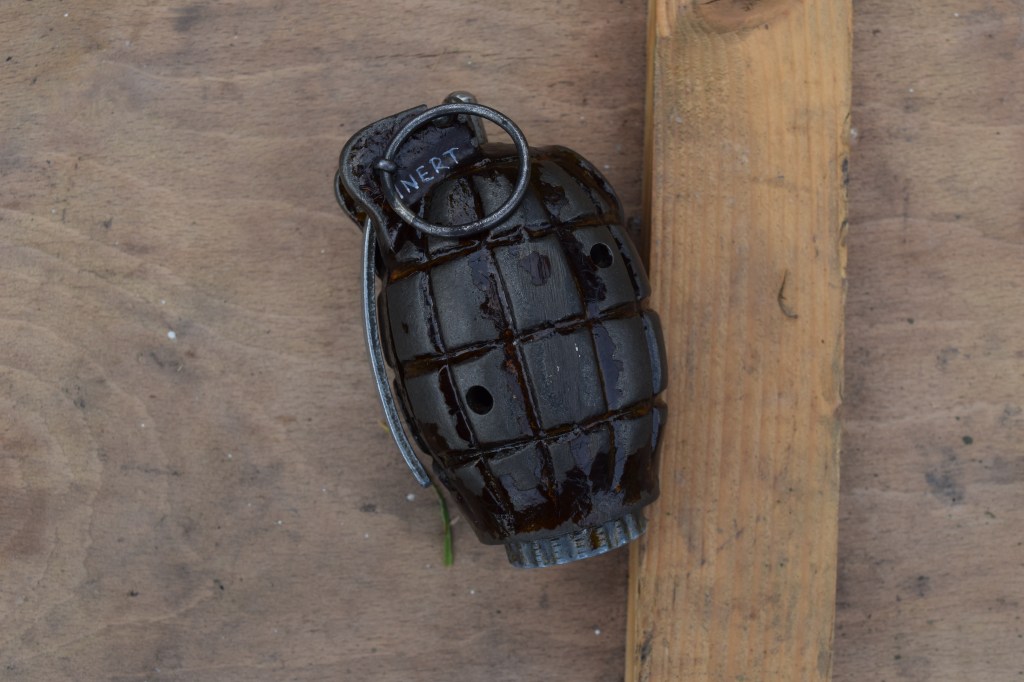
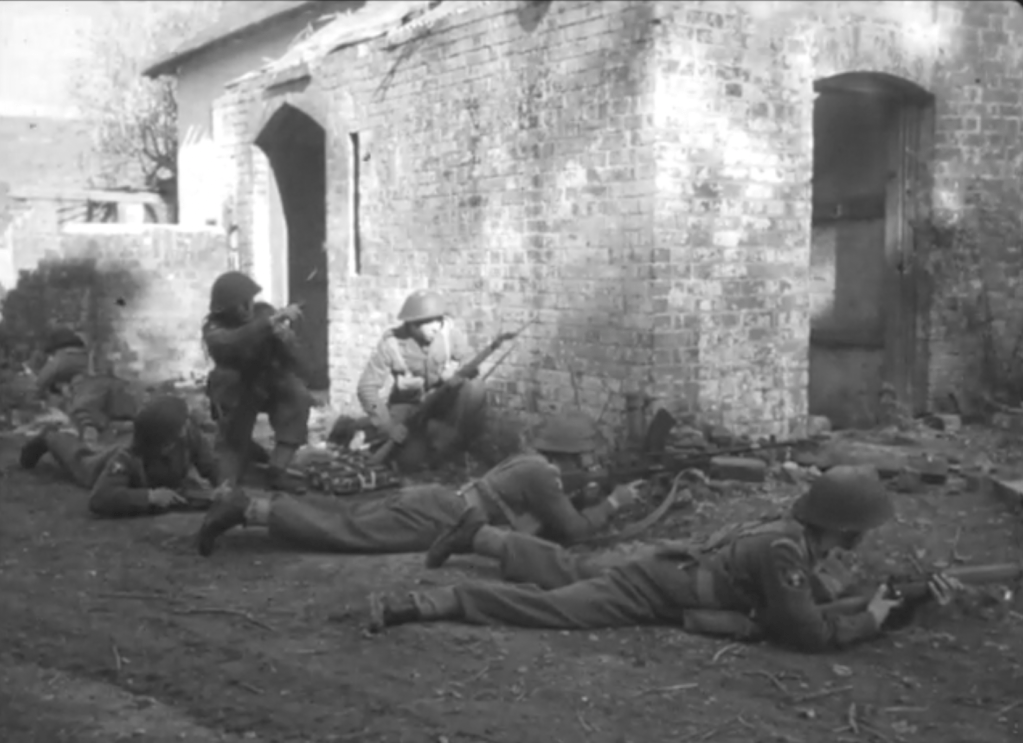
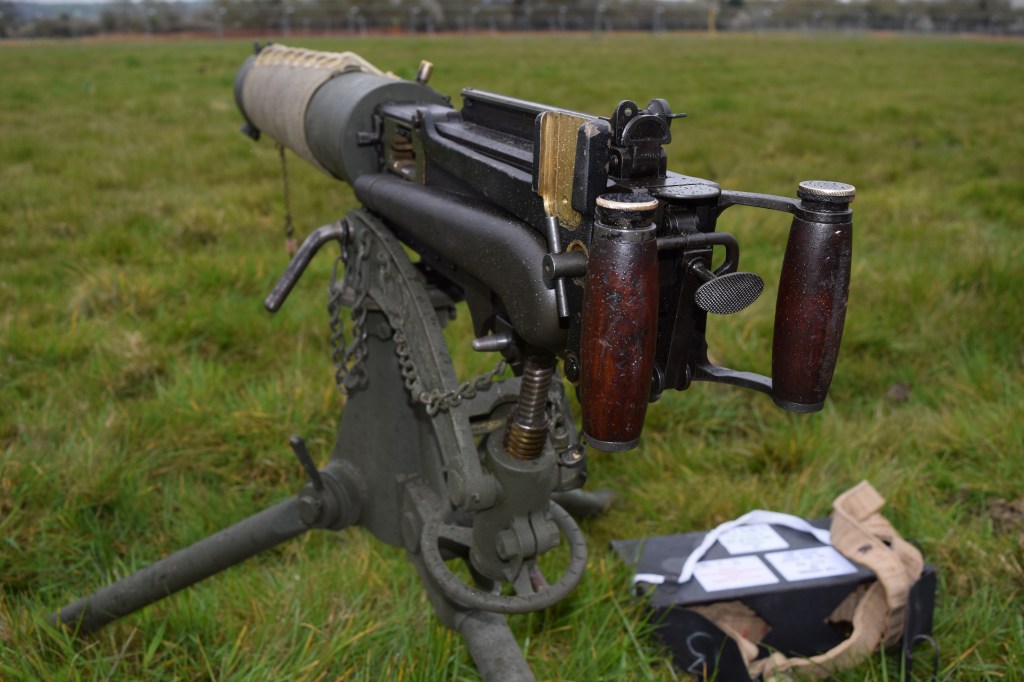
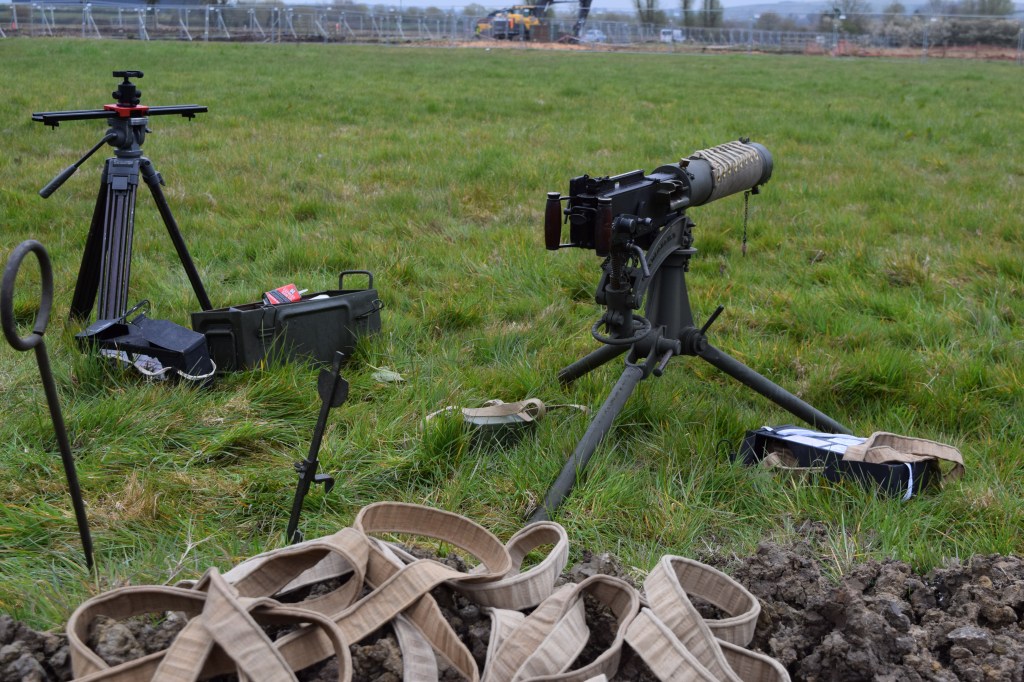
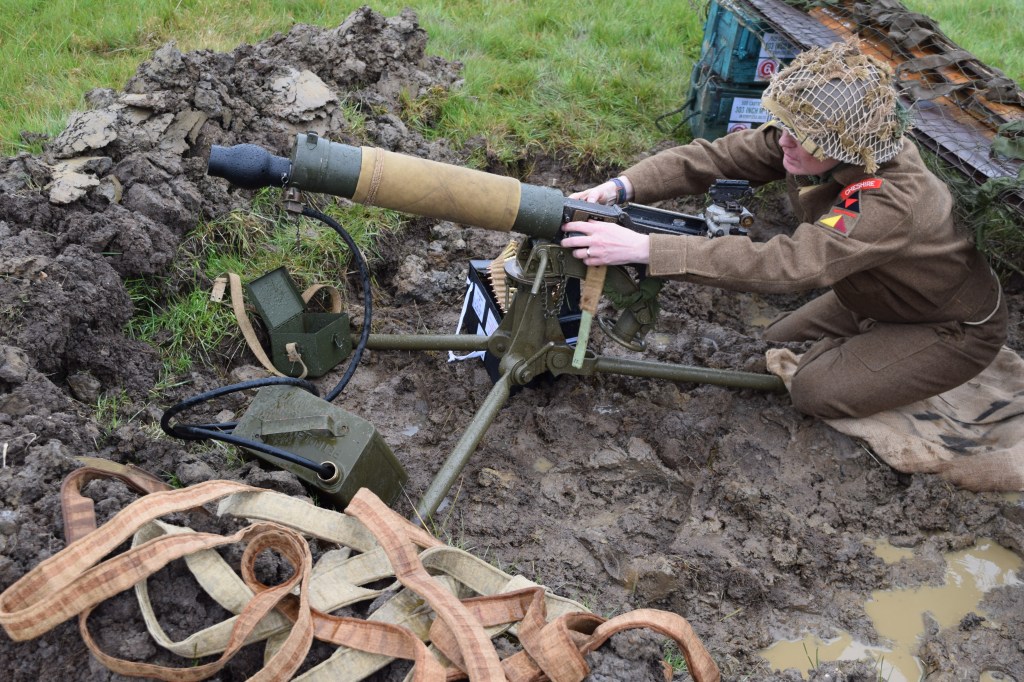
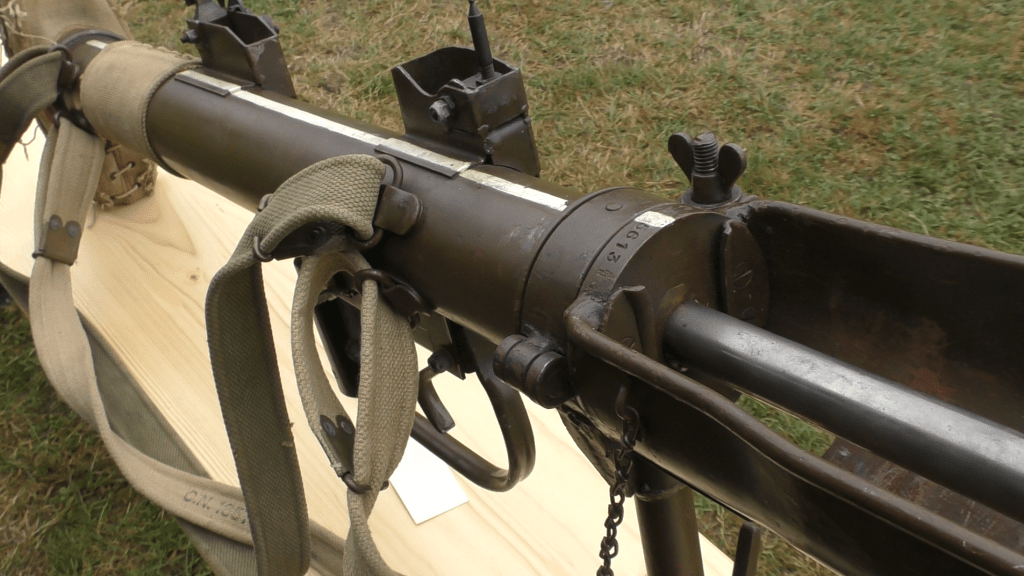
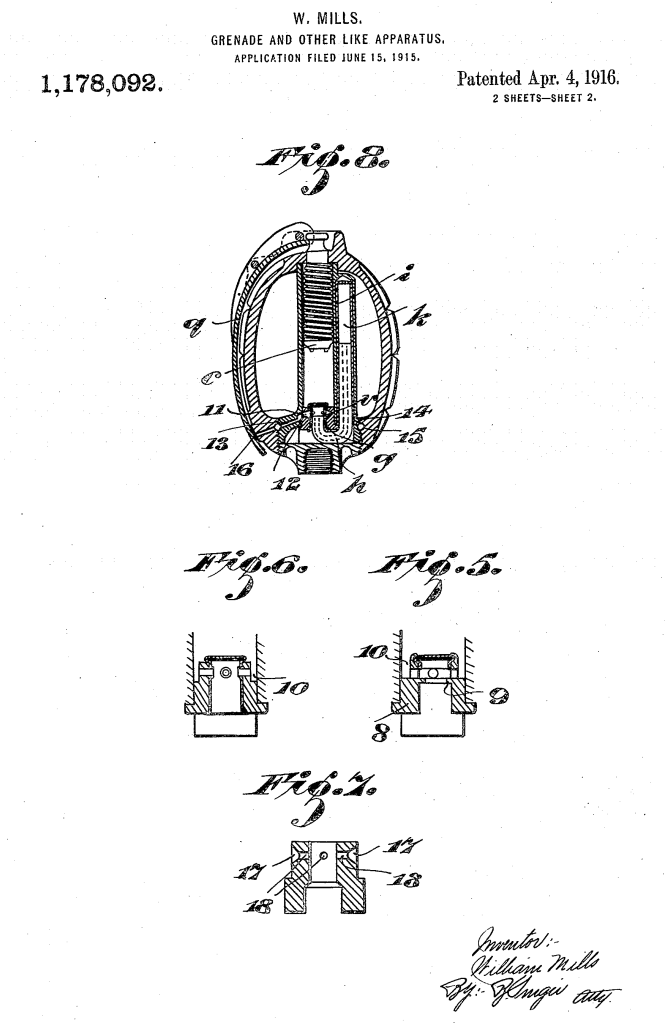
During the Cold War NATO was understandably interested in capable anti-armour weapons. In this video/article we will examine the Off-Route Mine which features in footage from several British Army training films. They show a team of Royal Engineers setting up an L14A1 off-route mine ready to ambush attacking Soviet tanks.
Unlike a conventional mine which detonated vertically when a vehicle drove over it, the Off-Route Mine would be tripped by a breakwire set across a vehicles likely path. When the wire was tripped or broken the mine’s charge would be electrically detonated and the blast would project horizontally.

What the British termed the L14A1 was developed in the early 1970s by France’s state arsenals. In French service it was known as the ‘Mine Anti char à action horizontale Modèle F1′ (or MI AC AH F1). It was manufactured throughout the 1970s and 80s by GIAT Industries.
The mine was essentially an electrically fired shape charge, it used the Misznay-Schardin effect rather than the Monroe effect. The former relies on a shallower, concave shape charge, which has a copper cone that is super heated by the explosion and fired out towards the target. This gave it the ability to project its cone further and removed the need for it to detonate in contact with the target vehicle.
The mine had an effective range of between 70 to 80 metres and according to the 1977 French manual the projectile created by the detonation could travel up to 6km. In terms of the mine’s effectiveness the same manual states that 40m was the optimal range but no closer than 2m.
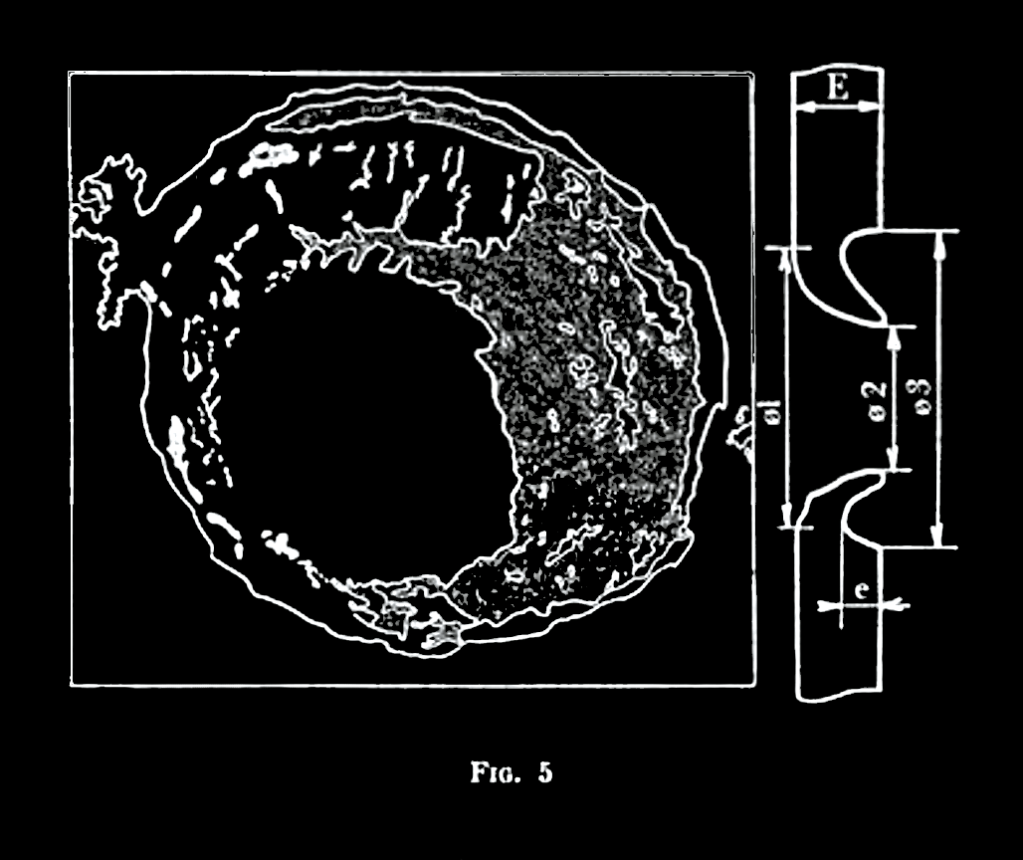
The manual also notes that “the slightest obstacle in the trajectory of the projectile (such as earth or shrubs) considerably reduces performance.” The diagram below from a 1977 French Army manual shows the effect of the mine on 70mm of armour at 40m, with 0-degrees of angle.
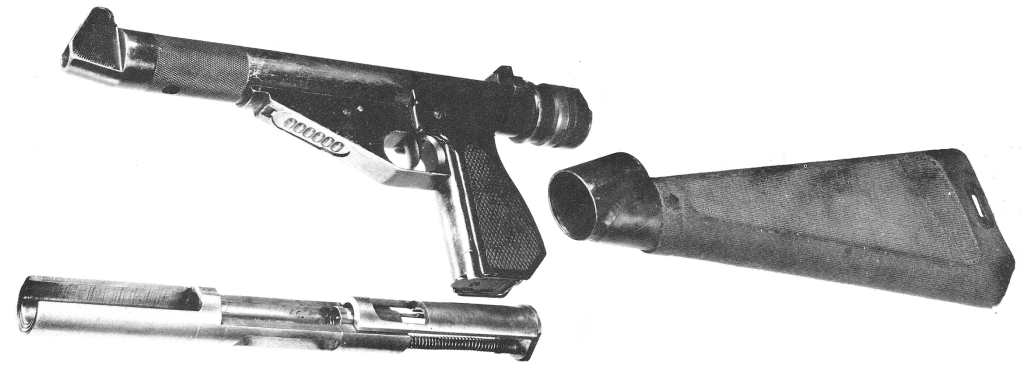
When detonated the mine could throw fragments in a radius of 100m and could throw armour shards from a successful strike up to 200m from the target. The British mines came in the L27A1 kit which included a pair of the L14A1 off-route mines as well as instructions, the break wires, a night sighting tool, and an adjustable stand for mounting.
The mine’s electorally-powered detonator was powered by D cell batteries, which Sappers complained had to be frequently changed. The mine itself weighed 12kg and was packed with just over 6kg of Hexolite explosive. There was also a training version, the L28A1, which fired a paint-filled sponge to mark the side of the vehicle and confirm a hit.
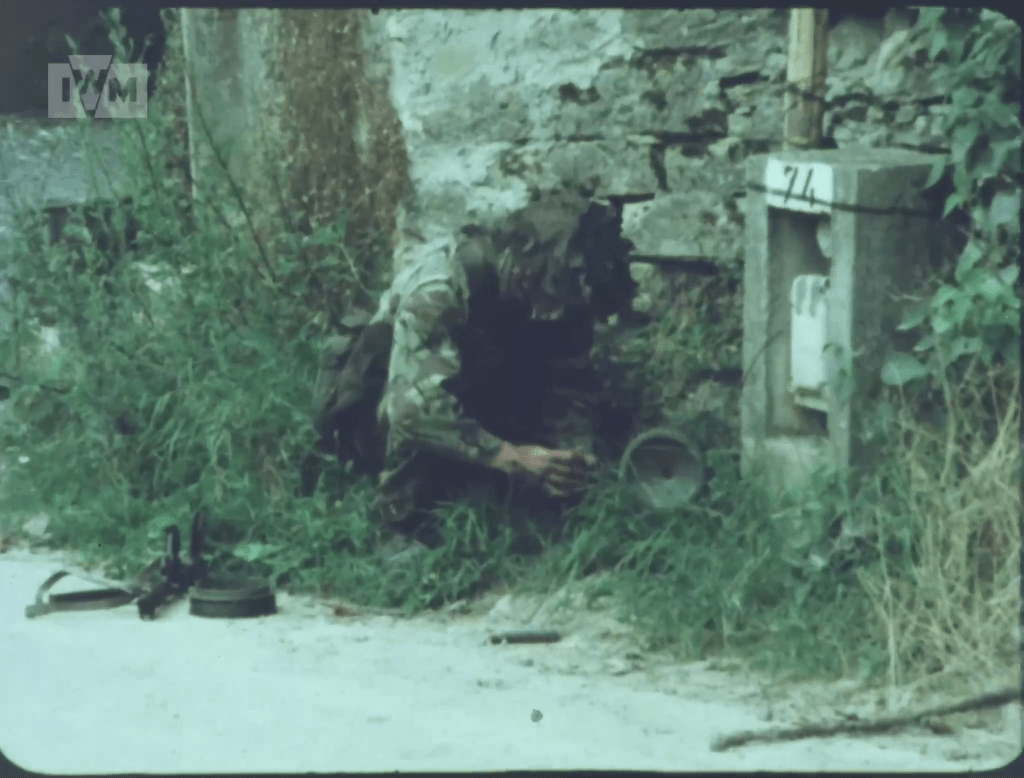

The Miacah F1 was removed from French service in 2001. An improved version, the F2, was manufactured in 1996 and used by the French until the mines were withdrawn in 2004 due to corrosion. While some mines may have remained in stores, as some have been seen as late as 2016, they contravened the 1997 Ottawa Treaty on anti-personnel mines because the break wire could in theory be tripped by a human rather than a vehicle.
It was replaced in British service by the ARGES off-round Anti-Tank Mine which fired a modified 94mm rocket with a tandem HEAT warhead. In 1997 it was reported that 4870 Off-Route mines were held by British Army stores, in line with the Ottawa Treaty this had been reduced to 0 by 1999.
If you enjoyed this video and article please consider supporting our work here. We have some great perks available for Patreon Supporters – including custom stickers and early access to videos! Thank you for your support!
Bibliography:
Landmine Monitor Report, 2004, Landmine & Cluster Munition Monitor, (source)
Landmine Monitor Report, 2000, Landmine & Cluster Munition Monitor, (source)
CNEMA Report, 2000 (source)
British Army User Handbook, Mine Anti-Tank Kit L27A1 (Off Route Mine), 1980
French Army MIACAH F1 Manual, 1977
Footage:
Fighting In Woods, British Army training film, 1982, (held by the IWM, DRA 1472)
Fighting In Villages, British Army training film, 1979, (held by the IWM, DRA 1401)