Way back in February 2024, I published an article/video discussing sightings of one of the so-called Franken-SAM systems provided to Ukraine by Western allies. The ASRAAM-armed system was developed and provided by the UK but until this year little information about it had been confirmed. On 10 May the UK Ministry of Defence confirmed that they system is called ‘Raven’ and a total of 13 of the systems have been pledged.

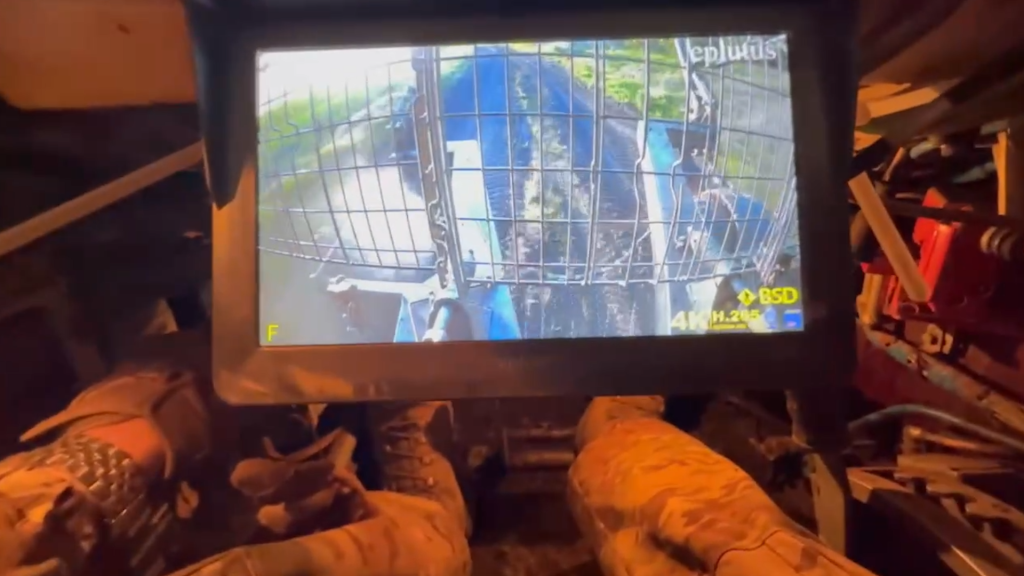
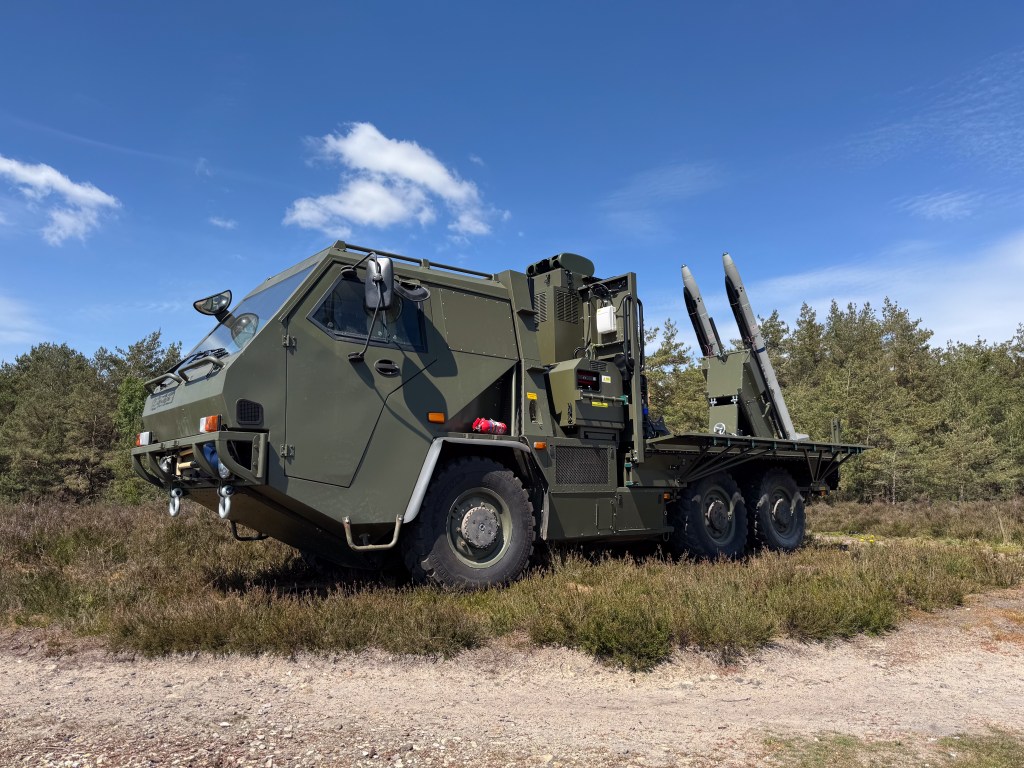
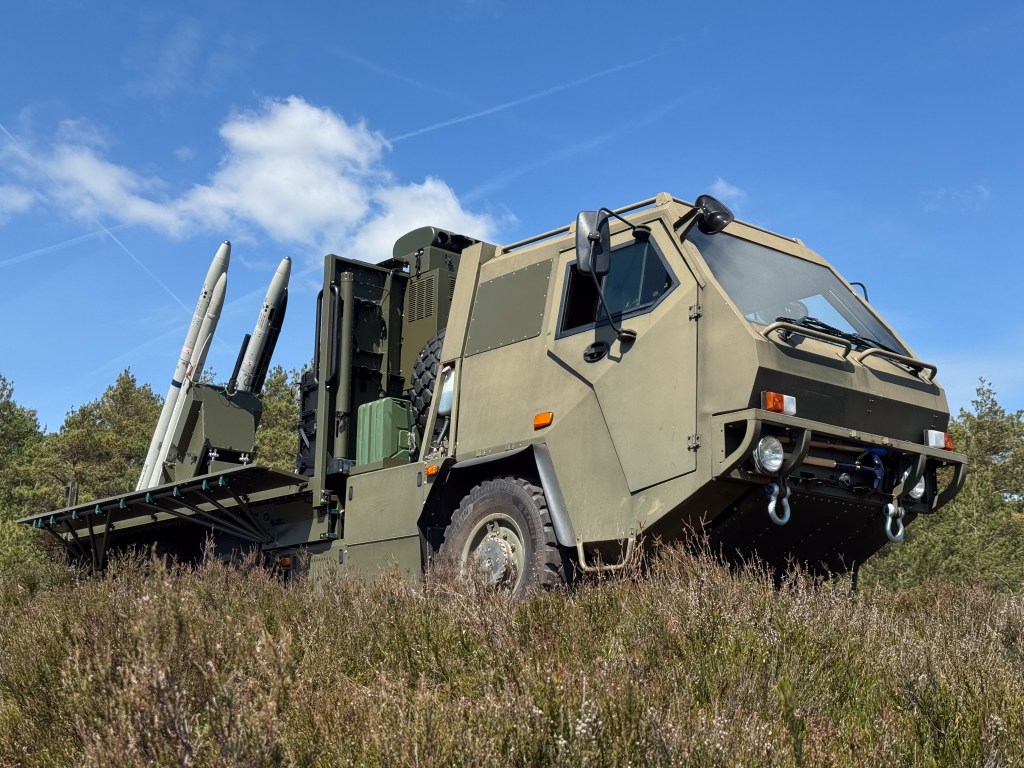
The previously available imagery showed that the system comprised two AIM-132 Advanced Short-Range Air-to-Air Missiles (ASRAAM) mounted on a Supacat HMT 600 (6×6) vehicle. The vehicles are believed to be former Soothsayer ECM carriers brought out of storage. Also visible is what appears to be a mast-mounted sensor unit positioned behind the cab, on the vehicle’s flatbed. This appears to be a Chess Dynamics Hawkeye which likely includes electro-optical and infrared sensors used for targeting.
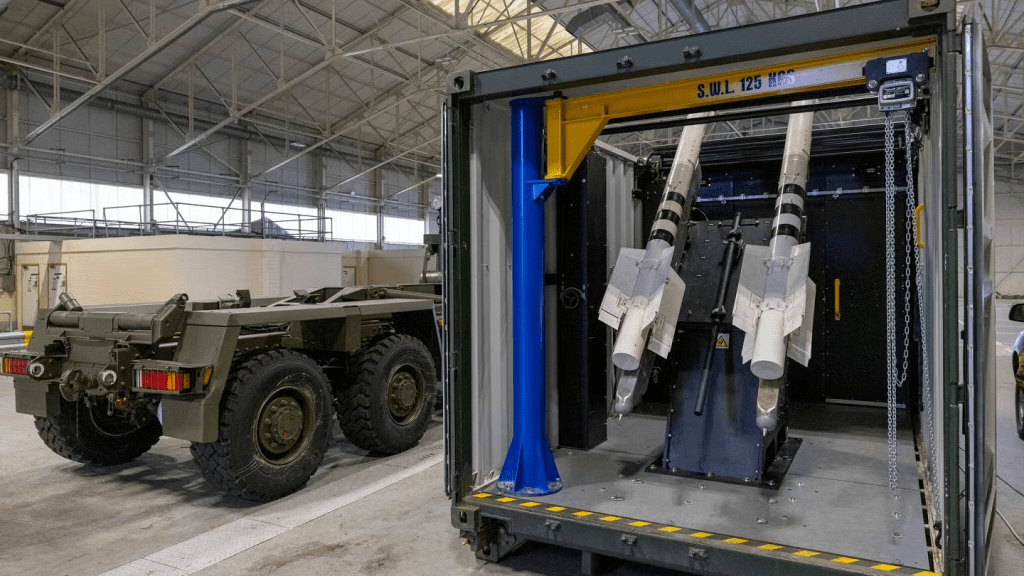

The UK-developed Raven is one of several ad hoc short-range air defense systems developed by the UK for Ukraine, the other being Gravehawk, a containerised system which utilises R-73 air-to-air missiles, which was unveiled in February 2025. Both systems are part of an effort to affordably and quickly bolster Ukraine’s air defences. In October 2023 a pair of videos shared by the Ukrainian air force gave a glimpse of the system in action. The both filmed at night shows a launch but the vehicle is not visible. The second, shared on 12 October, by Ukraine’s Air Command – South shows the successful engagement of a Russian long range loitering munition. As the darkness is lit up by the missile launch, the Supacat 6×6 High Mobility Transporter is briefly visible.
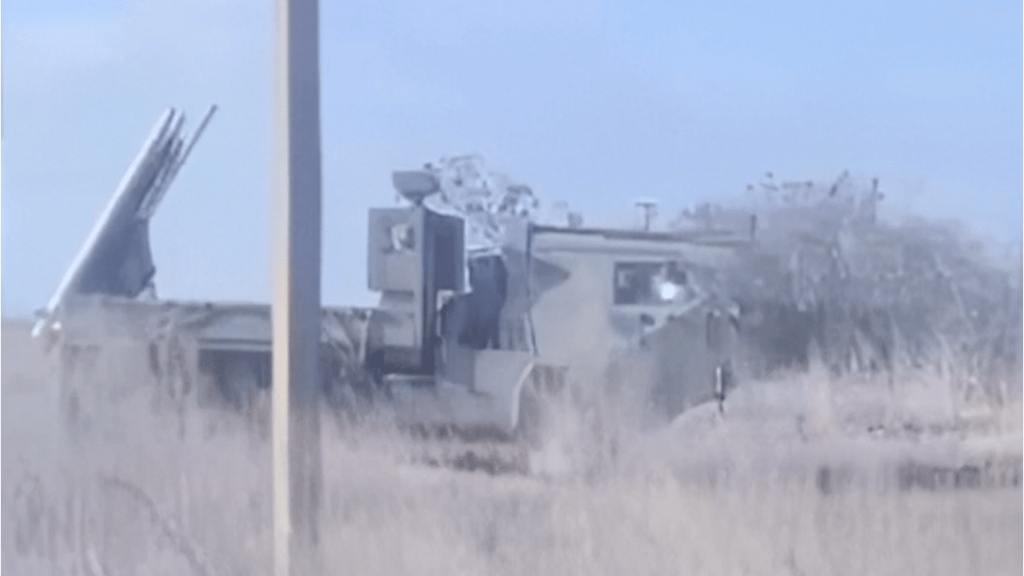

ASRAAM uses infrared homing and can lock onto its target after launch. It has an air-launched range of more than 25km but this is likely shorter when used in a ground launched role. The system may be used in conjunction with radar systems which feeds target data to the missile. A key feature of the ASRAAM is its ability to lock-on after launch, theoretically allowing it to be vectored onto a target in the air before it begins IR homing.
The system, however, isn’t ideal with limited ready-to-fire capacity on the launcher ramp, with just two rails, and no protection for the missiles themselves, from either the elements or from potential fragmentation or impact damage if attacked. The ad-hoc air defence system first saw action in Ukraine in August 2023, and represents an ingenious improvisation utilising a highly capable missile in an air defence role it was never envisaged in. In December 2023 UK Ministry of Defence summarised their development:
“In summer 2022, a joint MoD-MBDA team developed air defence systems to fire ASRAAM from the ground for the first time. Within four months of initiating the surface launched ASRAAM project, these air defence systems were developed, manufactured, trialled and Ukrainian crews trained on their usage, on UK soil, before being transferred into Ukrainian hands.”
In late 2023, it was reported that the UK had supplied “a handful” of the missile-equipped Supacat trucks. They were believed to be in use in near the front and in the Kyiv region, defending key infrastructure, against Shahed-136/Geran-2 long-range loitering munition attacks. In December 2023, the UK Ministry of Defence announced that a further 200 ASRAAMs would be provided to Ukraine and that the systems in-country had achieved a “successful hit rate reported as high as 90% against some Russian air targets.” ASRAAM’s payload, a 10kg blast-fragmentation warhead, is designed to destroy aerial targets with minimal collateral damage.

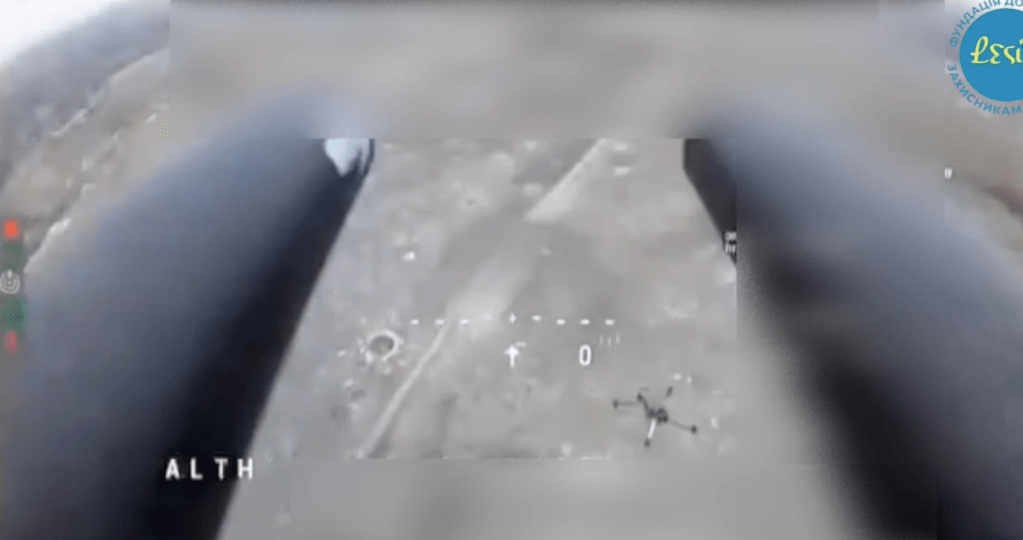
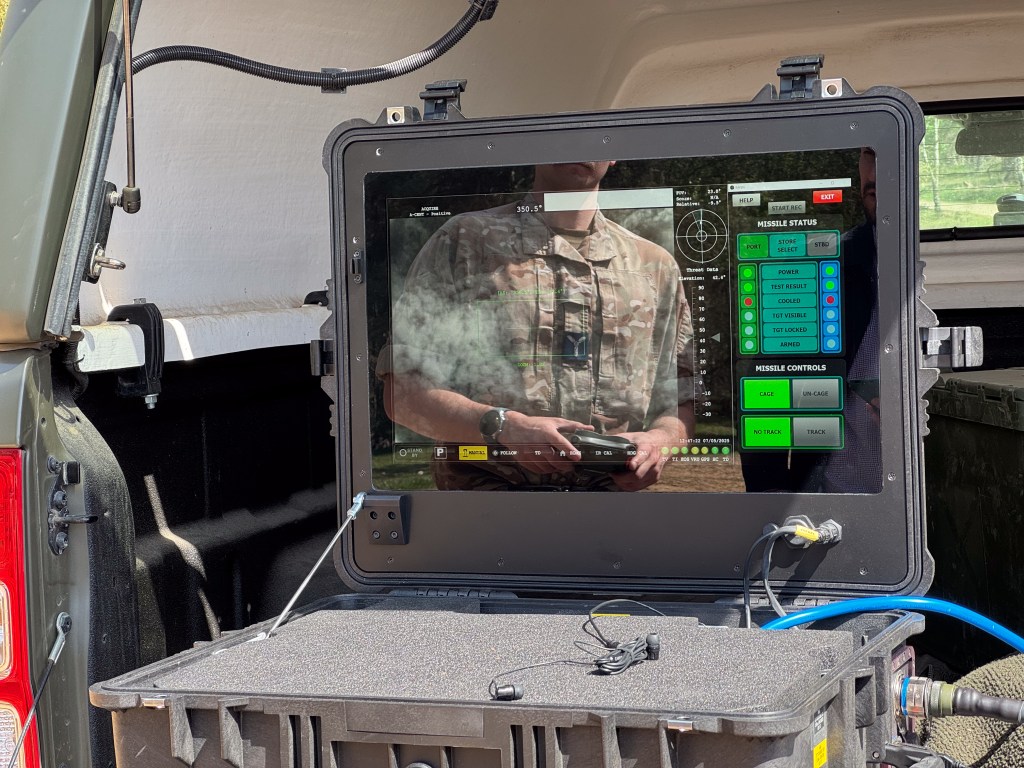
A number of videos showing glimpses of the system itself or the system in action were shared throughout late 2023 and 2024. On 12 October 2023, footage of a night launch against a Shahed one-way munition was shared including thermal footage from the systems sensors. In late February 2024, footage, again from the Raven’s sensors, showed the successful engagement of a Russian ZALA reconnaissance drone.
A month later on 20 March, both external and system footage of a daytime engagement of a Russian Supercam S350 reconnaissance UAV was shared. Later in March additional footage of what was also claimed to be a Supercam was also shared.

On 3 April, thermal camera footage of another UAV interception was posted on Ukrainian social media. The speed and vector of the missile suggests it was a Raven-launched ASRAAM. On 14 April 2024, a short clip showing an ASRAAM missile with a message written on it ‘Rowdy Company’, followed by footage of a night-time launch was shared.
In early May 2024, Russian Telegram channels shared drone footage of what they claimed as the destruction of one of the systems by a Lancet loitering munition. While footage of the systems in action is few and far between another daytime video of the system in action was shared in mid-September 2024, having been posted to TikTok.
Most recently, in late November 2024, a video containing footage from a number of Ukrainian anti-aircraft units showed several interceptions of Russian drones and a launch from what appear to be Raven system.
In March 2025, a couple of photos were shared by the UK Ministry of Defence showing Rachel Reeves, the UK’s Chancellor of the Exchequer being briefed on Raven during a visit to RAF Northolt, though the name of the system was not disclosed at the time they gave the best side-on look at the system to-date.
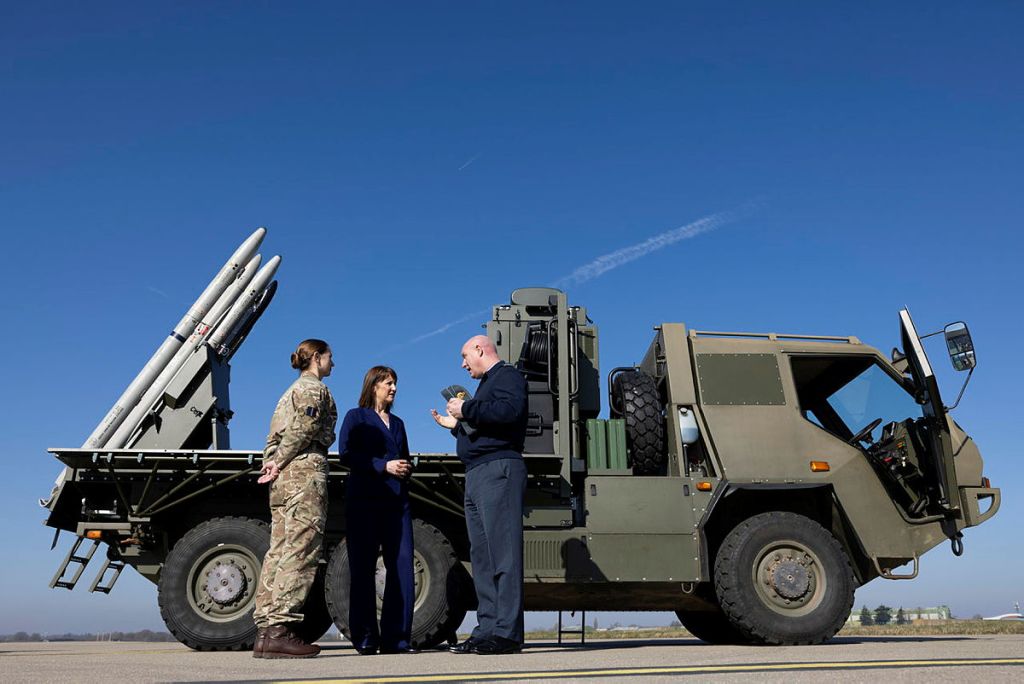

The UK Ministry of Defence unveiled the Raven officially on 10 May 2025. In a video posted to the UK MoD YouTube channel the system was shown in detail and some interesting stats were shared. Colonel Olly Todd, Military Assistant Head of Taskforce Kindred [Taskforce Kindred refers to the MoD’s effort to provide equipment to the Armed Forces of Ukraine (AFU), from UK stockpiles and rapid procurement.] noted that the UK has provided approximately 400 ASRAAM (which were near the end of their service life) to Ukraine and from 400 launches the systems’ engagement success rate stands at around 70%. The video also confirms that eight Raven systems were deployed to Ukraine in 2022 and a further five are set to be provided in 2025.
Raven was developed in just three months with experts from MBDA, Supacat at the RAF’s Air & Space Warfare Centre involved in the process. It combines a Supacat HMT-600 vehicle with the MBDA-manufactured ASRAAM using a bespoke launch assembly which integrates launch pylons taken from legacy UK aircraft including Hawk, Jaguar and Tornadoes. Unsurprisingly Raven and Gravehawk use the same control system and likely share the same system-integrated sensor units for tracking and identifying targets before locking on with the missiles’ seekers before launch.
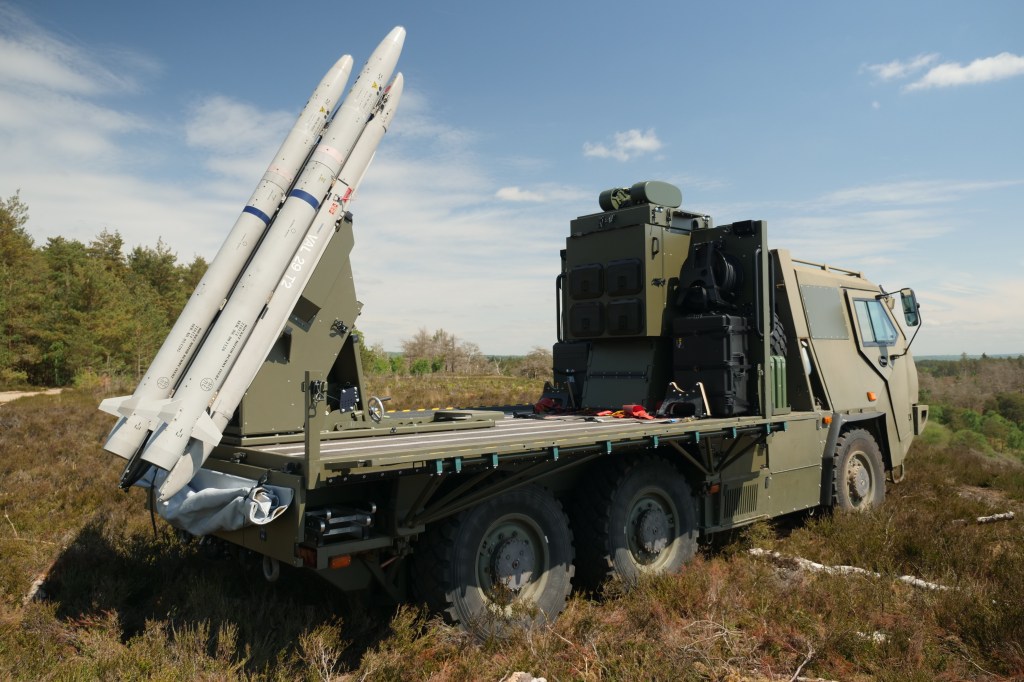

While ASRAAM is still in production it is worth noting that other than the UK, the only other current user is India – though several Middle Eastern nations have reportedly adopted it, this means the stock of older missiles ready for disposal will be somewhat limited. It is so far unclear if the Raven systems could also be adapted to launch other missiles such as the R-73 used by the Gravehawk.

Despite the potential limited availability of the missiles the relatively cost-effective price-tag of an ASRAAM, reported to be around £200,000 (or $260,000), makes the Raven a useful system for not only protecting key Ukrainian infrastructure but also, as has been seen in some of the footage available, engaging Russian reconnaissance drones which feed important information back to Russia’s command and control apparatus.
Updates – 25/07/25:
Update – 2/7/25:
The Ukrainian Air Force shared a video featuring the Raven giving an extensive look at it on operations in Ukraine.
The crew have painted up one side of the cab with a kill tally with the silhouette of various different drones. The visible tally includes:
– 17 Shaheds
– 1 Cruise Missile
– 17 Orlan 10 UAV
– 13 Supercam UAV
– 25 Zala UAV
Update – 27/10/25:
On 24 October, the Ukrainian Air Forces’ Air Command “West” social media shared a photo of a Raven system, noting that it had destroyed 24 Shaheds and several cruise missiles.
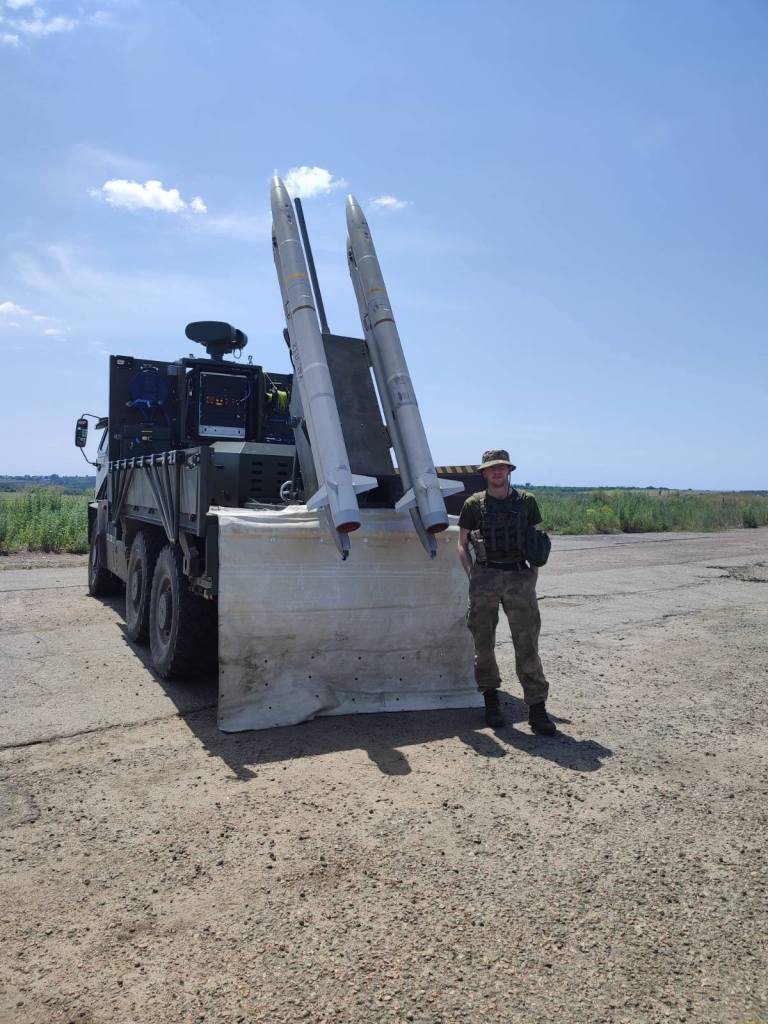

A video was also shared showing the successful engagement of Russian Kh-59 and Kh-101 cruise missiles.
Support Us: If you enjoyed this video and article please consider supporting our work here. We have some great perks available for Patreon Supporters – including early access to custom stickers and early access to videos! Thank you for your support!