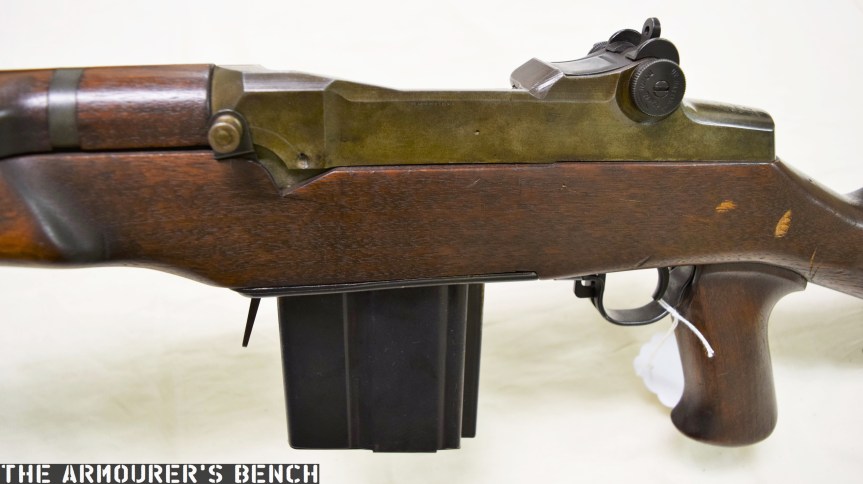
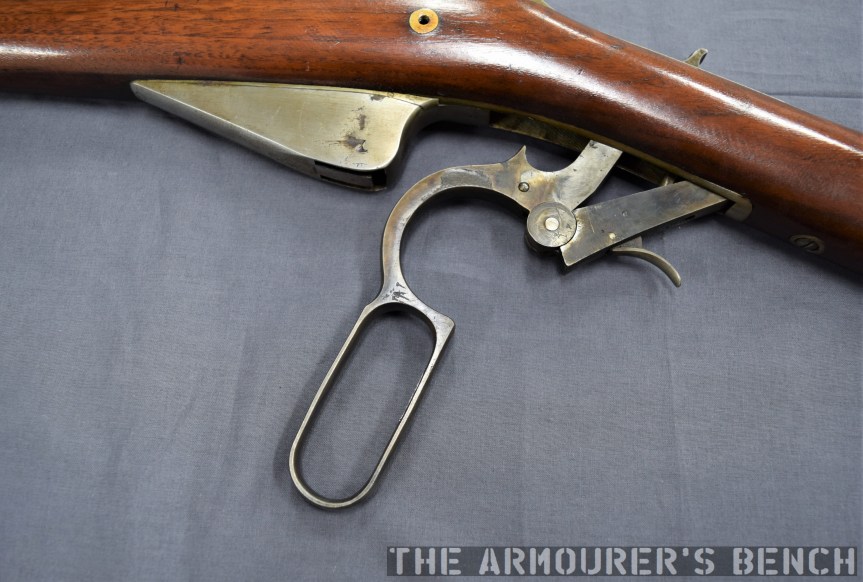
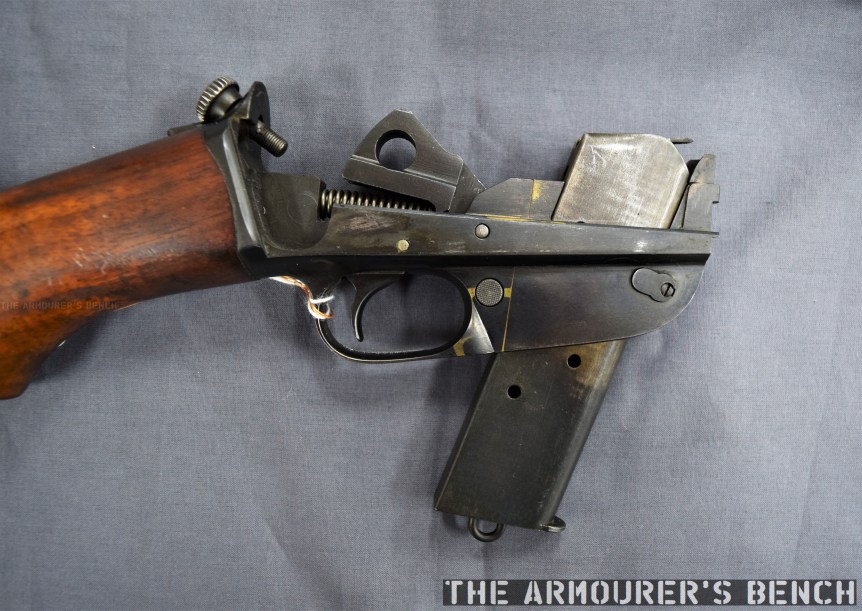
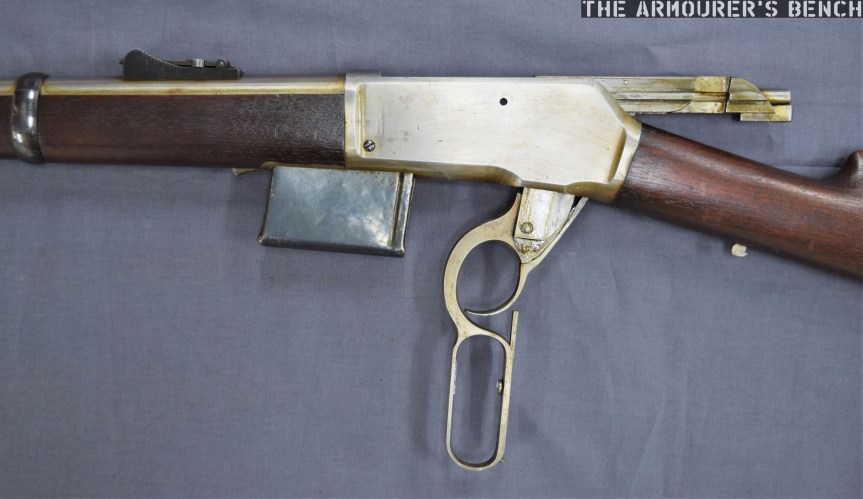
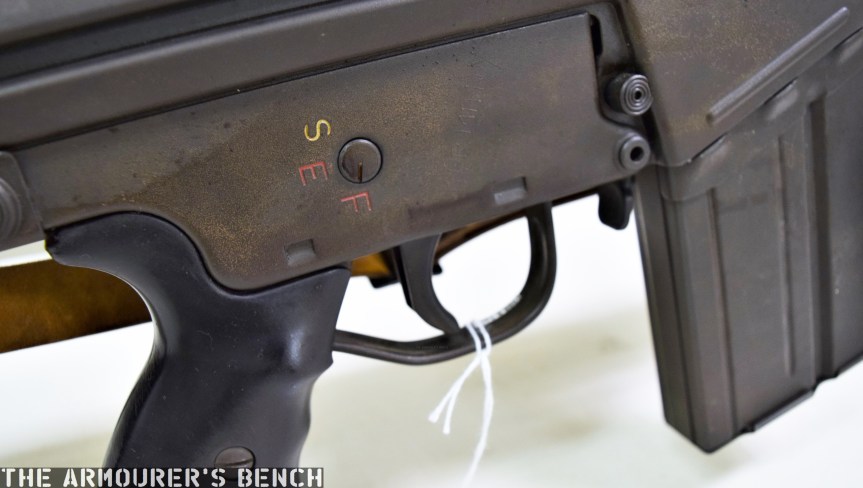
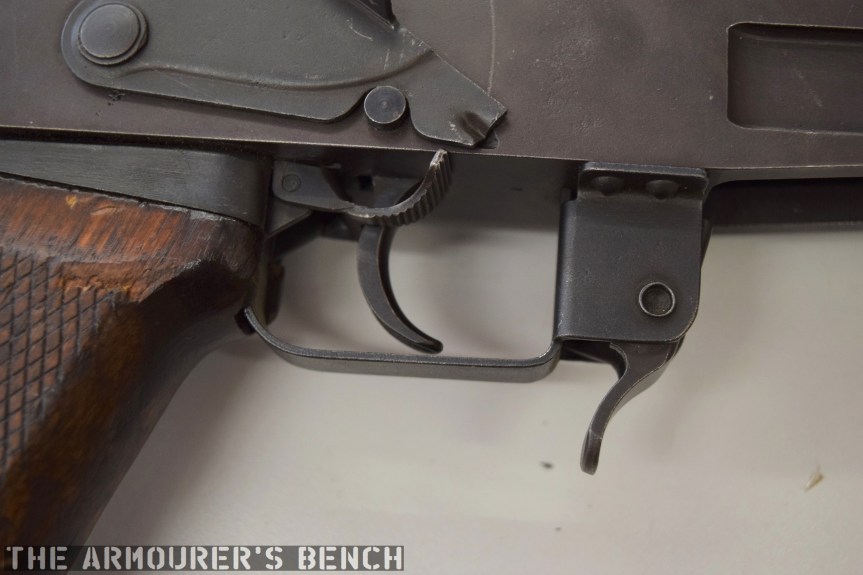
The weapon has a number different controls including a conventional AK-style safety-come-dust cover, on the right side of the receiver – which blocks the travel of the bolt. On the opposite side of the receiver it has a two-position fire selector for semi and full-auto – you can just about reach these when the stock is folded. The forward position is for semi and the rearward position is full-auto. Finally, the 64 also has an additional trigger block safety, taken from the SKS, which pivots forward to prevent the trigger from being pulled.

According to a report written in October 1971, by the Small Arms Systems Lab of the US Army Weapons Command Research and Engineering Directorate, the weapon has an extremely high rate of fire of over 1,300 rpm.
A cyclic rate that high was the result of a combination of back pressure from the suppressor, the ammunition used and its blowback action. The Type 64’s chamber was fluted with three longitudinal cuts to aid extraction at its high rates of fire. It should be noted, however, that the 1971 US army tests were carried out with standard velocity ammunition – rather than the specialised subsonic Type 64.

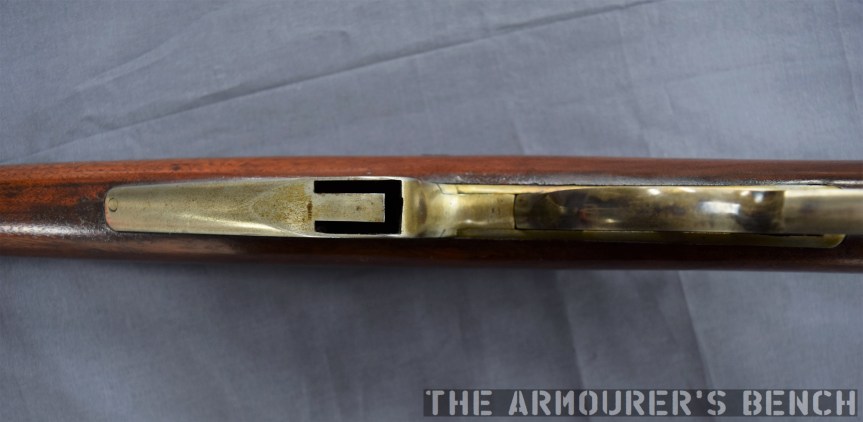
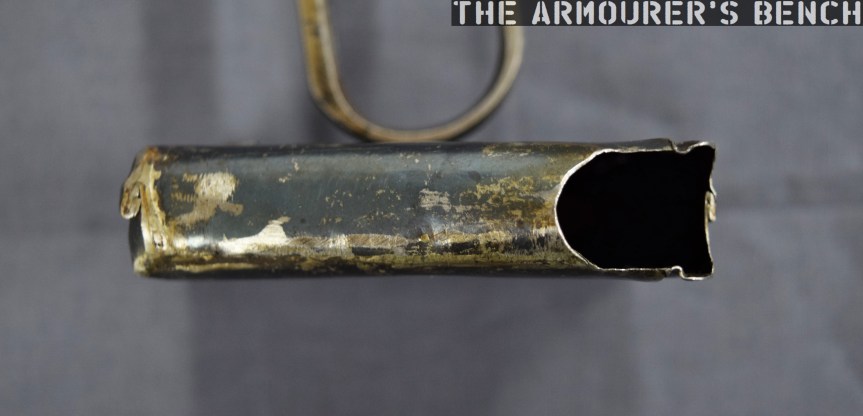
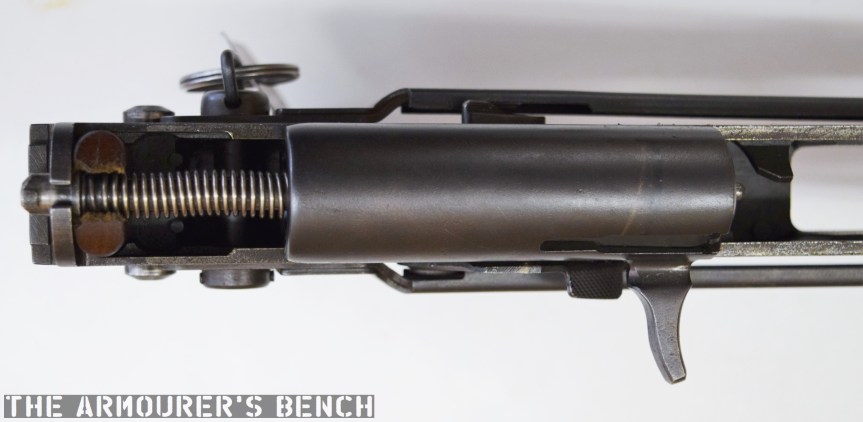
The top cover is removed by pushing in what at first appears to be a spring-loaded detent, but is actually the recoil spring guide rod. The front of the top cover is held in the receiver by a lip which fits into a slot just above the breech. The top cover itself is a thin piece of stamped sheet metal with the serial number stamped at the rear.

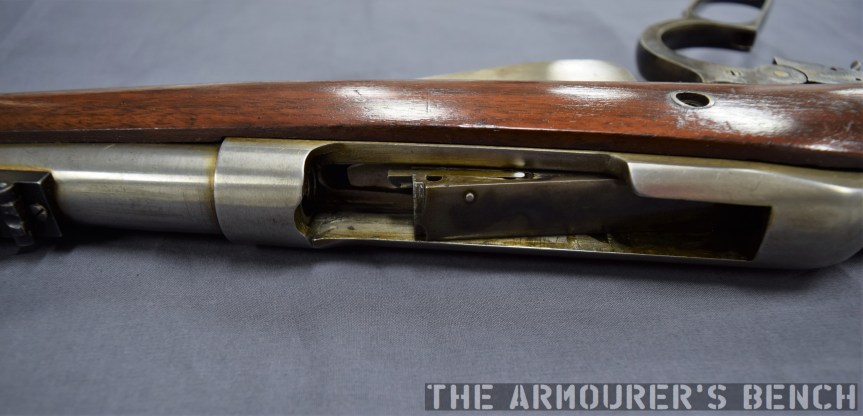
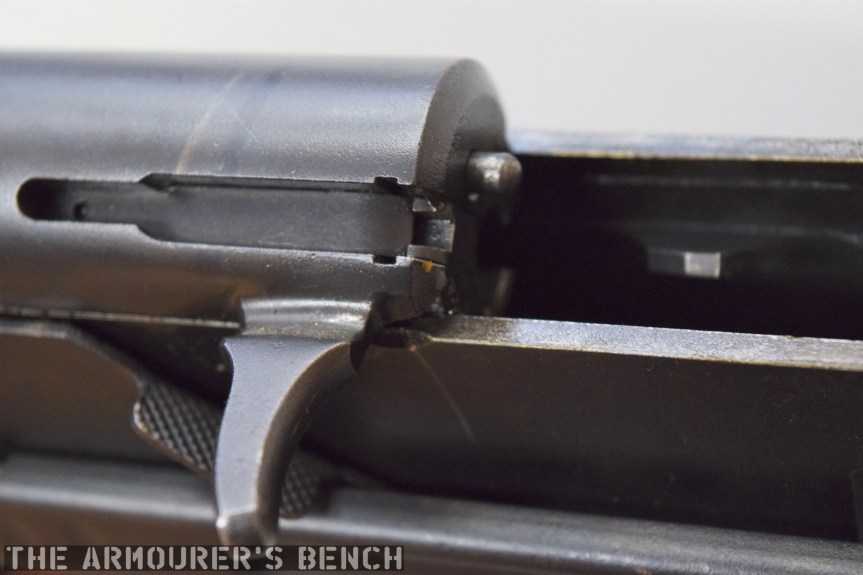
With the top cover removed we can see inside the action. The 64 has a single recoil spring held in place by a guide rod. At the rear of the receiver is a small plastic buffer, designed to both soak up some of the recoil energy and to help reduce action cycling noise. There is an ejector on the left side of the receiver and guide rails along which the bolt moves. To remove the bolt it is pulled fully to the rear and then tilt it upwards.

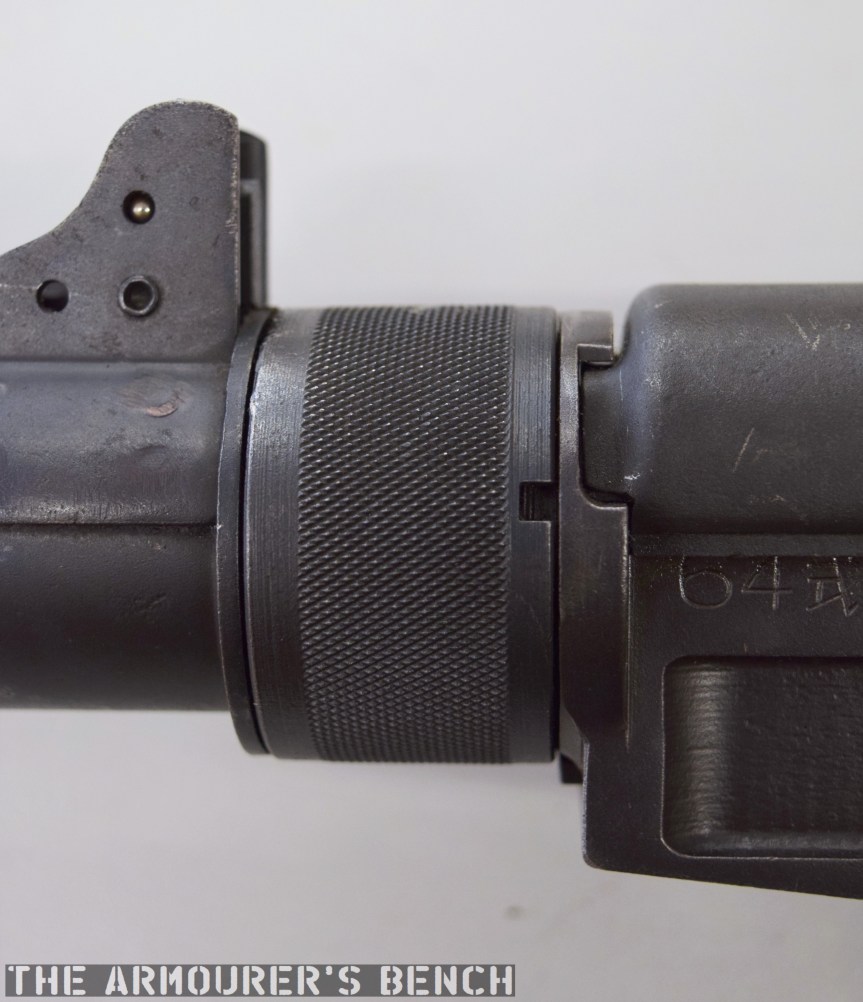
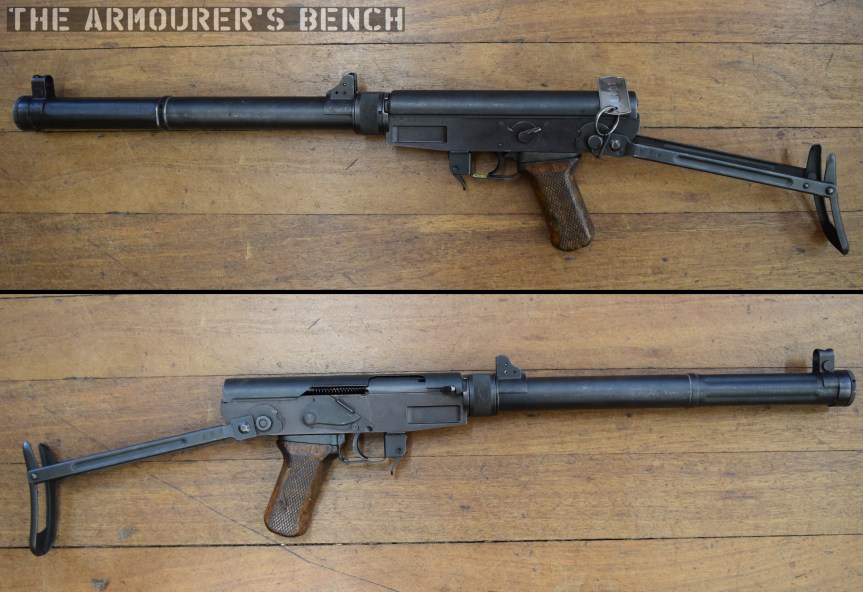
The Type 64 is a pretty compact weapon despite the length of its suppressor. It has an under-folding stock, with two spring-loaded buttons at the rear of the receiver which have to be pushed in to fold and unfold the stock. When folded the weapon is 25in (or 63.5cm) long, with the stock adding 8 inches when it is deployed. The weapon can be used with the stock folded, although some of its controls are partially obscured.
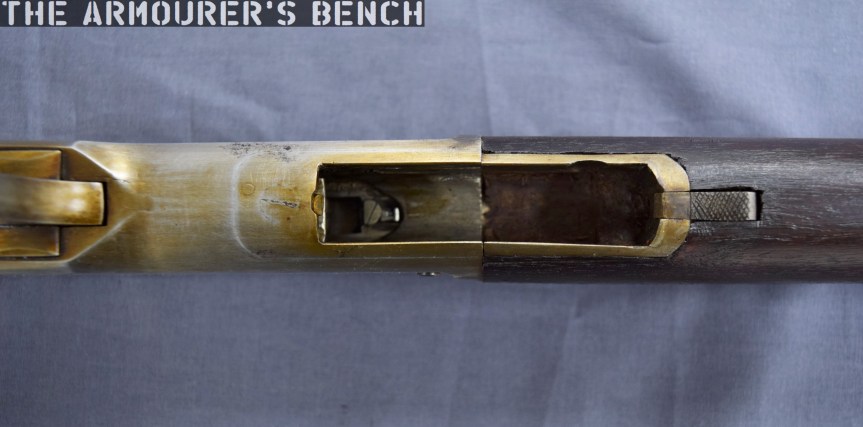
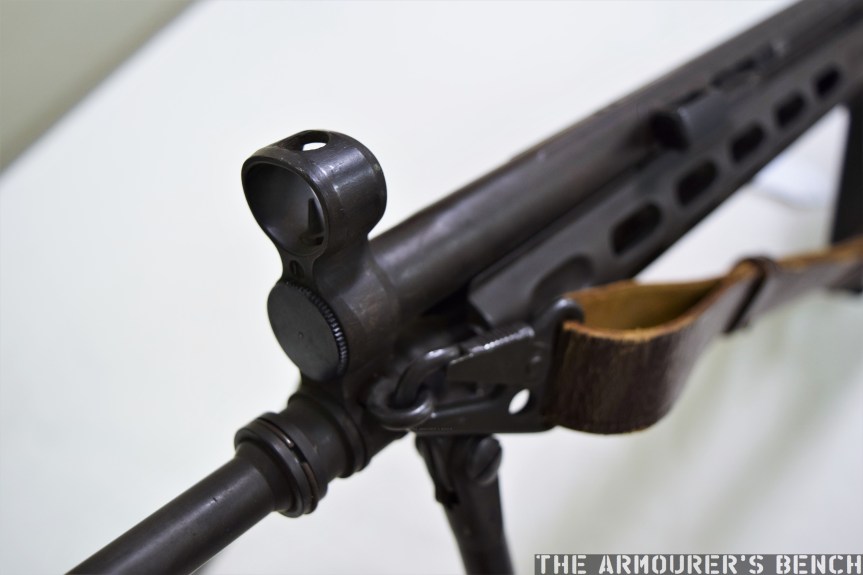
The suppressor is contained by a housing which attaches to the receiver by an interrupted thread. The Type 64’s barrel was ported with 36, 3mm vents at the muzzle-end while the suppressor has 12 metal dished baffles held captive on a pair of guide rods. The weapon’s sights are mounted on the suppressor housing which attaches to the receiver by an interrupted thread. Sadly, I didn’t have time to strip the suppressor itself but the photos below, from my friend Chuck over at Gunlab, show the Type 64’s ported barrel and baffles well.

The 1971 Small Arms Systems Lab report found that the audible report of the gun, was 150db at the rear of the receiver and 157db 12 feet down range, however, this is probably not the best indication of the Type 64’s capabilities as the report states that the gun was tested with Chinese Type 51 standard velocity 7.62x25mm ammunition. Ideally, the weapon would have been used with subsonic Type 64 ammo specially developed for China’s suppressed pistol-calibre weapons. Chinese sources reportedly put the weapons noise level at 84db when using subsonic ammunition. The US report did note that while its noise suppression wasn’t outstanding, it very effectively hid its muzzle flash.

It appears to have been primarily used by Chinese scouts and special forces and saw action during the 1979 Sino-Vietnamese War. In the late 80s the Chinese replaced the Type 64 with the suppressed version of the Type 85 submachine gun, also chambered in 7.62x25mm, which used the same magazines, the Type 85 had a tube metal and stamped receiver which was simpler to manufacture than the 64’s machined receiver. The Type 85 has subsequently been superseded by guns like the bullpup Type 05.
Special thanks to the collection that holds this weapon for allowing me to take a look at it. As always guys thank you for watching. If you enjoyed the video please share it with friends and help us
If you enjoyed the video and this article please consider supporting our work here. We have some great new perks available for Patreon Supporters.
Specifications:
Overall Length: 33.2in w/stock deployed
Barrel Length: 9.6in
Weight: 7.6 lbs
Action: Blowback, open bolt
Capacity: 20 or 30-round box magazines
Calibre: 7.62x25mm
Bibliography
Primary Sources:
‘Technical Notes: Chinese Communist 7.62mm Type 64, Silenced Submachine Gun’, US Army Weapons Command Research & Engineering Directorate Small Arms Systems Laboratory, J.J. Boccarossa, 27/09/1971
Secondary Sources:
Chinese Type 64 SMG, Small Arms Review, F. Iannamico (source)
Type 64 submachine gun (PR China), Modern Firearms, (source)
Chinese Type 64 suppressed SMG, ForgottenWeapons.com (source)