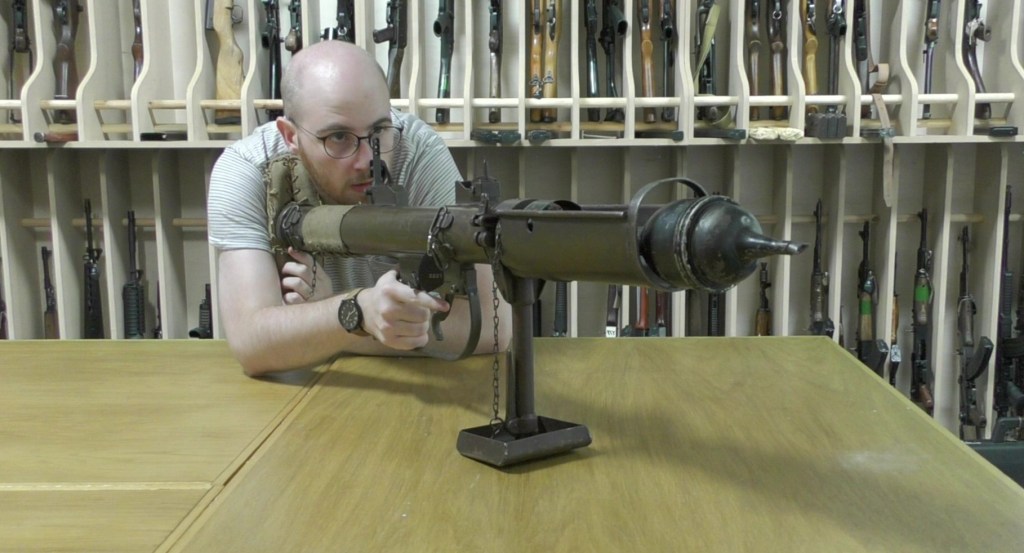
In late 1944, a platoon of Canadian sappers built an intriguing in-field adaptation to a Universal Carrier (sometimes known as Bren Gun Carrier) – they developed a PIAT Carrier.
The 16th Field Company, Royal Canadian Engineers were attached to the 3rd Canadian Division during operations in northwest Europe. Each Canadian division had a Divisional Royal Canadian Engineers Group attached to it, made up of several field companies. In November 1944, the 16th Field Company, RCE was located near Nijmegen.

The experiments which led to the PIAT Carrier were embarked on after the division’s commander, Major General Daniel Spry, put out a directive for ‘harassing weapons’ to be developed. The interesting adaptation was somewhat reminiscent of a miniature Soviet Katyusha or Commonwealth Land Mattress. While similar in concept to these multiple rocket launchers, it is important to remember that the PIAT isn’t a rocket launcher – but a spigot mortar.
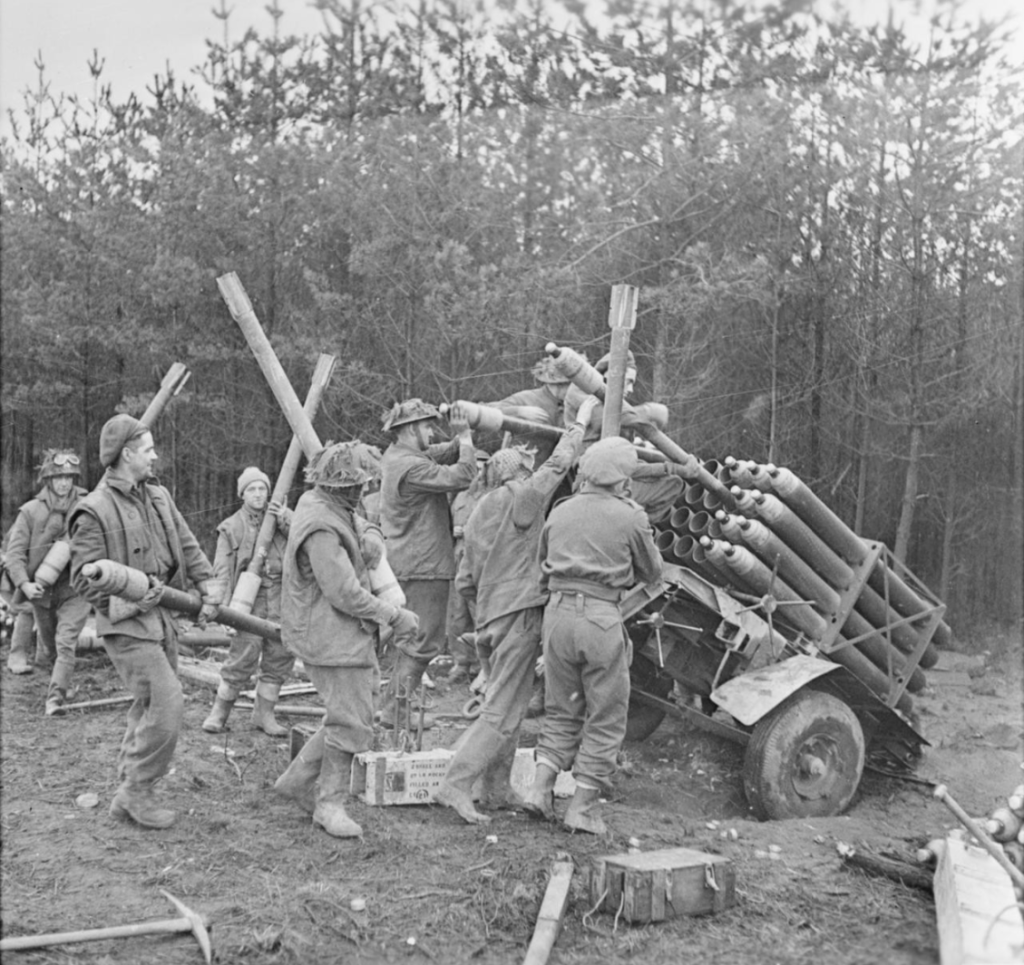

The Canadian engineers mounted the PIATs in two rows at an obtuse angle at the rear of the Universal Carrier, presumably for use in a limited bombardment role. The idea behind the outfitting of the Carrier appears to have been to utilise the PIAT in its secondary, indirect role as a mortar, perhaps for fire against buildings or to harass enemy positions. From photographs taken in the field we can see that the engineers of 16th Field Company fixed the PIATs into a wooden frame at the rear of the Carrier, they appear to have had their monopods removed, but some still appear to have their slings fitted.
Developing the PIAT Carrier
From further research and some digging through the 16th Field Company’s War Diaries, I found reports on the adapted carrier and even some diagrams showing how the bombs landed. The diaries also reveal that the Universal Carrier was not the first vehicle the PIATs were mounted on – the first tests were carried out on a truck.

In the war diary we get the first mention of the PIAT battery in the entry for the 15th November 1944. It reads:
“The GOC directed that each arm of the service should be prepared to devise some means of harrassing the enemy during the holding role of the Div present area and to act as a counter-measure to the Moaning Minnies [Nebelwerfer] employed by the Germans. The ORE decided that the Sprs could make use of the 24 PIAT’s held by the C in Div Engre. The tentative Idea being that these be mounted on a veh, or two vehs, that they be fired mechanically and possibly simultaneously with a multiple mortar effect. Lieut. Cameron and No. 1 Plattoon [sic] were given the task, experiments to be carried out tomorrow for this purpose all PlATs and ammunition were called into this Company from Div Engrs.”
The next day on the 16th November the diary recorded:
“Lieut. Cameron made a number of tests with his PIAT platoon In conjunction with the N.S.R. and found that the maximum range that could be attained was 300 yds. Maj Main will discuss this matter with CRE tomorrow.”
Then several days later on the 19th November:
“Lieut. Cameron gave a demonstration of the capabilities of the PIATs used to fire with a mortar effect, 18 PIATs were mounted in racks on one vehicle at an angle of 45 degrees and fired simultaneously. There was no jar to the vehicle, Max range obtained was 300 yds against the wind and 400 Yds with the wind, detonation of salvo was all within one second of time and covered an area 25ft in length by 15ft width.”
This short report concluded by explaining why the PIAT Carrier may not be field practical, noting that “The plan is not practicable at present as areas of firing are not available that would permit the vehicle moving up to 300 yds from target before firing.”
The first major test is described in a report dated 21st November. A total of 22 PIATs were available to Lieut. Cameron’s platoon. They mounted 18 PIATs in racks on the bed of a Ford Canada 60 cwt (60 hundredweight – 3 ton) truck, with the remaining 4 as spares.
The report explains that steel wasn’t available so wood was used for the racks. Which they also believed would have a “cushioning effect serving to shield the truck to some extent from the shock of recoil.”
The 18 PIATs were arranged in three rows of six PIATs with PIATs spaced 1 foot apart next to one another, with four feet between each row. The PIATs were angled at 45-degrees by a wooden plank attached to the side of the truck bed with the butt of the weapon bolted down under wooden struts.
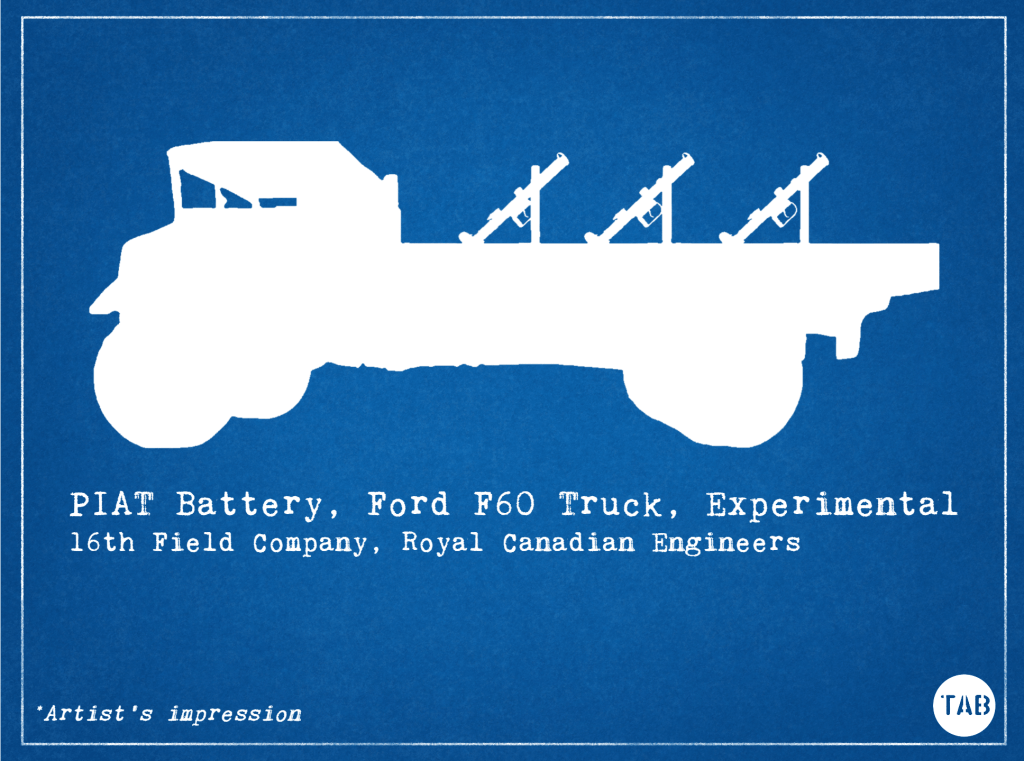
To fire the weapons rods were run along the rows aligned with the weapons’ triggers with bars of 1/2in steel running back between each one and back towards the font of the truck where the operator was stationed. The report describes this set up as ‘satisfactory’.
In the first test all three rows of PIATs were fired at the same time. The report’s findings note that in the first test all but one of the weapons fired, the bombs were in the air for an estimated 4 to 5 seconds and the time between the first and last bombs striking the ground was approximately ½ to 1 second.
The blast radius of the individual bombs is noted as 5 feet with 6 to 9 inches of penetration through gorse and sandy loam soil. The range was found to be 310 yards against the win and 400 yards with it. The wind was noted to be travelling as 20-25mph. From the diagrams accompanying the report we can see that the beaten zone had a maximum diameter of approximately 54 to 60 feet. With a mean point of impact around 15 to 18 feet wide.
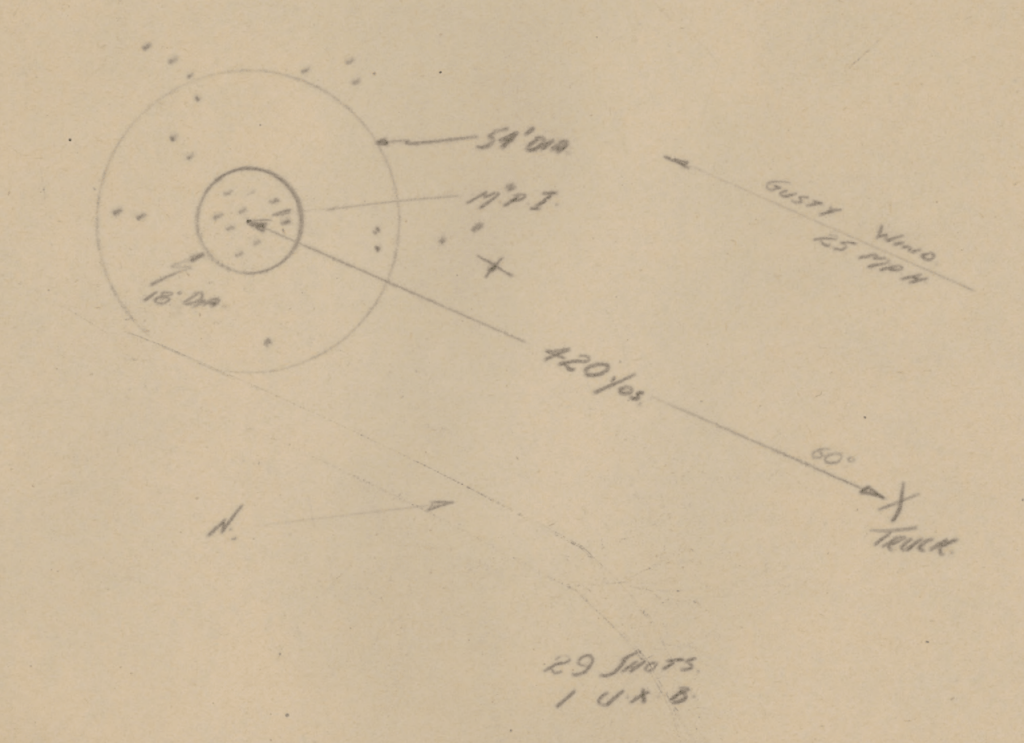
The second test saw the sappers fire two full salvos to test how quickly the rig could be reloaded. The reload time between salvos was recorded as 1min 20seconds. The second salvo saw 6 of the PIATs fail to fire due to a mechanical failure when one of the trigger rods broke. The extreme range achieved during this second firing was 420 yards with the wind.
During this first field test of the truck mounted system, a total of 65 bombs were fired and only one failed to explode down range. The racks were strengthened and the trigger rod repaired, it was also concluded that the racks could be spaced closer together without “effecting the pattern of the beaten zone” down range.
There is no further mention of the testing in the war diary during November but progress definitely appears to have been made, an entry on the 16th December notes:
“The use of PIATs mounted on a vehicle has had further experimental trials, 15 PIATs have been mounted on a Bren Carrier by this unit and a trial shoot was held today, Against a slight wind a range of 310 yards was attained with the area of burst covering 25 ft deep and 50 ft wide, no recoil was felt in the carrier.”
The last mention of the PIAT Carrier comes on 30th December:
“The carrier mounted with 15 PIATs was on trial during the afternoon before an audience consisting of the GOC and Officers of the Div. All visitors were impressed by the display. A range of 350 yds was attained and the accuracy on target was good.”
There are no further mentions of the PIAT carrier in the diary. It seems that development of the idea didn’t progress into 1945, by early February, the 16th FC RCE were involved in Operation Veritable. It appears that the operational requirement no longer existed.
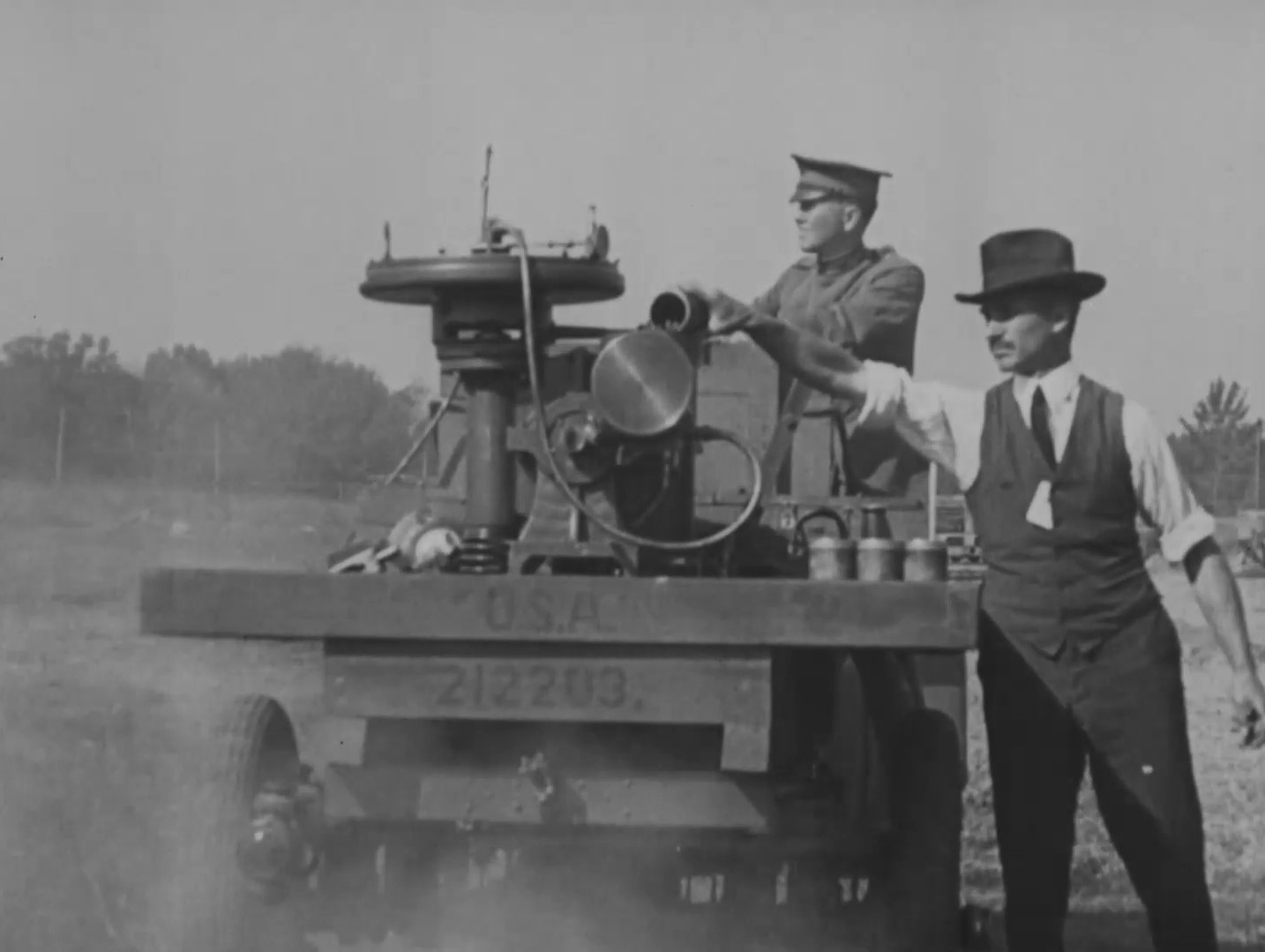
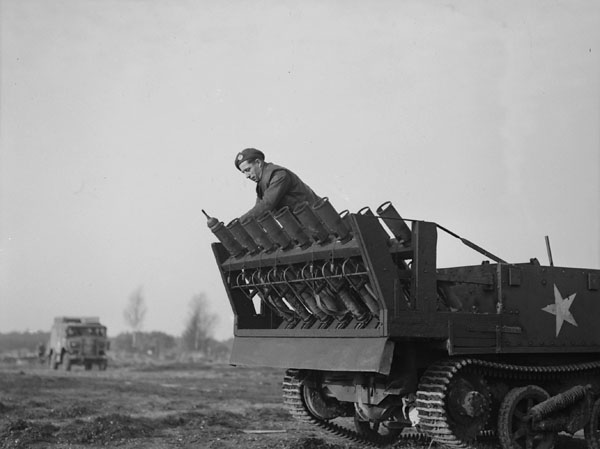
Lets take a closer look at how the adaptation was done. From the available photos, which were probably taken in mid-December 1944, we can see the trigger bar that was passed through the trigger guards of each of the PIATs, with the bar resting at the base of the trigger, it is unclear from the available photographs but this may have allowed the weapons to be fired either by row or all together.
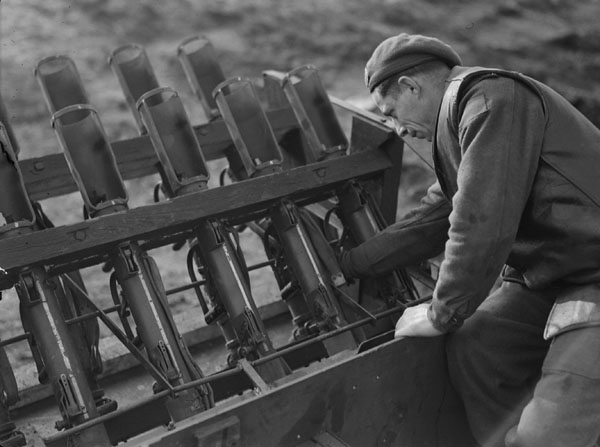

The sappers have built a wooden platform onto the back of the carrier with welded metal brackets holding the pieces together. The PIAT’s are held between two wooden cross pieces that have been bolted together. There’s a strip of metal running around the edged of the wooden frame that has been twisted 90-degrees and then welded to the carrier. It is also worth noting that all of the PIAT’s have had their butt pad covers removed and the feet of the PIATs’ rear end caps have been secured with a pair of brackets either side.

In the photograph above we see all of the PIAT’s held in their racks with their sights folded down, slings still attached, and we get a good view of the white indirect fire aiming lines. At the bottom of the photo we can see a trigger bar which when pulled appears to pull the triggers of the whole row at once. As an aside, note that the carrier has a ‘crooked’ Commonwealth allied star – to differentiate it from the US allied stars which were aligned with their top point at 12 o’clock
It appears that the battery of PIATs was aimed by reversing the Carrier towards its target, that would certainly have been challenging and a fairly dangerous task given the relatively short range of the PIAT even when used as a light mortar.
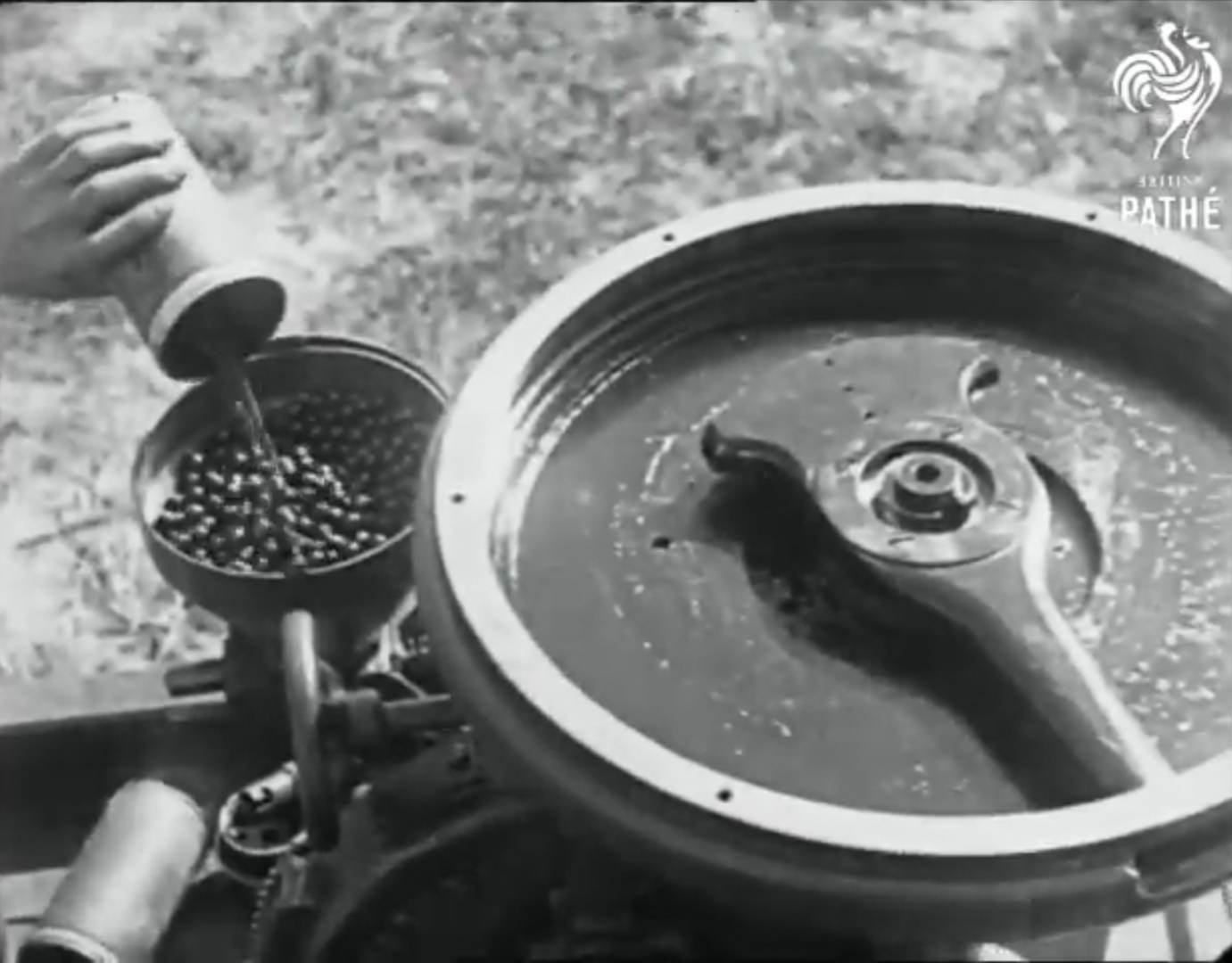
From this photograph below, of a Canadian sapper loading the PIATs, we can see all of the spigot tube stoppers dangling on their chains. The sapper is loading the bomb from the front of the bomb support tray and has angled the tail up to slide the projectile loading clip into the projectile clip guides on the face of the PIAT.
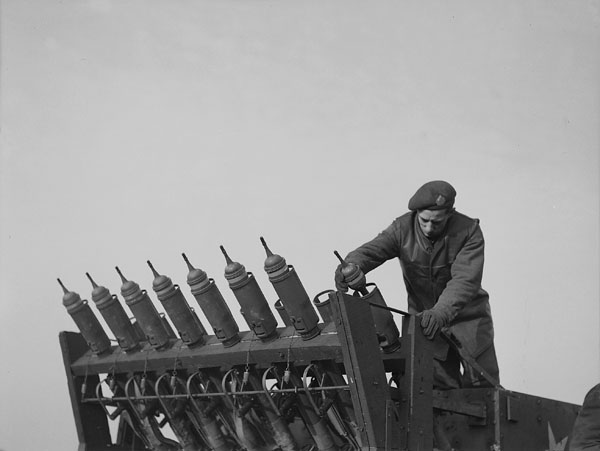

It also appears that sandbags are being used as a counterweight at the front of the carrier. The combined weight of the PIATs and their bombs (about 555 lbs) as well as the weight of the frame would have been considerable.
In the final photograph below we see the sappers preparing the battery to fire with a sapper in the foreground removing bombs from three bomb carriers. While in the background on the right we can see another sapper carrying bombs forward from another set of bomb carriers. I would guess that it was perhaps decided to mount 15, rather than an even number, PIATs as the bomb carriers held three round each – with 5 bomb carriers needed to reload the battery of PIATs.
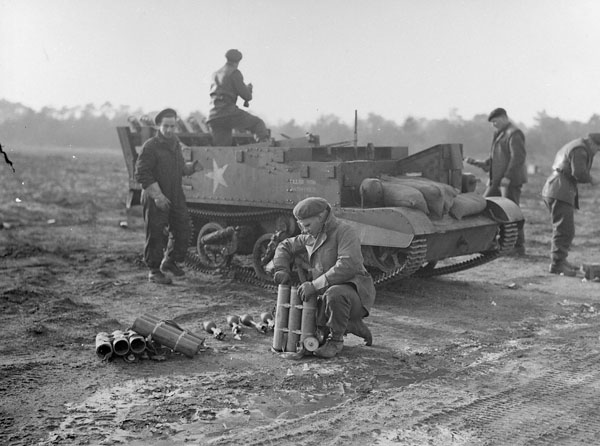

While sadly we don’t have any footage of the test we’re very lucky to have this selection of brilliant photographs courtesy of the Library and Archives Canada. It would seem that the limited range of the PIATs made the concept of a PIAT Carrier too impractical to field – but a maximum range of 400 yards may have offered some interesting tactical options for dealing with defended buildings or field works.
Perhaps need for a response to the enemy Nebelwerfers was answered by the introduction of the longer ranged, harder hitting Land Mattress. Despite this the ‘PIAT Carrier’ is a fascinating piece of resourceful engineering – an innovative, field-expedient adaptation that brought together two classic bits of British and Commonwealth kit – the PIAT and the Universal Carrier.
If you enjoyed the video and this article please consider supporting our work here. We have some great perks available for Patreon Supporters. You can also support us via one-time donations here.
Bibliography:
War Diaries of 16th Field Company, Corps of Royal Canadian Engineers, Library & Archives Canada (source)
All photographs courtesy of Library & Archives Canada (source)