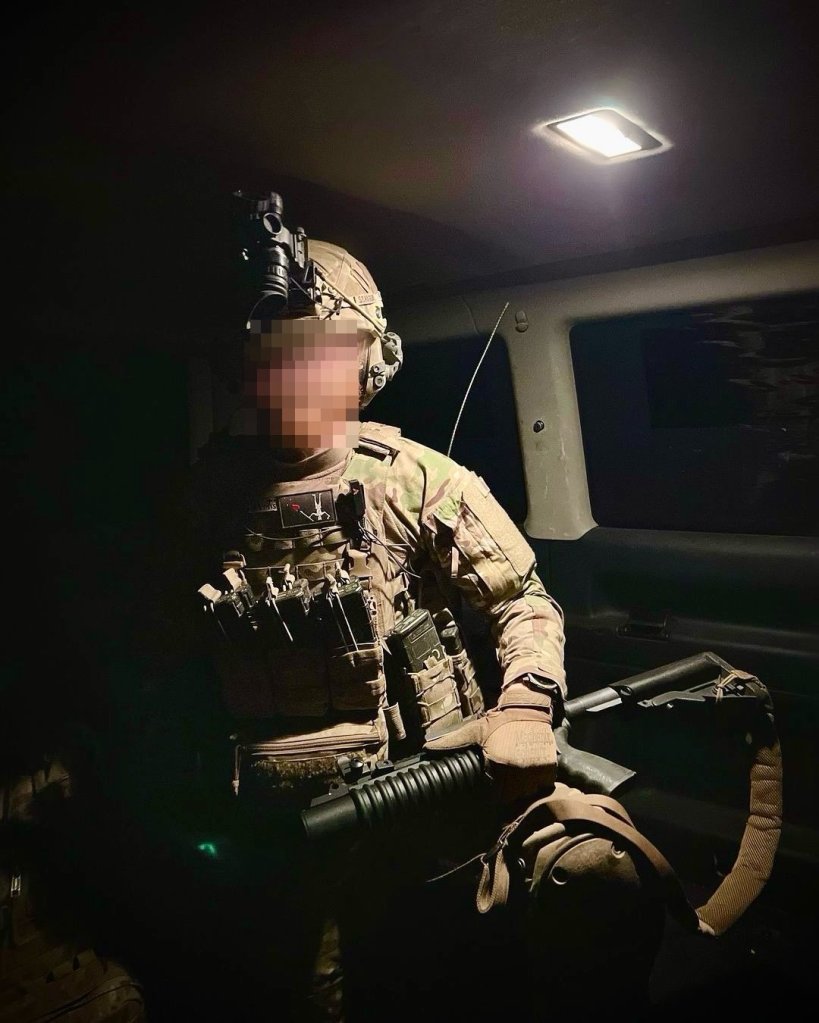
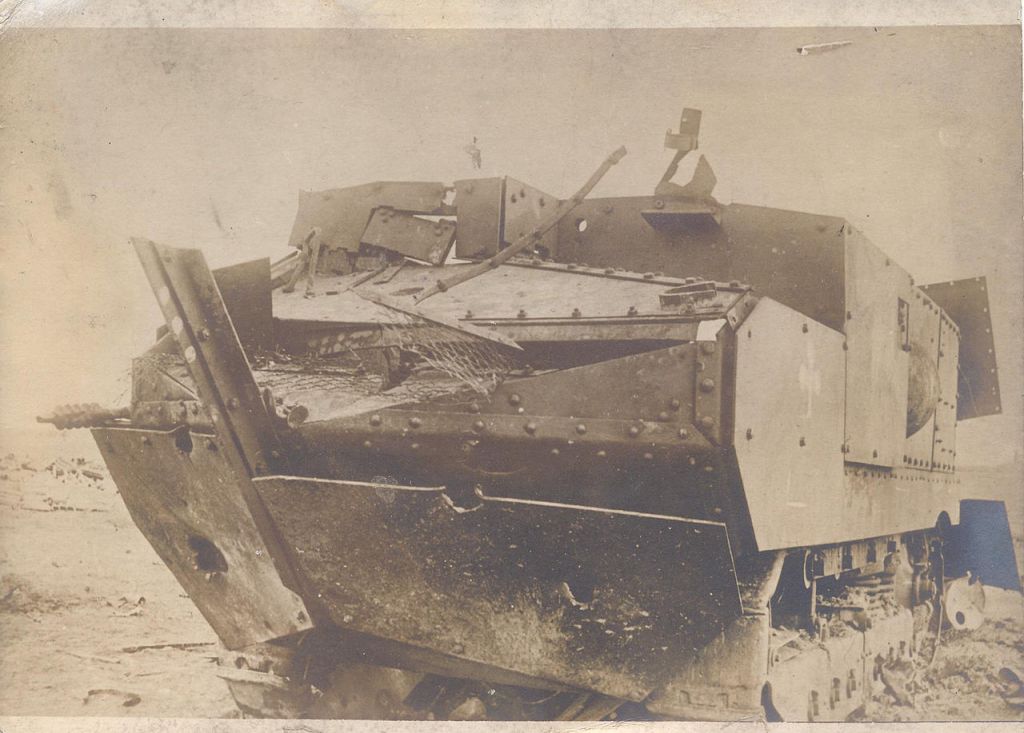
In a recent article/video we looked at the proliferation of Russia’s unusual ‘Turtle Tanks’ which are protected by ad hoc, locally fabricated counter-FPV shells. Since then we’ve gotten a good look at several more Turtle Tanks and our first look at the driver’s point of view.
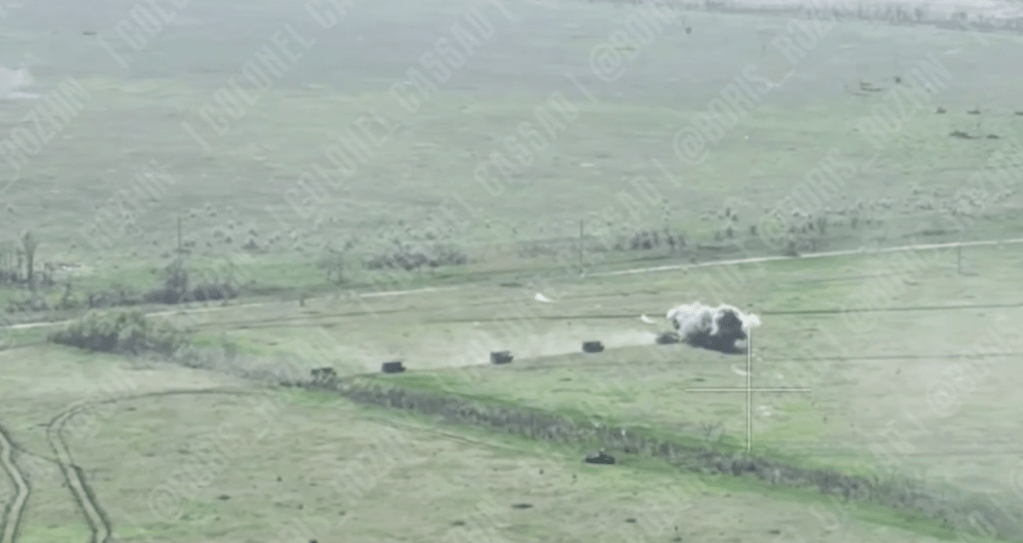
Footage, filmed on 27 April, of another Russian armoured assault into Krasnohorivka shows a column of four infantry fighting vehicles with what appear t o be counter-FPV shelters following a tank with a ‘cope cage’
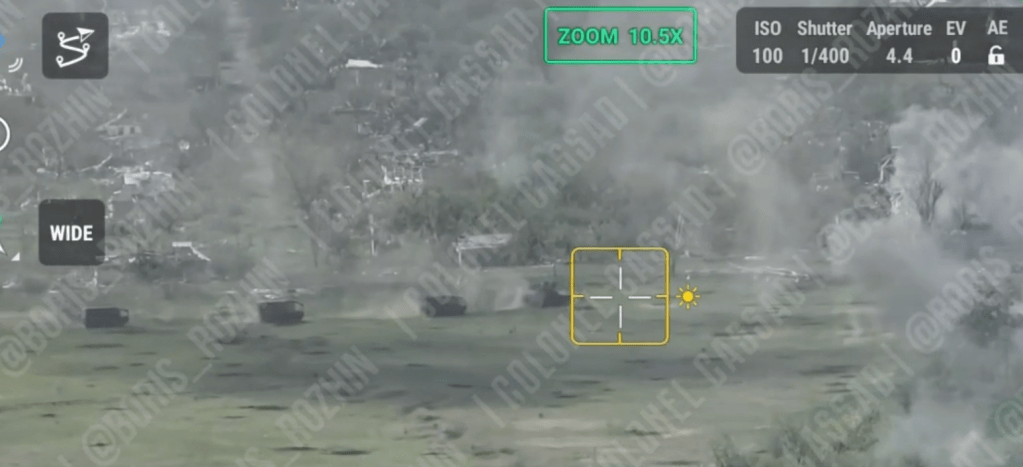
On the 29 April, a Ukrainian Telegram channel posted a short video of a ‘Turtle Tank’ attack in the Bakhmut direction, noting that [machine translated]: “the equipment is stupidly scalded with metal, from 5 units it was possible to destroy a tank and an armored personnel carrier. A lot of FPV was spent on one tank. Everyone laughs at their construction of barns, but in fact they work like hell.” The tank appears to have a box like shelter with a sloped forward roof over its gun and glacis. As seen in earlier videos the tank is leading a column of armoured vehicles during the assault, clearing a path for them. It appears to detonate a mine with its mine plough and retreats.
At the start of May a pair of T-62s with hybrid counter-FPV shelters were seen in photos taken by a UAV, location unconfirmed. These images illustrate the blurring of the lines between ‘cope cage’ equipped tanks and the ‘turtle tanks’. Like the earlier turtle tanks they’re fitted with EW sets & KMT-6 mine ploughs but do not have shells made entirely from sheet metal. Instead, they appear to have used chainlink and gratings, one piece of which appears to have Kontakt (explosive reactive armour (ERA) mounted. One of the vehicles appears to have been used to transport supplies. One T-62 has broken tracks, the other top damage.

Around the same time the Ukrainian 79th Air Assault Brigade shared video of Russian attacks near Novomykhailivka, in Donetsk, the footage included a brief clip of a ‘turtle tank’ with a small forward opening, camouflage over its shell frame and no sign of a mine plough or roller fitted. On 2 May, the 33rd Mechanized Brigade shared footage from thermal camera-equipped FPV drones showed a Russian tank being used to transport troops, the profile of the counter-FPV shelter is visible but the low definition of the thermal footage makes it difficult to analyse its construction. The vehicle, however, appears to be equipped with a mine plough and possibly an EW module.
Also on 2 May, Ukrainian drone fundraiser Teoyaomiquu shared a video of a Russian assault near Ivanivske which shows a pair of Russian armoured vehicles with counter-FPV shells, one of which deploys a smoke screen. The 1st Assault Battalion of the 5th Separate Assault Brigade also shared footage from the Russian assault showing the shell-equipped vehicles.
On the 5 May a short video was posted by a Russian combatant which showed an entirely enclosed MT-LB with steel plates surrounding the top of the vehicle and its wheels. It also has an additional mesh roof cover to add additional top protection. Two cutouts in the side and one in the front for the driver also have mesh covers to give some visibility. On the same day video of a destroyed BTR-MDM which had been encased in a counter-FPV shelter was shared, showing the rear of the vehicle enclosed.

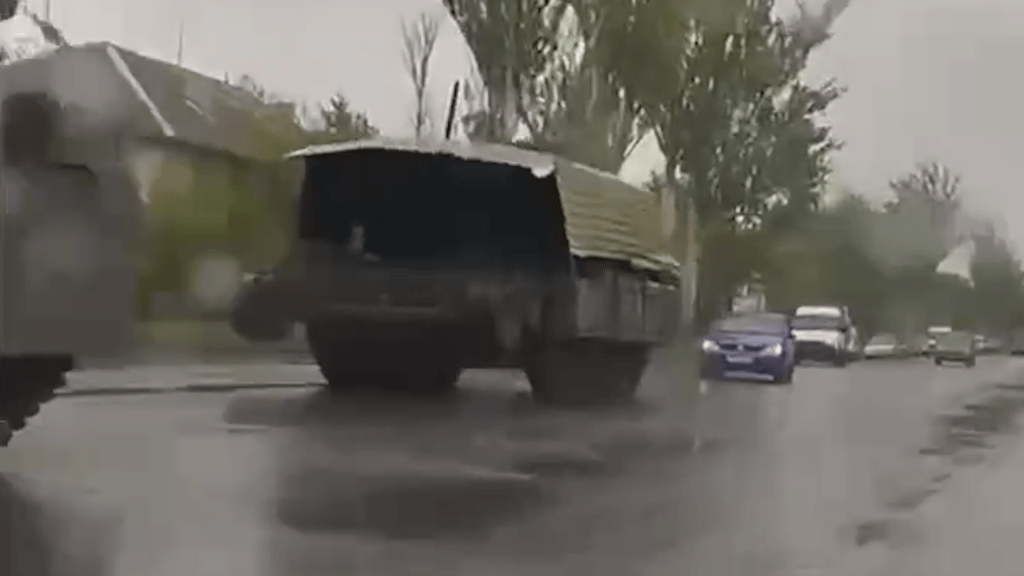
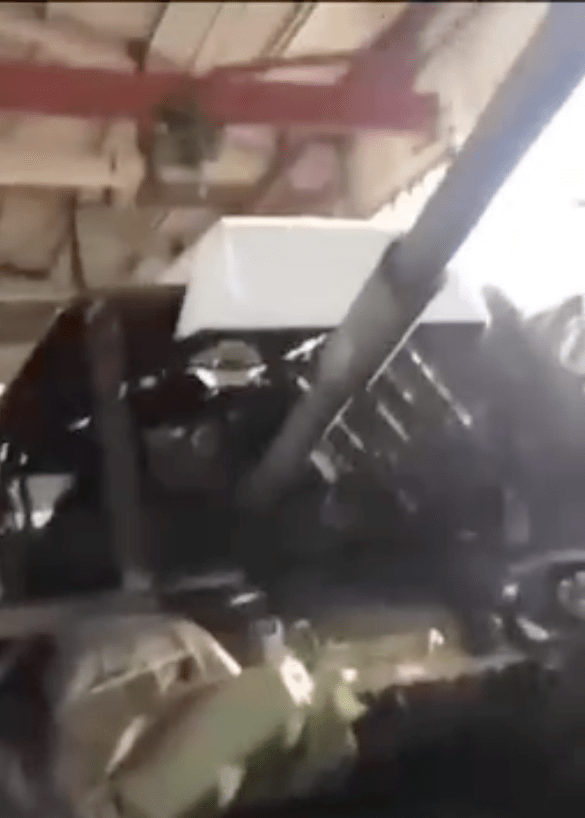
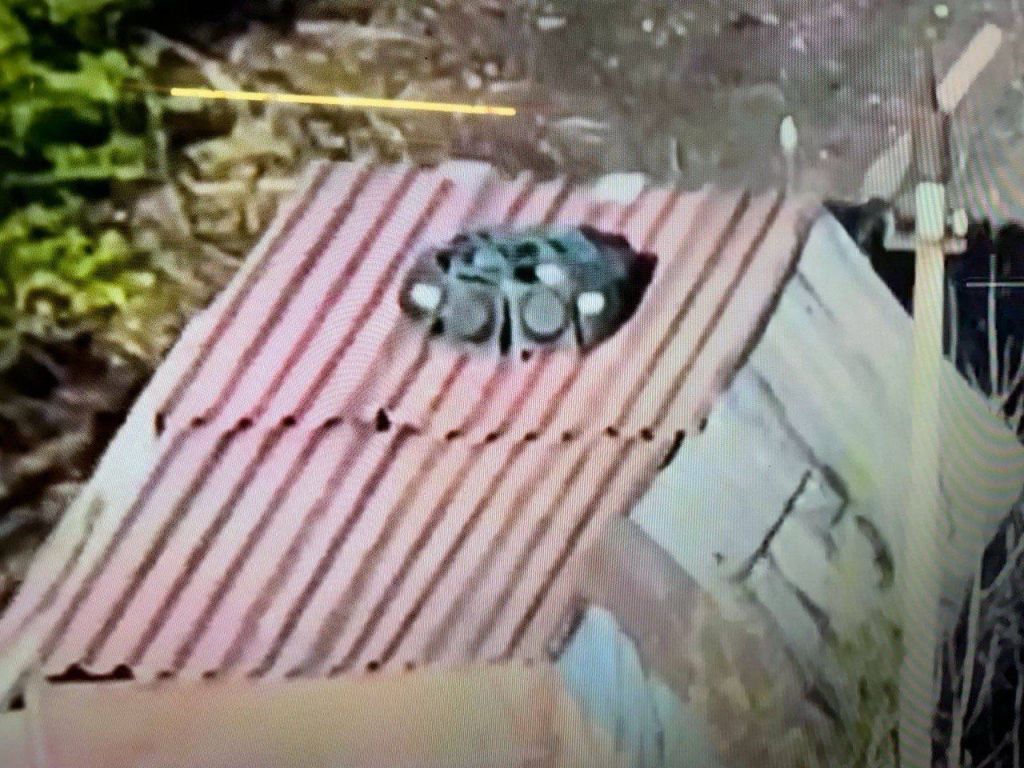
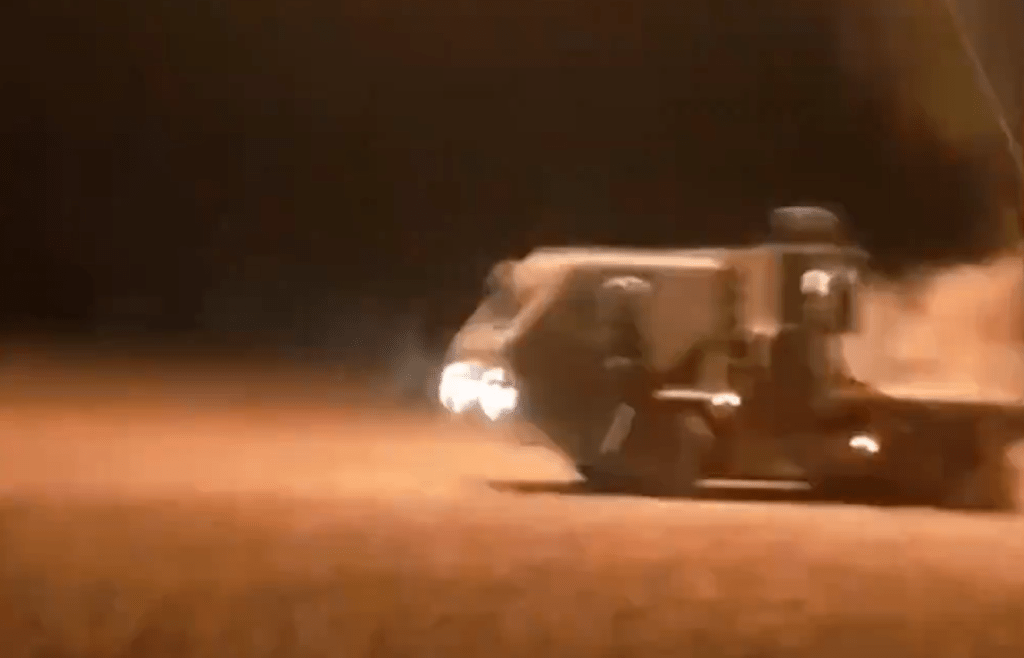
Perhaps the most striking evolution of the ‘Turtle Tank’ appeared on 5 May, a tank completely enclosed except for a small gap at the front. Protective grills made from cages completely cover the outer metal sheets of the counter-FPV shell. One Russian telegram channel likened it to a rolling ‘poultry farm’. The vehicle also has a KMT-7 mine roller. Additional video of the porcupine-like tank gives us the first look at what it is like driving one of these ‘turtle tanks’, with his hatch open the driver has an almost clear view ahead (apart from the solid awning above him and the partial grill cage protection to his front) but no view to the left or right front quarters of the tank.
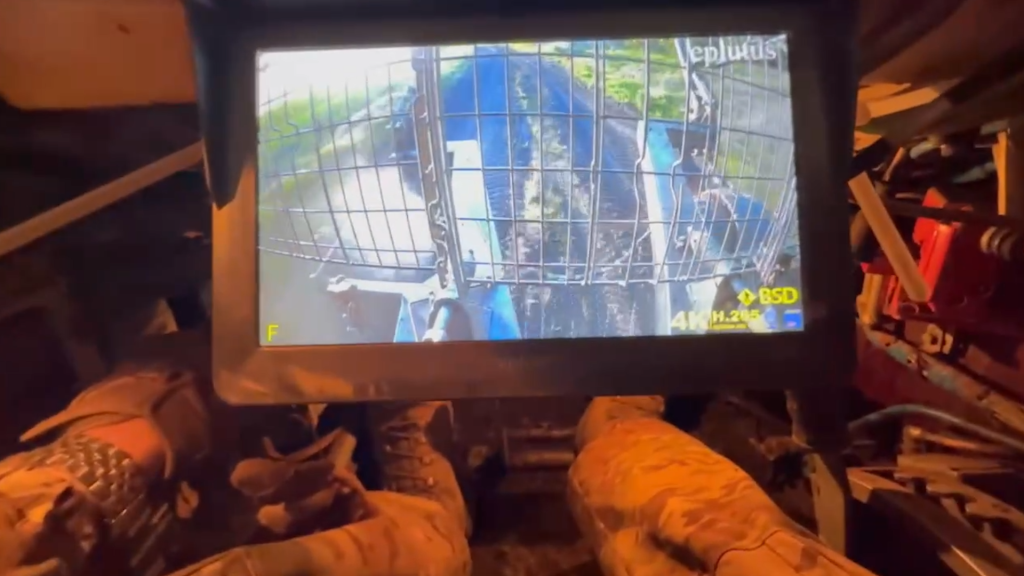
Several days later footage from inside what appears to be the same tank shows the driver steering by video monitor. The readout on the monitor suggests the video’s resolution is 4K H.265 but the field of view appears limited, with the camera seemingly positioned on the shell’s awning looking down between the KMT-7’s two rollers. The system used is from Russian automotive accessory company Eplutus and appears to be one of their rear view camera monitors.
Another piece of UAV footage shows another ‘turtle tank’ with a much boxier shell. It again has all of the major features seen in earlier examples: a sheet metal shell which encloses most of the top part of tank, a set of mine rollers and a EW jammer module on the roof. Some sources suggest the footage was filmed near Bilohorivka, in Luhansk. It’s unclear when the footage was filmed but the vehicle appears stationary with access grates to the tank’s rear deck left open.
The 7 May saw evidence of the proliferation of t he ‘turtle tank’ concept with Russian social media sharing photographs of a ‘Turtle Tank’ fabricated by the Russian 40th Naval Infantry Brigade, these indicate that the concept is continuing to proliferated, perhaps without any central influence. The tank is encased in a counter-FPV shelter made up of three large metal sheets, a poorly fabricated angled roof which slopes at the rear with a flat top and a wire mesh slopping front piece. Additionally on the floor there appears to be a chair curtain similar to those seen on other ‘turtle tanks’. The rear has an extended deck and appears to be enclosed. A skirt of Kontakt-1 ERA has been roughly added around the skirt. As with other Turtle Tanks the ‘V Turtle’ is equipped with what appears to be an RP-377 electronic warfare jammer. It also has a KMT-6 mine plough fitted. A large white V has been painted on the sides of the shell and Russian flag rings added to the barrel.

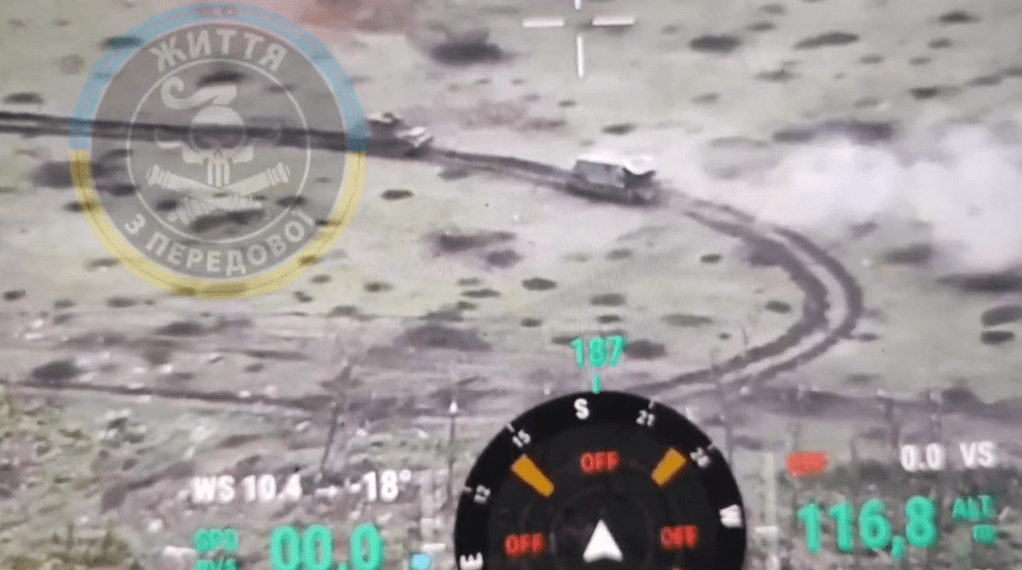
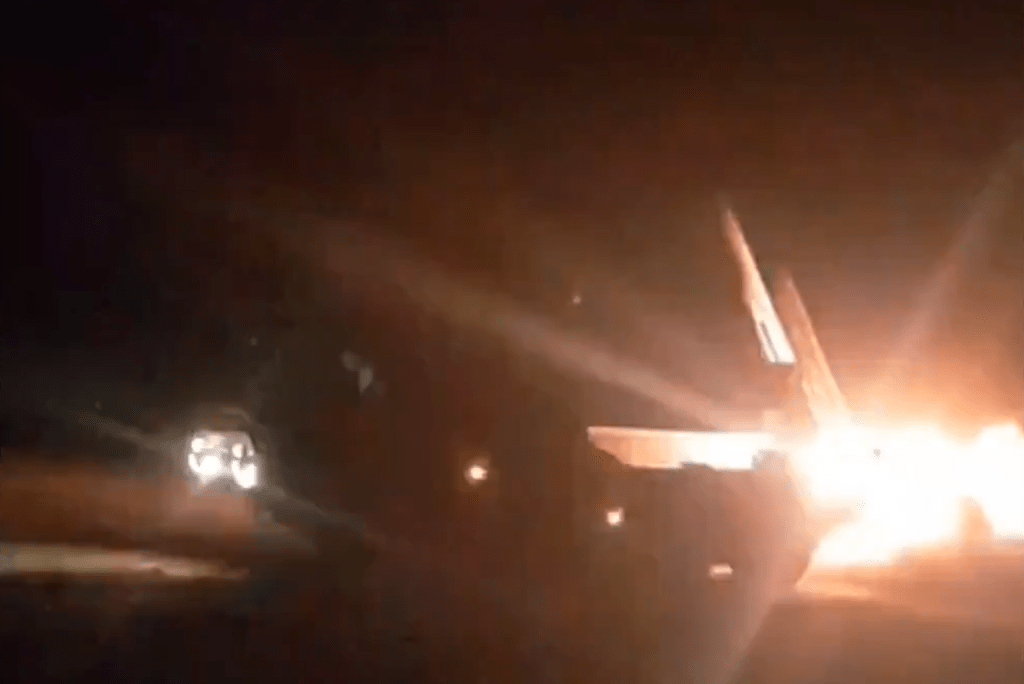
On 10 May, footage of an FPV drone attacking an immobilised ‘turtle tank’ emerged. The tank is again enclosed by a counter-FPV shell and has a mine plough. The feed from the drone also suffers from some interference as it approaches the vehicle suggesting that an EW module may be present nearby, perhaps aboard the tank. However, it appears that a mine has damaged the tank’s tracks and the vehicle has been abandoned allowing an FPV to attack via an open rear hatch. The footage was reportedly filmed during the first day of the new Russian offensive towards Kharkiv. This again shows that not only is the concept proliferating but also that the ‘turtle tanks’ are still vulnerable to conventional anti-tank weapons like mines.
Also on the 10 May, the Russian military channel, Large Caliber Trouble, shared a photo of the porcupine turtle tank which had been damaged by FPV strikes showing the cage bars bent and some holes in the counter-FPV shell. The post claims that the tank was “attacked by 40 kamikazes, [but] thanks to electronic warfare, most of them fell and only 8 FPVs were able to cause damage.” The condition of the vehicle after the engagement is unknown. The suggestion that a large number of FPVs attacked the tank supports the earlier Ukrainian comments about ‘a lot of FPV [being] spent on one tank.’

A key question is how can the Turtle Tanks be defeated? Basically just like any other tank can be: anti-tank guided missiles with tandem warheads, dense mines belts, direct hits by artillery, use of multiple FPV drones to damage and breach the shell with additional drones to exploit gaps made.
We will probably see further proliferation of the ‘turtle tanks’ in coming weeks but with time the Ukrainians will probably find ways to engage these protected tanks more effectively, as is so common in war there will probably be a continued evolution of measure and counter-measure.
Update – 13/5/24:
On the 8 May photos of a Russian T-72B3 being fitted with a counter-FPV shell were posted. OSINT account Naalsio noted that while the tank had tactical markings denoting the 68th Guards Tank Regiment, 150th Motorised Rifle Division, 8th Guards Combined Arms Army, Southern Military District, the original Telegram post said that the work was carried out by the 104th Separate Tank Battalion of the 7th Guards Airborne Assault Division. In the photos we can see the assembly of a frame projecting from the tank’s sides with slightly angled sheet metal being welded to the sides.
Ukraine’s Presidential Brigade shared some FPV footage of what may be another ‘Turtle Tank’ near Vuhledar. The resolution of the footage is low but the vehicle appears to have an EW module on top of its counter-FPV shell. Its unclear if the shell is solid sheet metal or if its is a mesh screen which covers the top part of the vehicle and has been shrouded in camouflage netting.
On 13 May, photographs of a T-80U with shell were shared with at least some of the work seemingly being completed in the field with a welder hooked up to a generator. The outer framework of the shell is visible and the sheet metal used seems to be well rusted. Markings visible may suggest the tank belongs to the 3rd Motor Rifle Division’s 752nd Motor Rifle Regiment.
Also on the 13 May, the 3rd Assault Brigade claimed that the 3rd along with the 66th Mechanized, and 77th Airmobile Brigades had engaged Russian forces on the Kharkiv front and struck a ‘turtle tank’ with FPVs.
Footage of what may be the ‘turtle tank’ which was immobilised during the initial assaults on the Kharkiv front shows the shell badly damaged and its left-side track lost its KMT-6 mine plough is still present however.
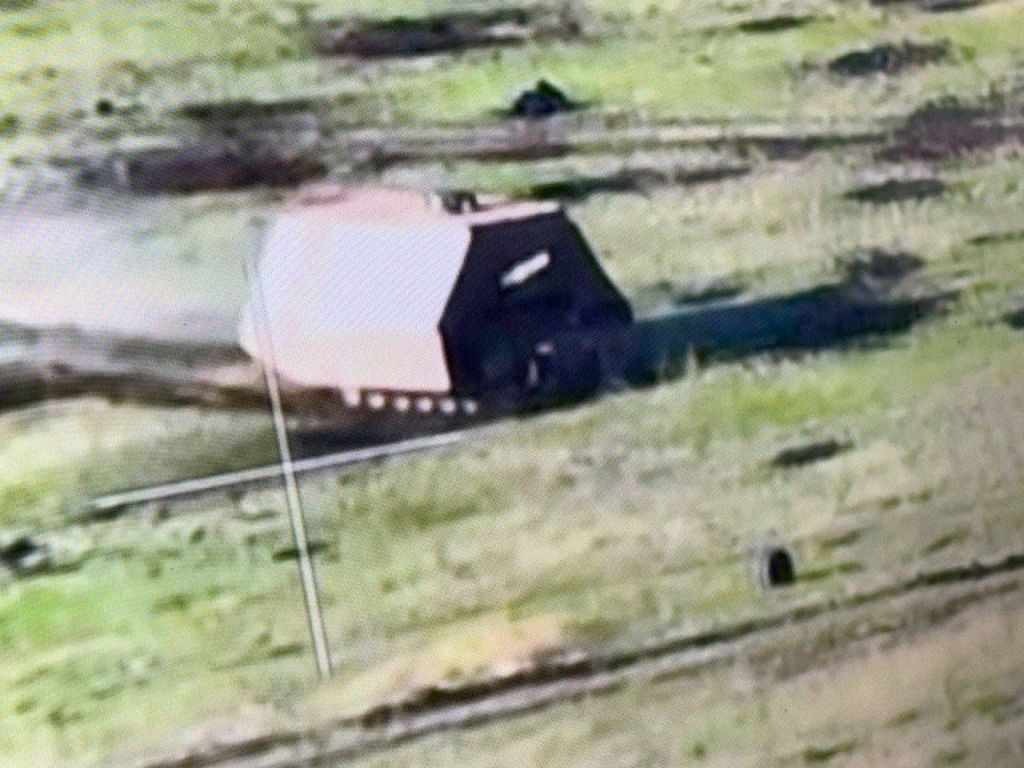
The clearest imagery of of a knocked out ‘turtle tank’ which has appeared so far also emerged on 13 May. Three images taken by an observation drone show a T-62 which shares a numerous construction characteristics with the earlier ‘porcupine turtle’ seen on 5 May. It has similar protective grills made from cages completely cover the outer metal sheets of the counter-FPV shell. However, its rear is not enclosed by sheet metal but a combination of sheets and grating.
The tank doesn’t have any visible electronic warfare equipment but is fitted with what appears to be a BTU-55 dozer blade mounting point (H/T – Ross) which is no longer present and not visible in the available imagery (although what appears to be a KMT-6 mine plough can be seen on the ground behind the tank). The tank is clearly has signs of fire damage along its side and rear and the front portion of its shell as been blown inwards and warped, cause unclear though it may have been an artillery strike, ATGM hit or an FPV. Intriguingly, inside the shell appears to be an earlier pre-existing ‘cope cage’ shelter on the turret which does not not a part of the outer shell structure.
Update – 14/5/24:
Further examples of tanks equipped with counter-FPV shells, which both sides increasingly refer to as ‘сарай’ or sheds. Drone footage of a Russian T-72B3 equipped with a ‘shed’ was shared early on 14 May showing the vehicle on fire, with smoke billowing from its roof, and under attack by FPVs. The footage has reportedly been geo-located to Novovodyanoe, in the Luhansk region. Again the shell is made up of sheet metal with a rear hatch and an additional mesh roof screen. The tank has a broken track and one shot from the footage appears to show the vehicle surrounded by TM-62 anti-tank mines suggesting the vehicle entered a mine field. The vehicle does not appear to be fitted with a mine plough or roller.
Additionally imagery of another T-62-based ‘turtle tank’ were also shared, date and location unknown, but the now standard construction of a rough internal framework made from box metal and then sheet metal welded onto the frame. From the photos it appears it may be fitted with a mine plough. Only one side of the shell has been completed but there is also a small ladder welded onto the frame at the rear for access to the engine deck. Intriguingly, we can also see that the frame itself has been welded to the tank’s turret with two angled struts meaning that the tanks turret cannot be traversed at all.
Update – 15/5/24:
On the 14 May, footage of another knocked out ‘turtle tank’ emerged showing a burning tank near Andriivka in Donestsk. The tank appears to have been part of an armoured assault which may have been halted by artillery fire. The tank appears to be a T-62 fitted with KMT-6 mine plough. The vehicle is on fire with a significant portion of its shell blown off on its right side. The video also shows an FPV drone striking the tank from the rear.
On the evening of 14 May, the 79th Air Assault Brigade shared video of another Russian attack in Novomykhailivka, in Donetsk. This showed several intriguing vehicles including a hybrid-turtle which had a layer of tyres under some cage armour and a camouflage net. [Additional footage here] Another brief shot showed a tank, with no visible main gun, moving across open ground. It is equipped with a KMT-7 mine roller and a counter-FPV shell/shed which is open fronted with no additional protection such as a chain curtain or wire cages. It appears the assault was met with both artillery and FPVs.
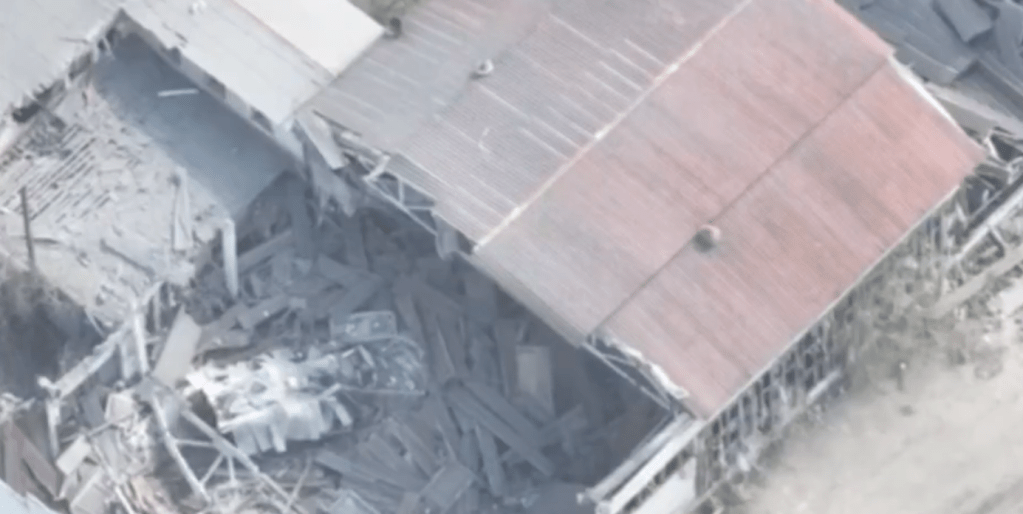
On the 15th observation drone footage was shared of a badly damaged, burning ‘turtle tank’ which was destroyed by the Ukrainian 72nd brigade during a Russian attack in the Vuhledar sector. The date of the engagement is unconfirmed but the video shows the vehicle being destroyed in a spectacular explosion, likely due to a cook-off of ammunition.
On the 15 May another image of a converted T-72 in Donetsk emerged. Visible in the photo is a sheet metal counter-FPV shelter equipped with a layer of outer wire cages. A KMT-6 mine plough is fitted and a chain curtain protects the turret while providing decent visibility for the tank’s frontal arc. Additionally a commercial surveillence camera has been attatched to the roof of the shell. An АЕК-902 smoke discharger is attached to the top of the shell and ERA blocks have been attached to the skirt and then enclosed partially by a wire screen.
Support Us: If you enjoyed this video and article please consider supporting our work here. We have some great perks available for Patreon Supporters – including early access to custom stickers and early access to videos! Thank you for your support!