The fighting in Ukraine has seen a wide range of small arms in use ranging from the cutting edge to the antique. We’ve seen a number of older weapons like Mosin-Nagant rifles, M1910 Maxim machine guns and DP light machine guns in service with both sides. [We’ll take a look at those in future videso] The TT-33 pistol, a pistol which first entered service 90 years ago, is another older weapon which is again seeing action. The examples seen in theatre are likely a mix of privately owned firearms and pistols drawn from Ukrainian stores.
Introduced in the mid-1930s to replace the 1895 Nagant revolver, over a million TTs have been produced. Designed by Fedor Tokarev the pistol became the Soviet Union’s primary side arm, seeing service during the Second World War alongside the Nagant.
The TT-33 is a semi-automatic pistol, chambered in 7.62×25mm. It feeds from an 8 round single stack magazine and uses John Browning’s short recoil tilting-barrel action. The TT is an extremely robust pistol and remained in service well into the 1950s with the Red Army and continues in service around the world even today.

Pistol use in general in the current conflict doesn’t appear to be prolific but a considerable number of combatants are frequently seen carrying side arms. Everything from Makarovs and Stetchkins to more modern Glocks and Ukrainian Fort handguns. Pistols are often carried by soldiers working in roles which frequently see them separated from their service rifle and by those who prefer to carry a secondary weapon.
While we’ve seen TT-33s in the hands of Russian and Ukrainian separatist troops in this video we’ll largely focus on Ukrainian use. At the fall of the Soviet Union a considerable amount of surplus small arms fell under Ukraine’s control, including substantial numbers of TT pistols. While not general issue it has been in service with the Ukrainian Army, National Guard and the Border Guard Service. This video definitely isn’t an exhaustive survey of TT use in Ukraine but lets take a look at some examples:
At the start of April 2022 the training department of the command headquarters of the Ukrainian Territorial Defense Forces have published a number of high quality videos showing how to disassemble and clean the TT.
The Ukrainian YouTube channel, Boys from the Forest (ХЛОПЦІ З ЛІСУ) shared a video looking at the TT in May 2022. They concluded their video by shooting a block of explosive reactive armour with the pistol – to no effect. In June Alina Mykhailova, a medic with 1st separate mechanised battalion “Da Vinci Wolves” shared a photo of some firearms used by the unit, including amongst other things – a TT pistol.
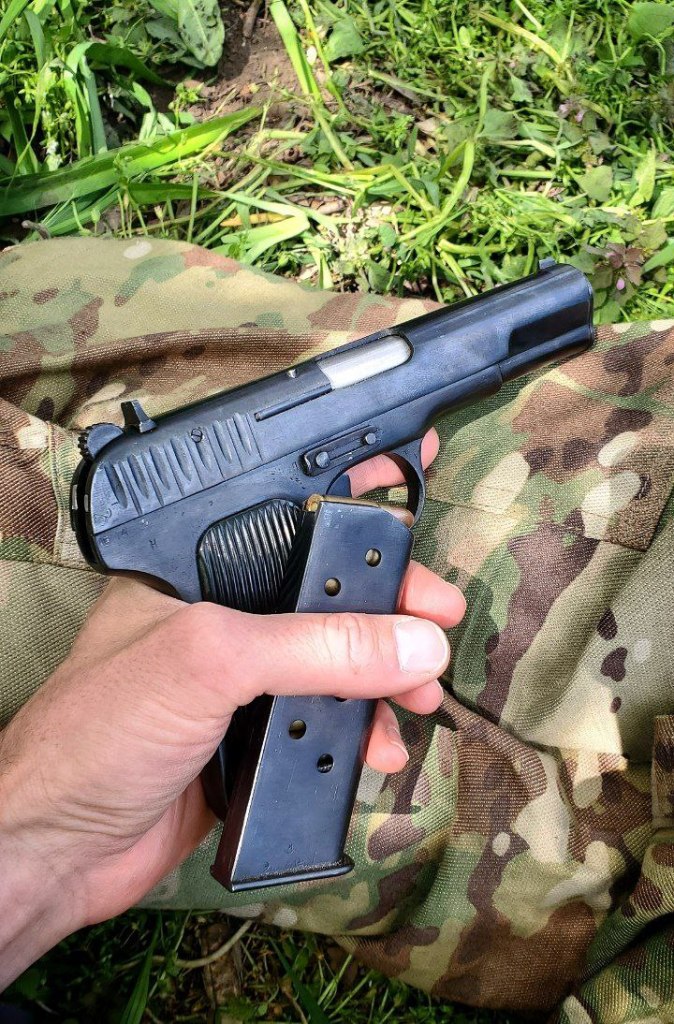

In around August some members of a TDF unit posed with a Nestor Makhno banner and a DP light machine gun and a TT-33 pistol. A Russian news report from around Soledar, published on 5 August, featured an interview with a soldier carrying a TT in a front pouch of his load bearing equipment. On the 12 August a Ukrainian operator shared a couple of photos of his side arm, a 1945-dated, Izhevsk manufactured TT-33 with wooden grips. Date and location they were taken wasn’t shared.
In an interesting video posted around the 25 August, a TT-33 is used to test some captured Russian steel plate. Yurii Kochevenko, an officer of the 95th Air Assault Brigade, shoots a one of the plates point black with TT he carries in a webbing holster. The 7.62x25mm round doesn’t cleanly penetrate the plate but appears to impart enough force to crack the metal.
At the end of November the Military Institute at the National University in Kyiv shared photos of cadets taking part in a shooting championship using TT pistols.
On 30 December, the 247th Separate Battalion of the TDF’s 127th Kharkiv Brigade shared a photo of Vitaly, a member of the battalion, armed with an AK-74 and on his plate carrier he has a TT in a Cytac holster. These tactical holsters for the 90 year old pistol retail for around 780 Hryvnia. On the same day Ukrainian personnel shared an update video from their position in Bakhmut, one of them is carrying a TT on his plate carrier.
A TDF officer, call sign Witch, has been seen numerous times carrying a TT-33 as her sidearm. Videos posted to her TikTok on 24 December and 12 January show it in a holster on her plate carrier, with a coil lanyard fitted. A video shared by the TDF Public Relations Service on 19 February also gives us a good look at the TT carried by Witch.

On 26 February 2023, the TDF’s 127th Kharkiv Brigade shared a gallery of photographs featuring the TT on their instagram page. The caption notes that: “Despite the fact that this pistol was actively used even during the Second World War, it is simple in design, reliable in operation, small in size, comfortable to carry and always ready to defeat the Russian invaders.”
A Ukrainian special operations unit shared a photo of a member of the unit sat beside a Russian prisoner while holding two TT-33 pistols, one in its original finish and the other was a camouflage paint job. Most recently at the start of March a Ukrainian marksman active around Bakhmut shared a photo of his position with a rotary grenade launcher, a UAR-10 and a TT pistol.
In addition to the original TT-33s seen in theatre there are also a significant number of former-Yugoslavian M57s which while externally very similar have some improvements, including a slightly longer grip that allows the magazine to hold an extra round.
Update – 25/6/2024:
Support Us: If you enjoyed this video and article please consider supporting our work here. We have some great perks available for Patreon Supporters – including early access to custom stickers and early access to videos! Thank you for your support!
Bibliography:
The Procedure for Partial Disassembly and Assembly of a TT pistol, TDF, (source)
Rules for cleaning and lubricating weapons on the example of a TT pistol, TDF, (source)