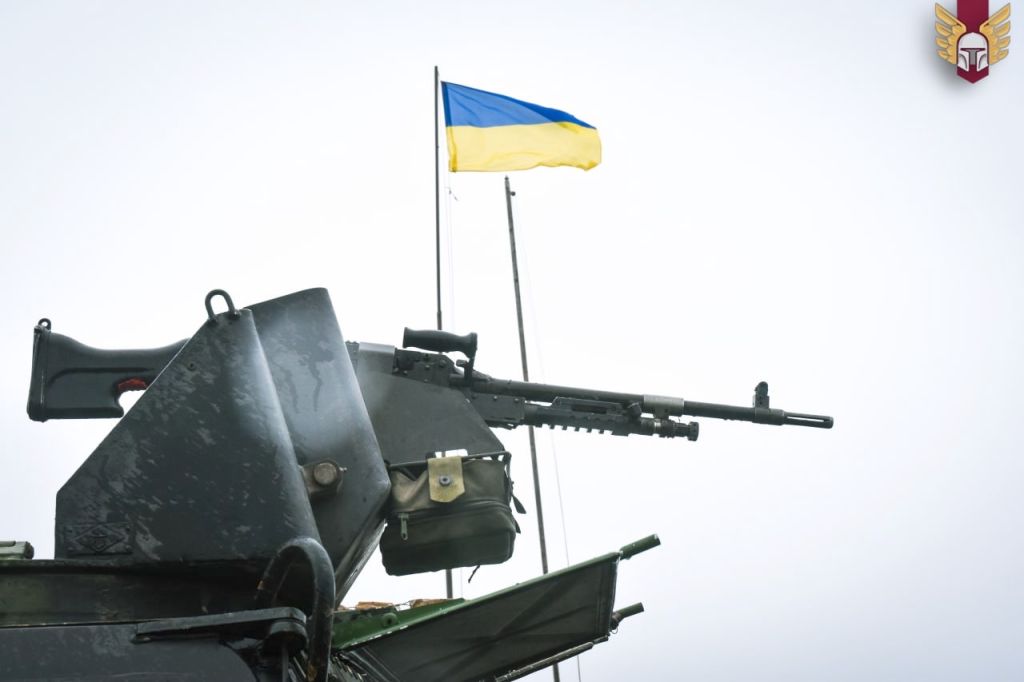
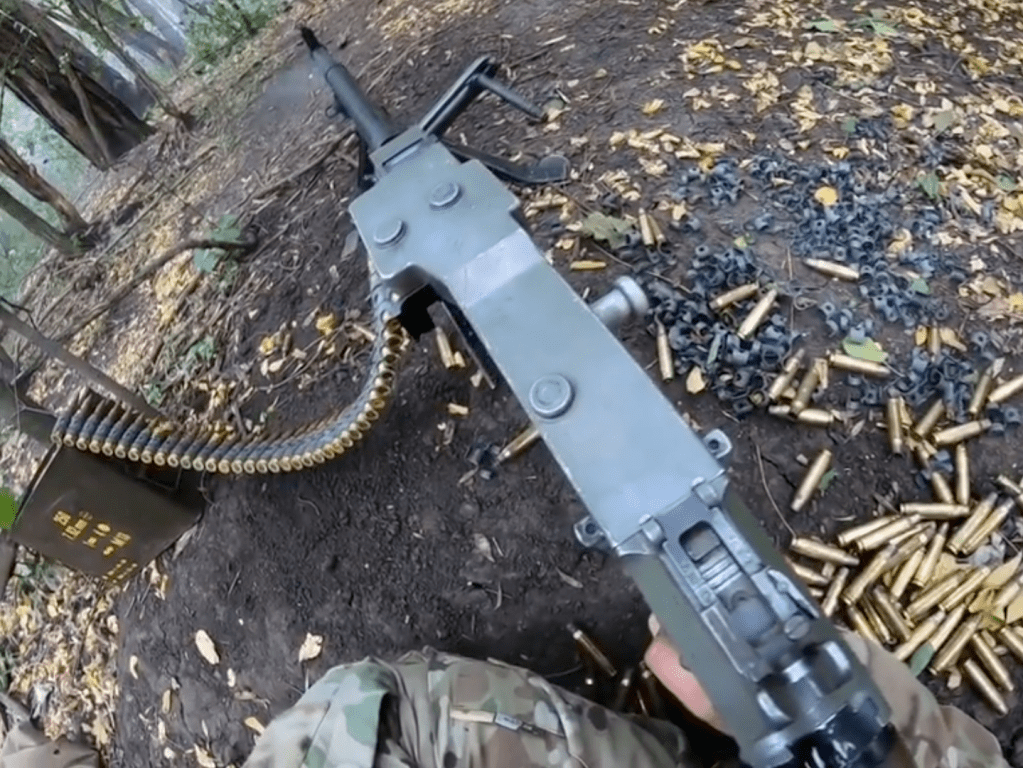
There are a lot of different types of general purpose machine guns in use in Ukraine and one of the most surprising to appear so far is the M60. The first appearance of an M60 in Ukraine came in September 2024, when the 23rd Mechanised Brigade shared an album of training photos which included an individual firing an M60D.

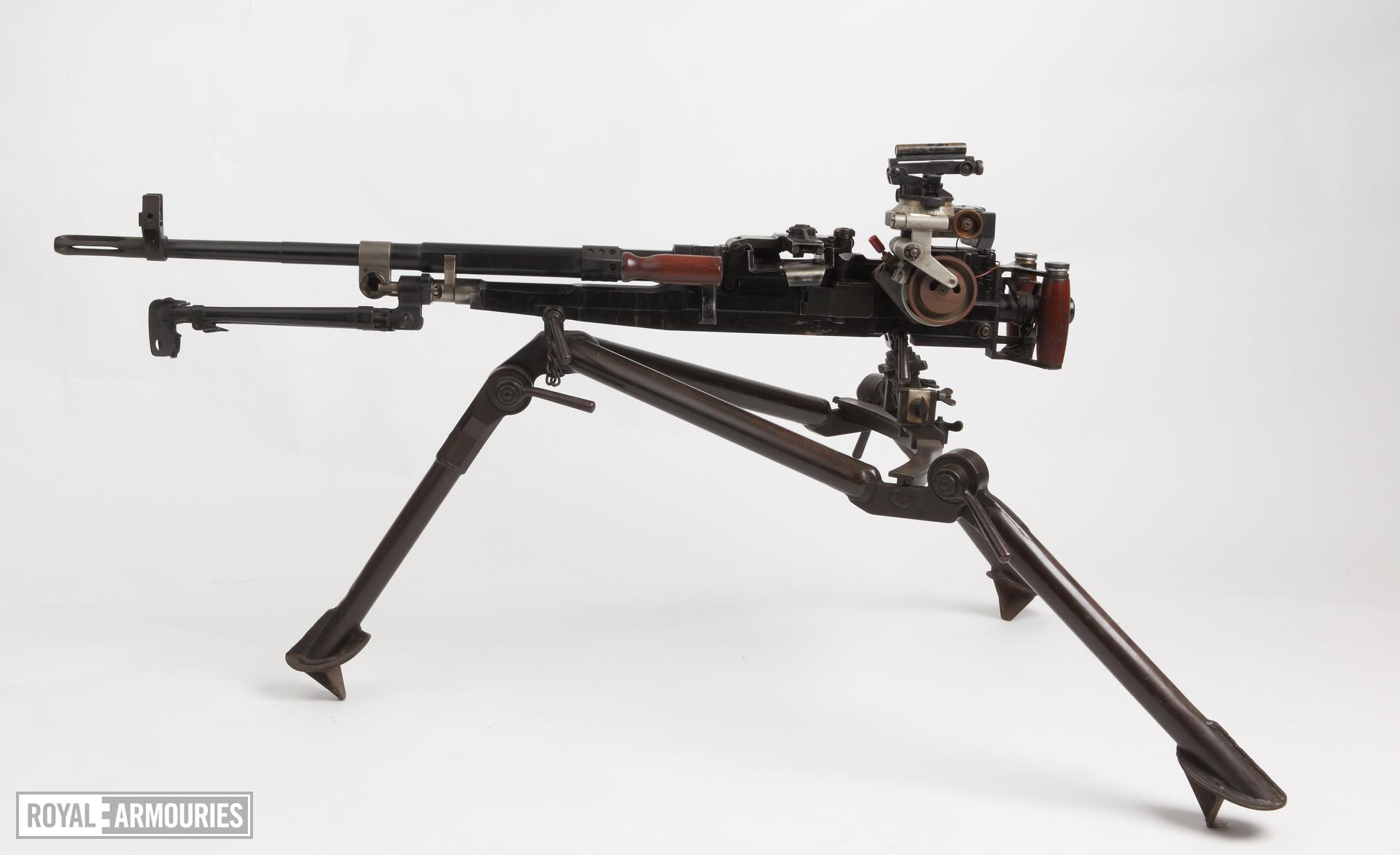
A month later the same brigade shared another photograph of the M60D. The M60D is usually mounted on helicopters as a door gun and as such it has been adapted with no stock or traditional rear sight, instead it has a pair of rear spade grips and a large ring sight. It’s unclear how many M60Ds are in Ukraine or where the guns originated from as a number of potential donor countries operate M60Ds as door guns. It may be the case that a donor nation provided the gun aboard a donated helicopter, we have previously seen French AANF-1 GPMGs appear in Ukraine – likely supplied with VAB APCs. Alternatively, the gun(s) may simply have been provided by a donor for whom it was surplus to requirements and ready for disposal.

Another sighting of an M60D came in May 2025, when the 65th Mechanized Brigade shared a series of photographs of a machine gun team training with one of the guns. Sadly, no markings are visible to confirm if this might be the same gun as previously seen with the 23rd Mechanised Brigade.
The M60D is not the easiest variant to utilise in a ground role with the absence of a stock to shoulder the weapon making it somewhat difficult to aim and keep on target while firing. It does have a folding carry handle but it also had an exposed trigger linkage which is far from ideal for ground use. The best use for this variant would probably be as a pintle-mounted an anti-air gun.

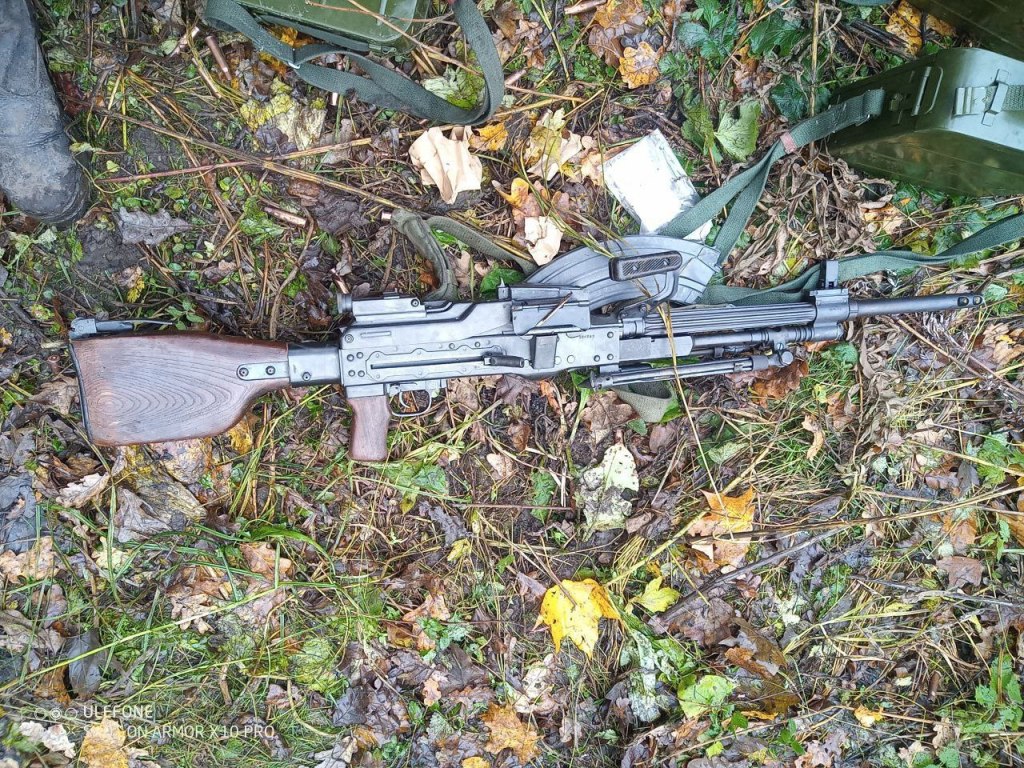
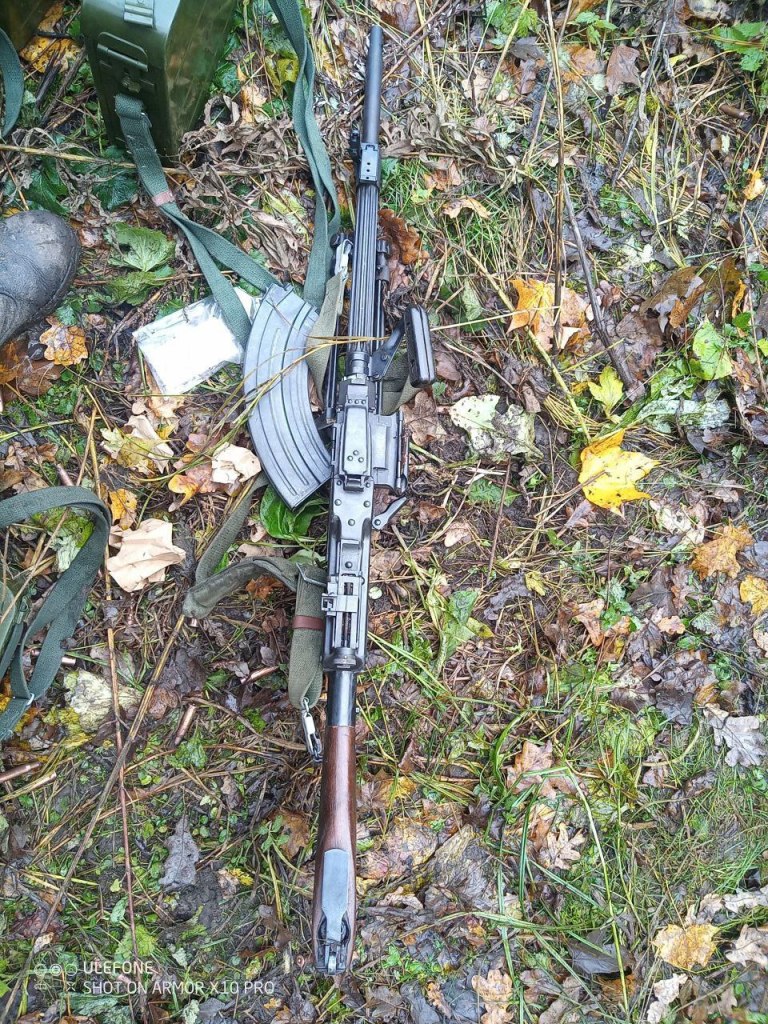
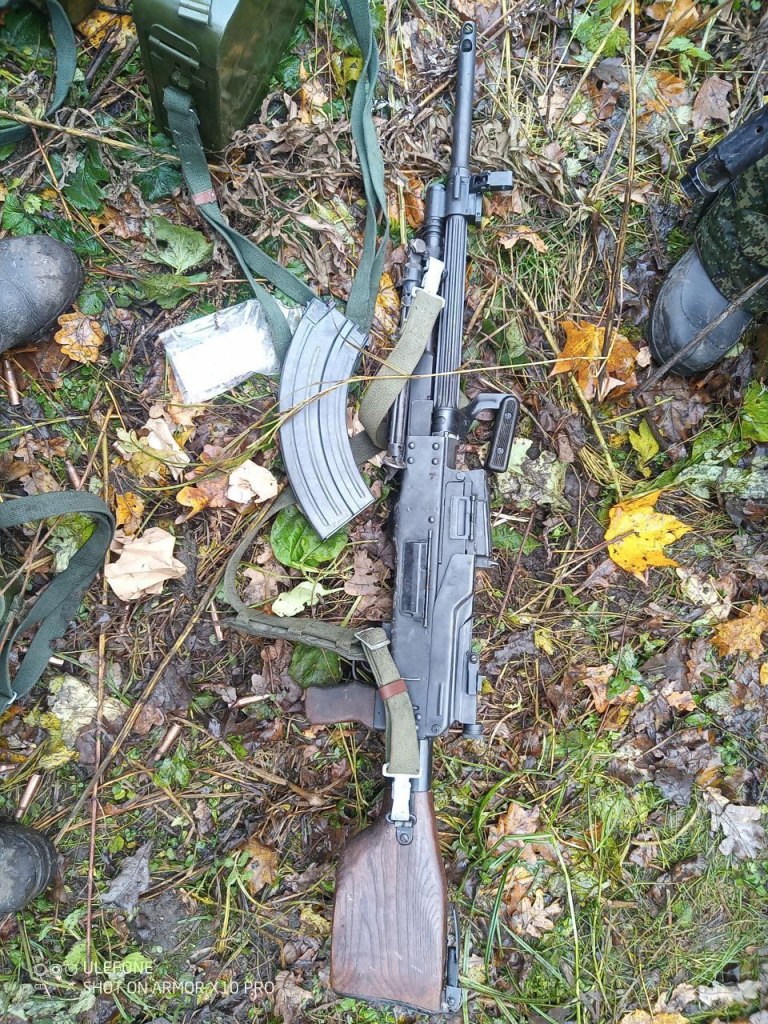
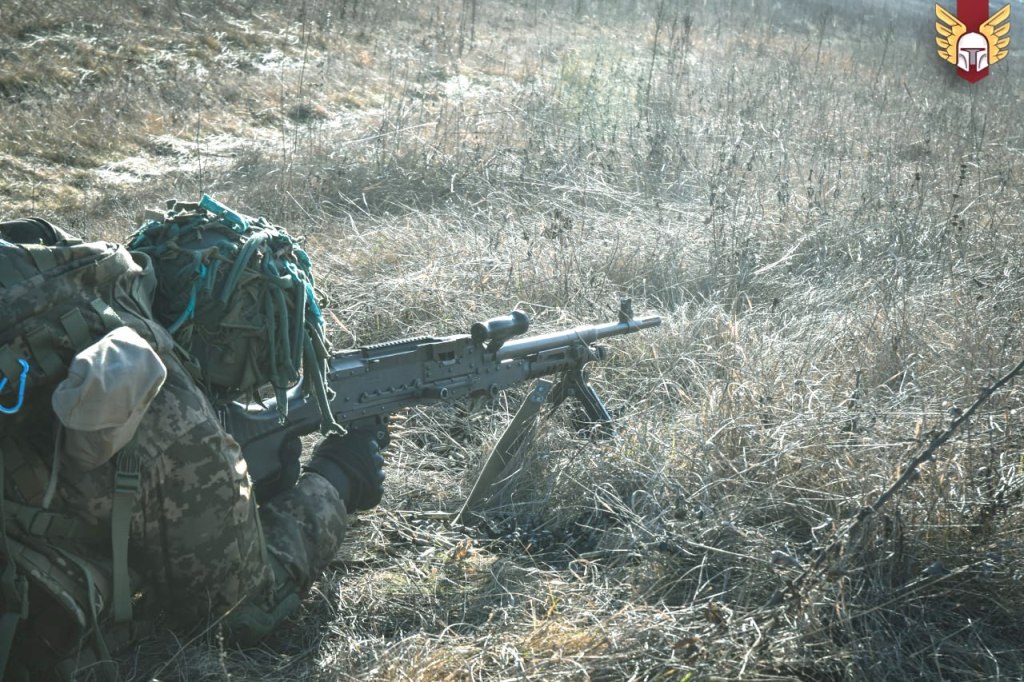
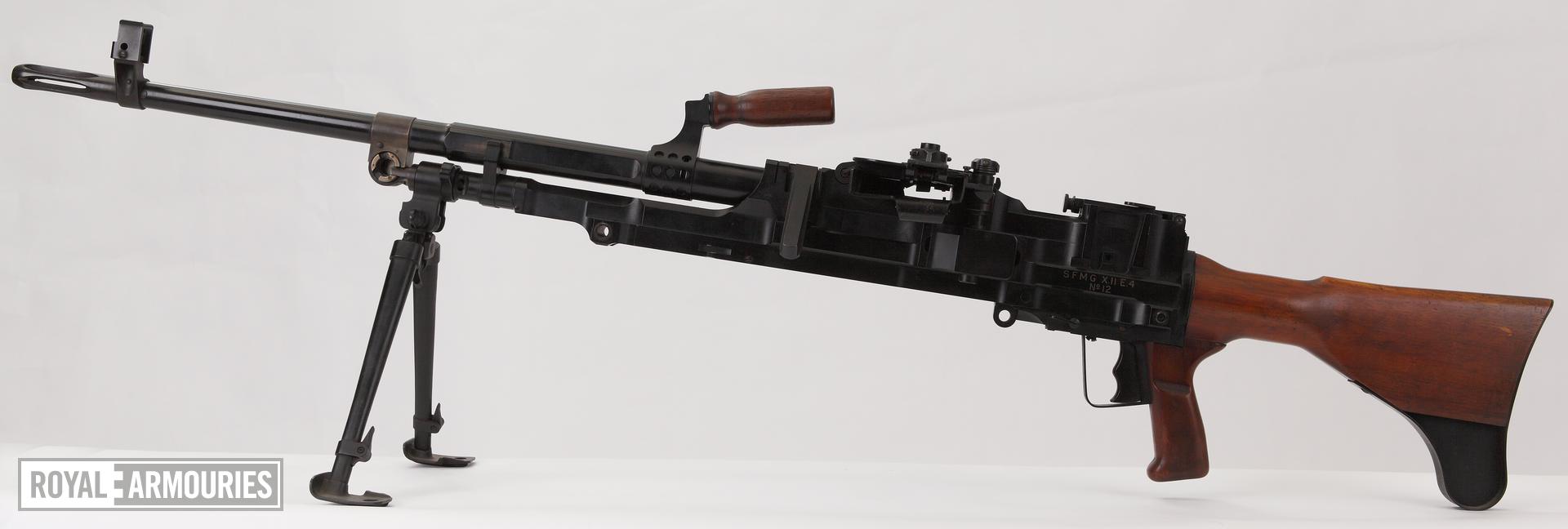
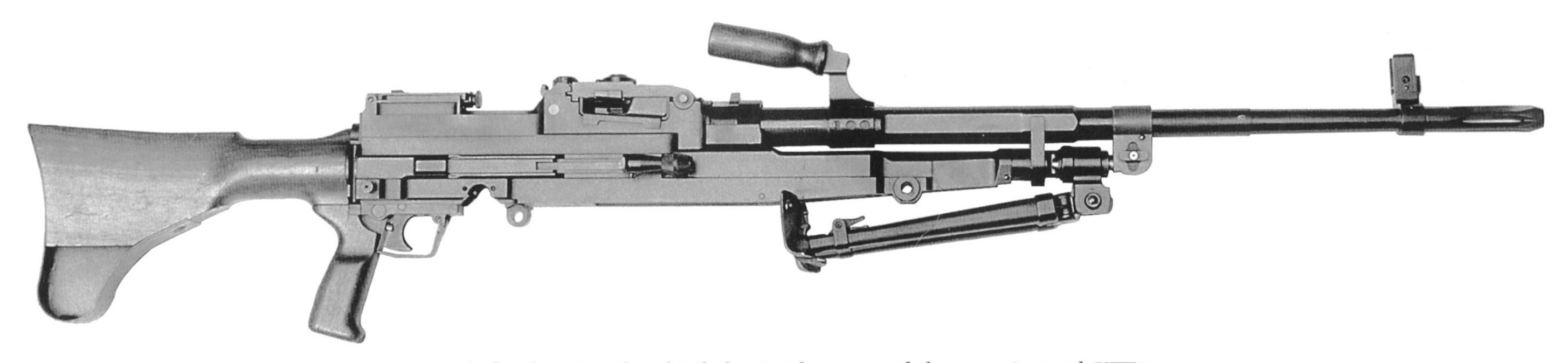
Most recently a new variant of the M60 was seen in a photo posted, on 18 July, by the 20th Separate Regiment of Unmanned Systems “K-2”. The gun appears to be either an M60E3 or an M60E4, with what appears to be a 22 inch barrel, the first ground role variant to be seen in-country. As with the M60Ds it is unclear where this M60 may have originated from, there are only a small number of nations which operate the weapons which may have donated it. Elements of the Czech Republic’s special operations forces operate E4s in small numbers but its unclear if this is the source of the gun seen in the recent photo.
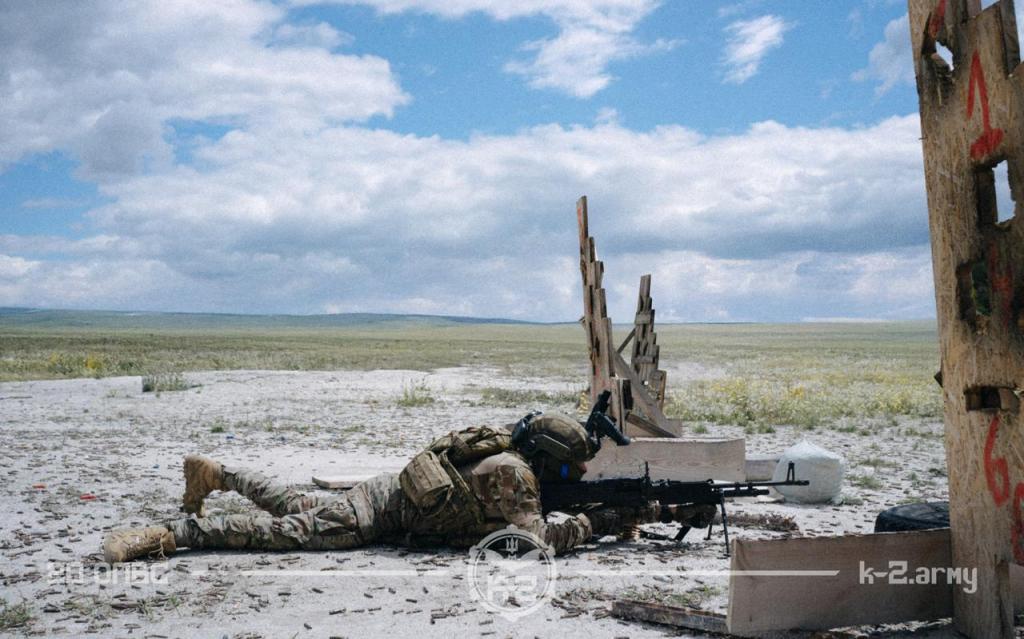

It remains unclear just how many of the various variants of M60 are on the ground in Ukraine and where they came from but it is one of the weapons that I’ll continue to track, if you spot any let me know!
Update 12/10/25:
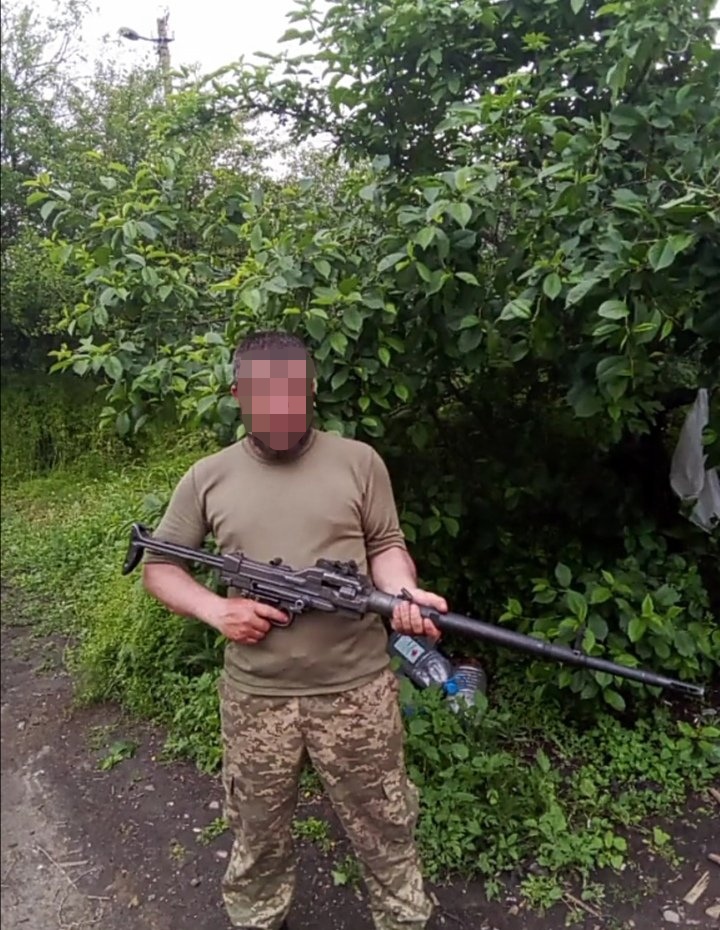
Serhii Filimonov, a member of the 1st Assault Regiment (Da Vinci Wolves), has shared several photos that appear to include an M60E4.
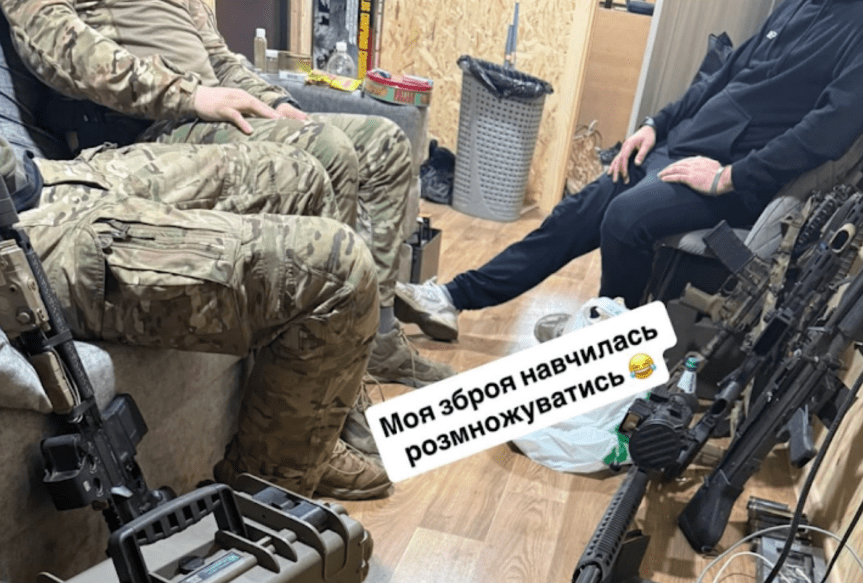
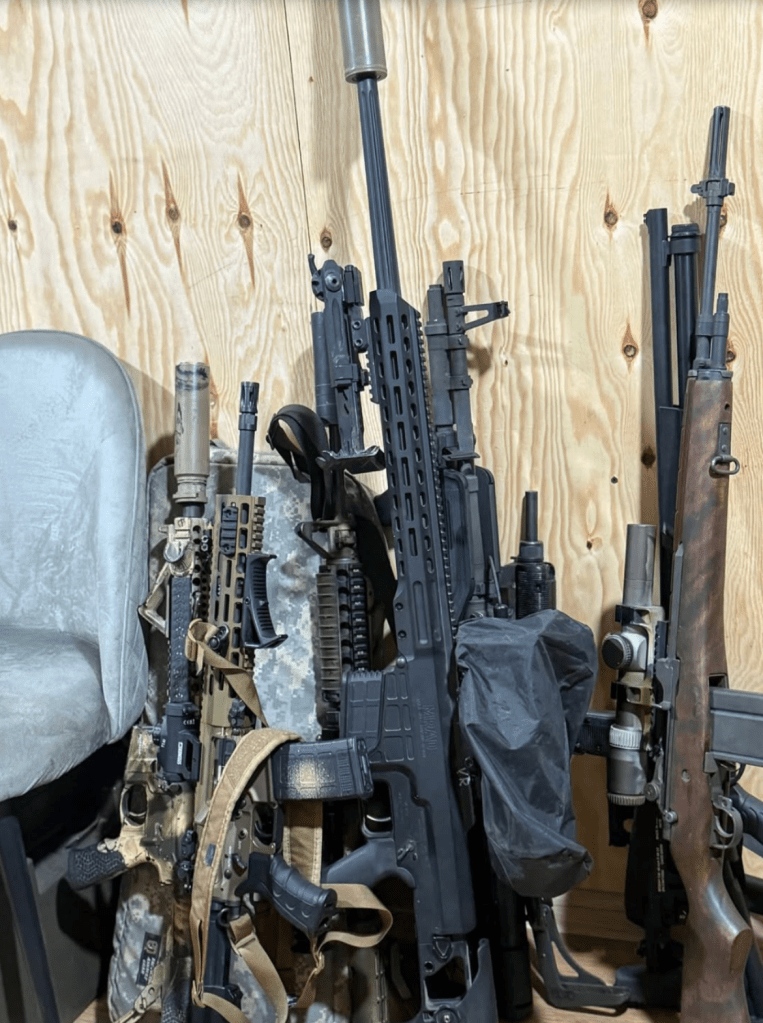


There is also a short video of him firing the weapon. Below is a still from the video.
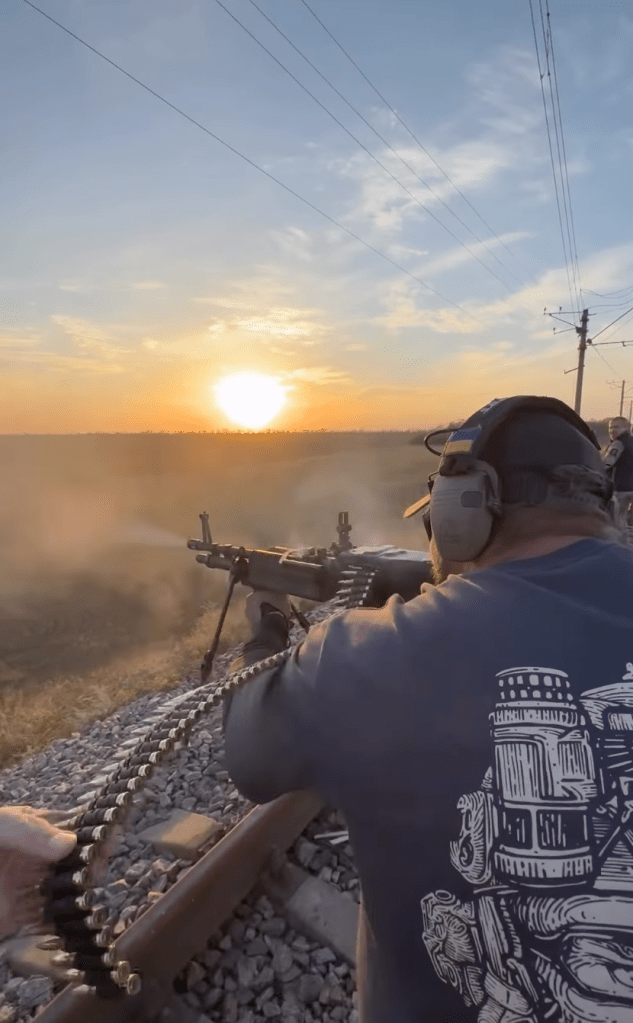

Update – 17/11/25:
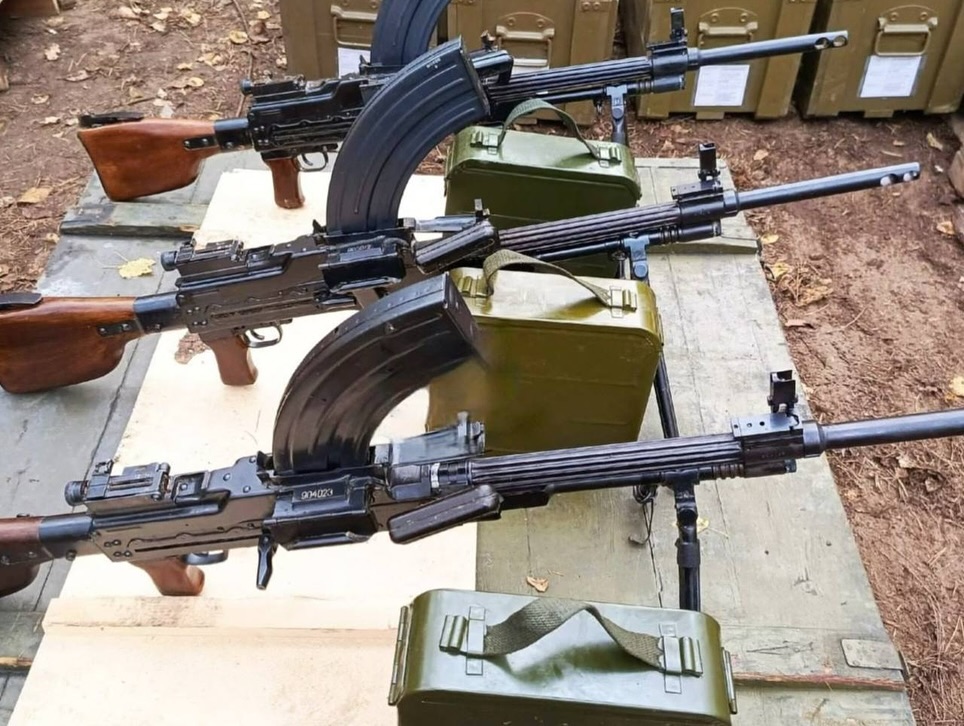
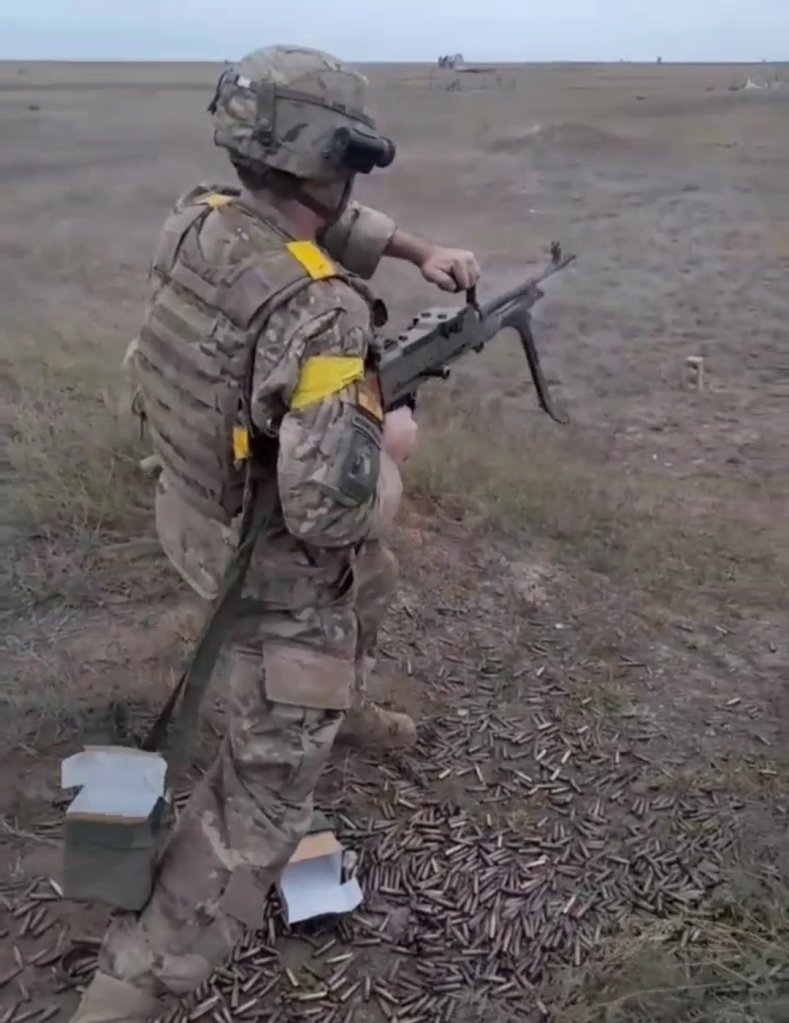
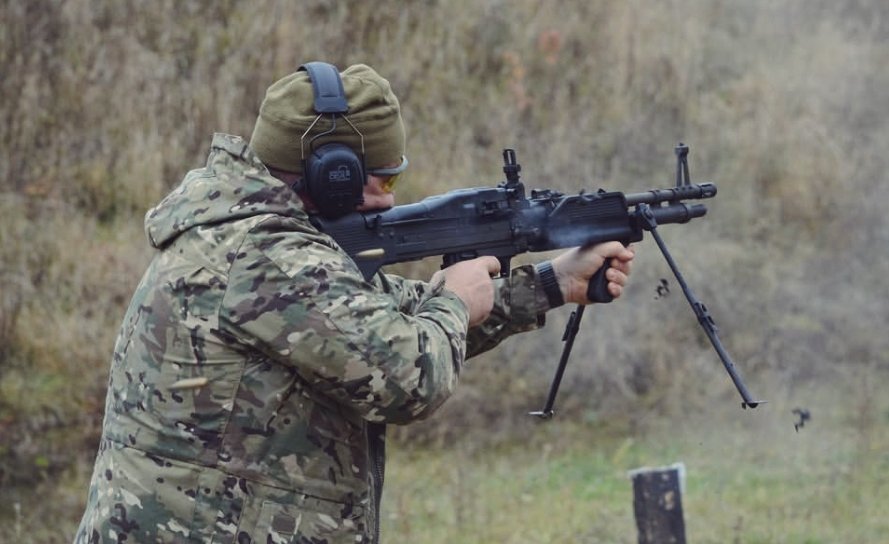
On 14 November, Raven Group, affiliated with the Ukrainian Directorate of Intelligence, shared a serious of range photos featuring an M60E4 (in what appears to be the Mk43 Mod 0 configuration). [H/t to Praise the Steph].

Support Us: If you enjoyed this video and article please consider supporting our work here. We have some great perks available for Patreon Supporters – including early access to custom stickers and early access to videos! Thank you for your support!