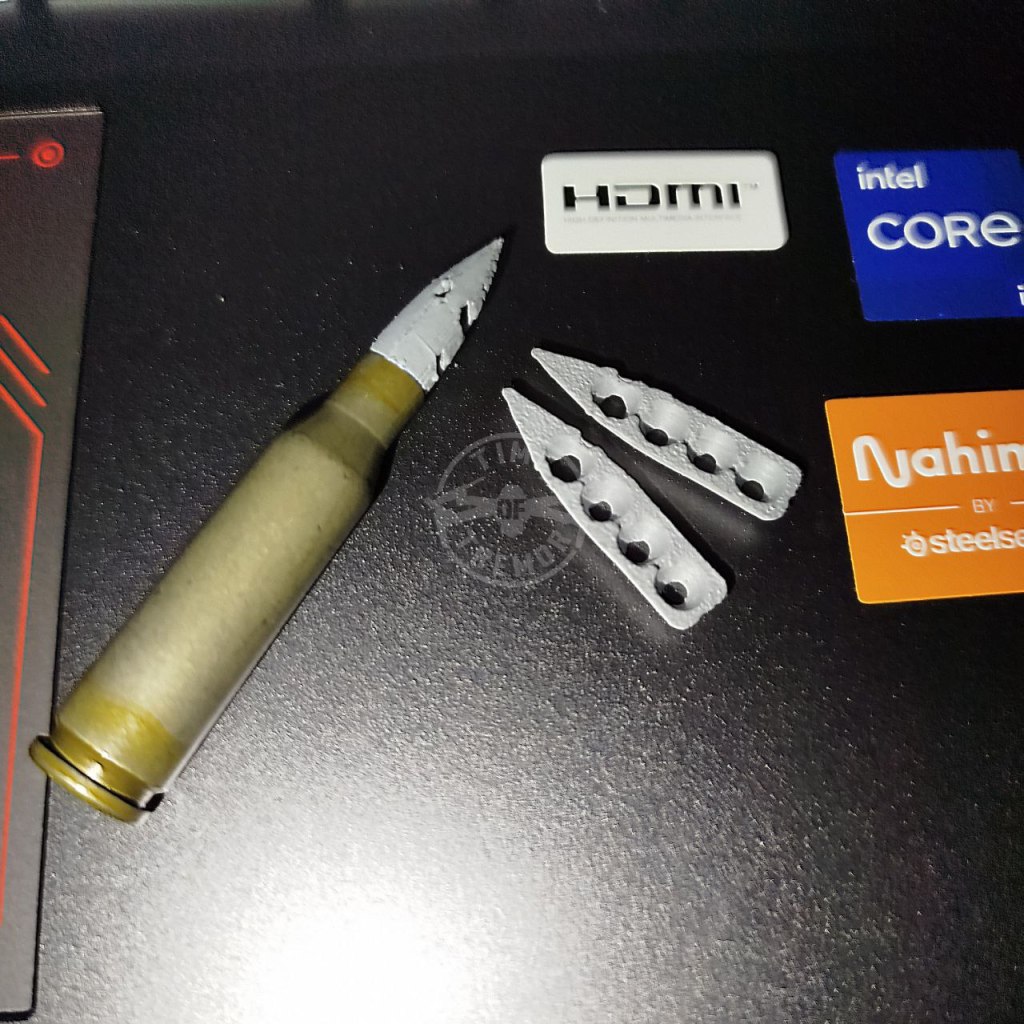
Back in December I published an article/video examining the Russian practice of creating a rudimentary anti-drone round from a 5.45x39mm cartridge case and a handful of ball bearings (BBs). The BBs are encapsulated in shrink-wrap tub ing and then loaded in the cartridge case like a conventional bullet. This was seen to be relatively effective with evidence of multiple workshops independently producing the ammunition.

The ad-hoc production of the ammunition has been seen in locations ranging from kitchen tables to well-laid out large workshops. The rounds have also been tested by Ukrainian forces and there has been some interest in replicating the buckshot cartridges but its unclear if this has come to fruition as yet, shotguns appear to be more prevalent for Ukrainian forces.
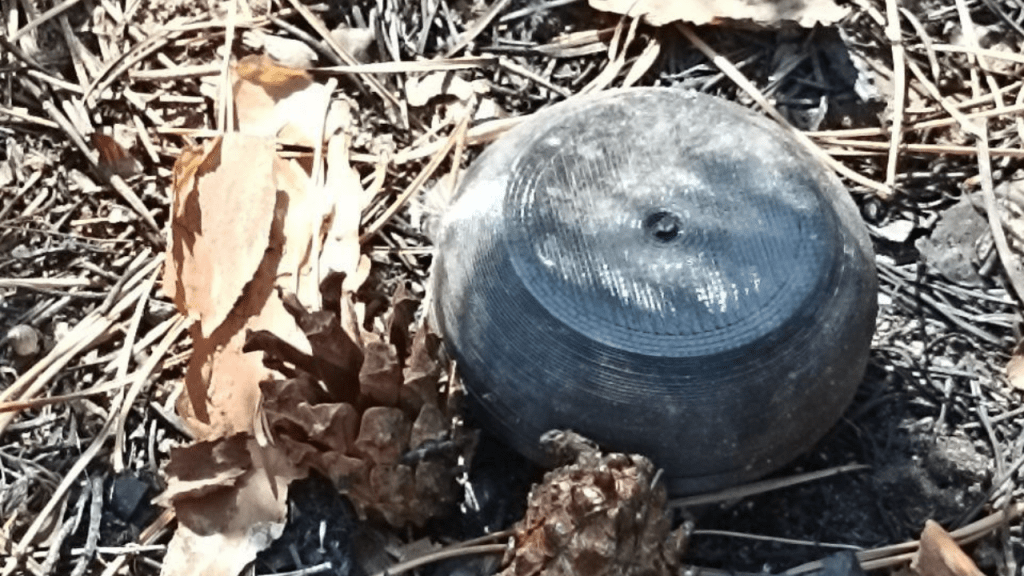
3D printing has become a key element in so many aspects of the ongoing war so it was inevitable that it would be leveraged in making this ad-hoc anti-drone ammunition. It appears that several Russian workshops have now developed 3D-printed sabots to replace the shrink-wrap tubing. It appears that this move towards 3D printed sabots is an effort to prevent the barrel being fouled by plastic from the tubing. This is an issue which has been highlighted in a number of posts including a bore scope video published by Ukrainians who tested the home-made rounds. The shrink-wrap likely disintegrates in the barrel leaving behind polymer residues whereas the 3D printed sabots seem to remain intact until they leave the barrel.

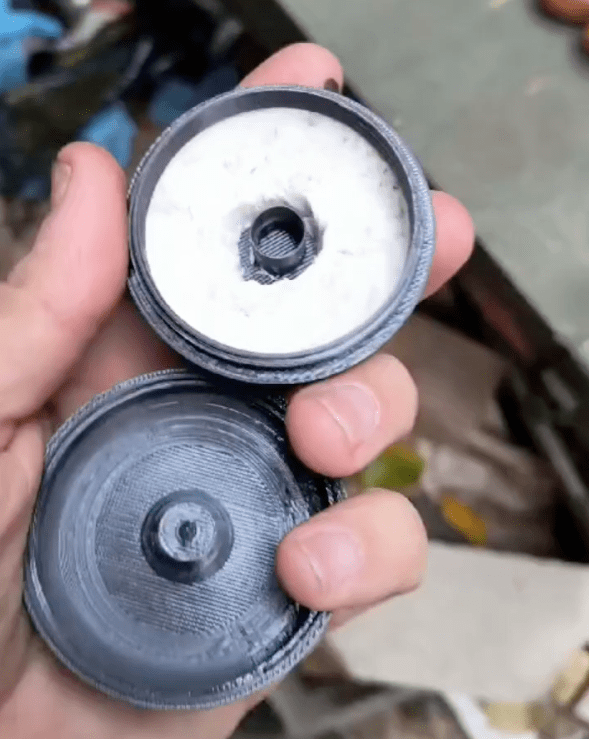
The first sighting of the 3D printed sabots came on 23 February, when a Russian telegram channel shared a video showing the printing and assembly of the anti-drone ammunition with 3D printers printing a bullet-shaped sabot. The design and production was attributed to the assault detachment of the 33rd regiment of the 20th Guards Motor Rifle Division. The design consists of a two-piece clam shell-like design which encapsulates the BBs and can be loaded into a 5.45 cartridge case like a conventional projectile. The video shows three 3D printers printing the sabots which hold 4-rounds each. It then shows how the standard cartridge’s projectile is pulled from the case, the sabots are loaded with BBs and then the sabot is tapped down into the case.

The video then shows an individual firing full auto at a target, said to be 75m away away – thought the distance is difficult to verify. It then cuts to a shot of the rifle disassembled and the individual filming states that after four magazines there is no plastic residue in the gas system, barrel or action.
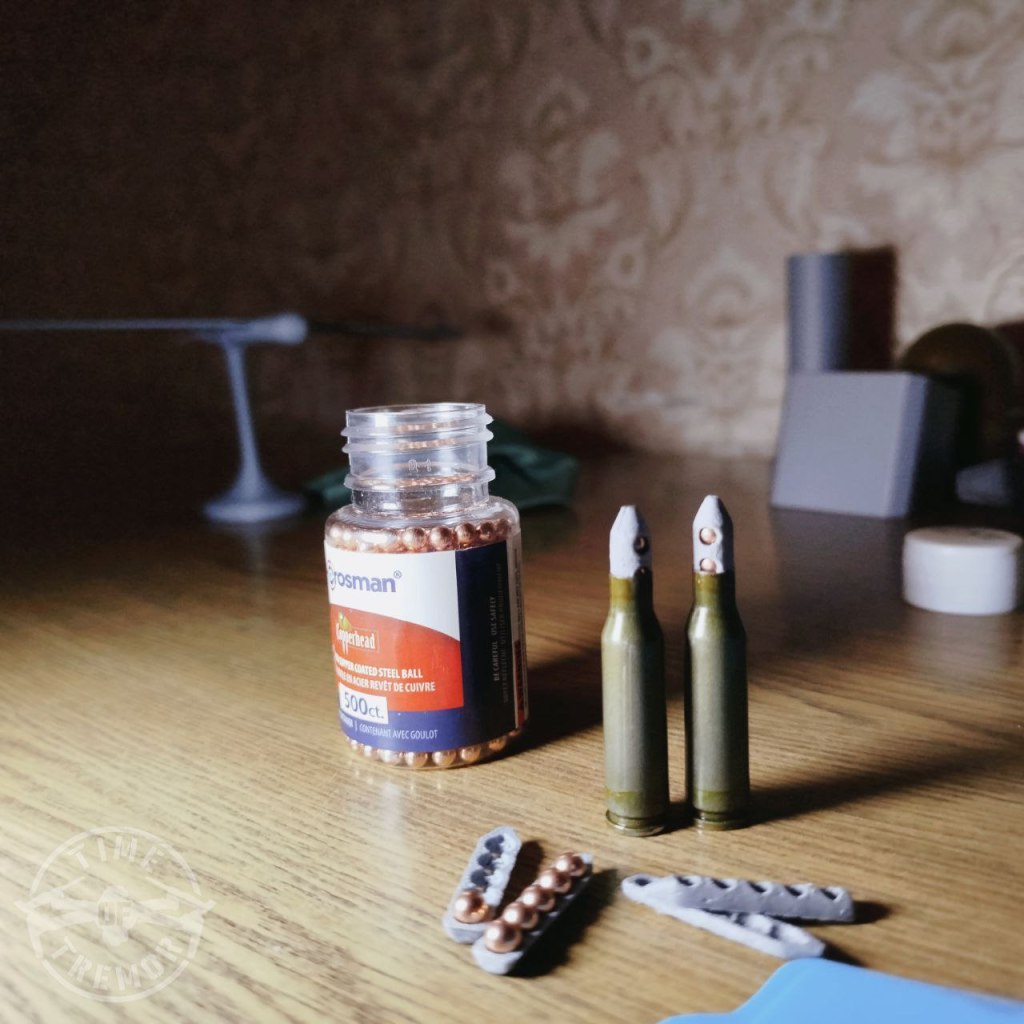
On 26 February, another Russian Telegram channel, Time of Terror, which describes itself as run by a special forces drone group, shared a photograph of a cartridge loaded with sabot with the two halves of an empty sabot next to it, stating that they had been asked to develop the sabot by a subscriber and that tests were ongoing. The nose of sabot has a notably less pronounced point compared to the first example. A day later the same Telegram channel shared another photograph of the ammunition this time with a five-BB sabot, next to a bottle of Crosman copperhead BBs.
Several days later, on 2 March, a short video showing a version of the sabot without the pointed nose was shared. It appears that the point of the sabot’s nose has been filed down. The video’s captions reads [machine translated]: “Based on the feedback, certain modifications were made. After checking them and collecting feedback from other units, we will stop at the most working version.” The video shows a few bursts being fired and several hits on a target down range. The video appears to have been filmed somewhat close to the frontline.

Later the same day another photo of some of the ammunition was shared, notably with the sabots seated at different depths. The caption mentioned the changes that have been made based on feedback [machine translated]: “In the new version, the diameter of the bullet base was reduced by 0.2mm and a chamfer was added instead of rounding, the diameter of the first solid cut-ring was reduced, which ensures easier pressing.”
On 4 March, the same Telegram channel shared a video demonstrating the assembly of one of the rounds. The video shows the pulling of a bullet and then the filling of the sabot with five BBs before the two halves of the sabot are pressed together and placed in the cartridge and tapped home with a hammer. The video’s caption reads [machine translated]: “At present, we observe significant potential in the application of the proposed modernization. Tests are ongoing, collecting data, which is necessary for forming a final conclusion on this issue. It is proposed to begin developing a prototype of equipment for an accelerated pressing procedure.” This would suggest the use of a conventional bullet press rather than a pair of pliers and hammer.
The video also includes footage of testing showing the ammunition being fired at a small rectangle of cardboard. The first two strings have a horizontal spread but with most of the BBs appearing to hit the target. A series of bursts shows the more hits on the target. The engagement range appears to be around 20-25 metres.

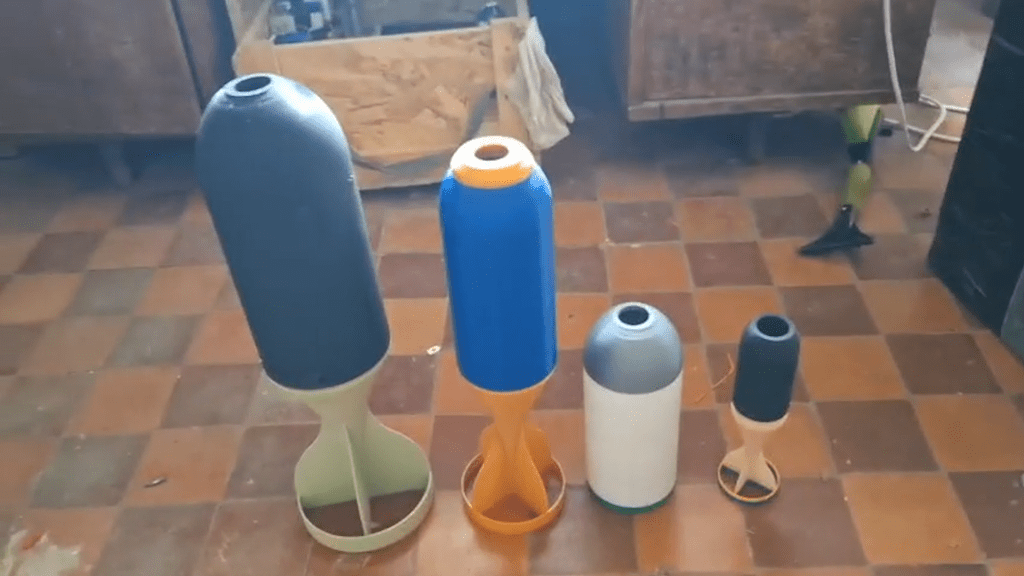
On the same day they also shared a short clip of a PKM machine gun being loaded with a belt holding three rounds of anti-drone 7.62x54mmR ammunition. Not much can be seen in the video but its likely that the 7.62 sabots can hold six or seven BBs. The caption notes [machine translated]: “In parallel, tests are being conducted for the modernized rifle bullet 7.62… Three rounds were fired in single mode. Results will be added later, looking ahead I will say that there is potential.”
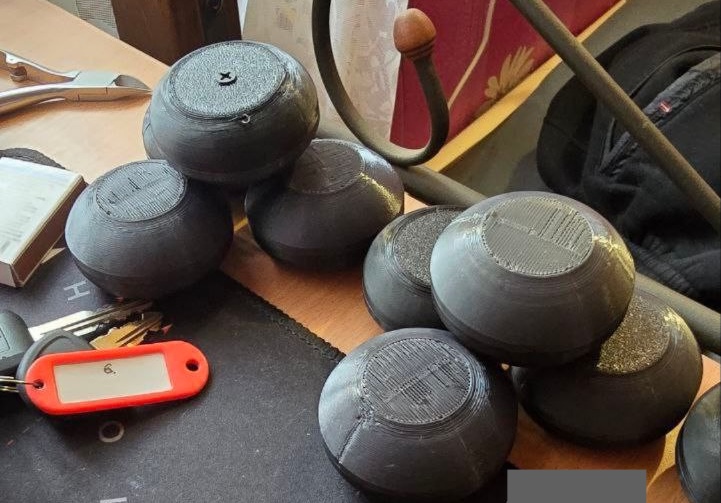
The usefulness of having a machine gun with a belt of the anti-drone buckshot ammunition is somewhat debatable, while perhaps not ideal for a patrol or an assault having a belt of anti-drone ammunition while defending a position may be useful. A post from 8 March, shows the development of a loading punch and the use of nail varnish on the nose of the round as a means of adhering the nose of the sabot together preventing it parting. The most recent post from Time of Terror features couple of photos of a large batch of five-BB sabots. The caption states: “made a batch of 10,000. The test variants showed a very satisfactory result. I am waiting for further feedback and hope to put an end to this process as soon as possible.”
The evolution of these makeshift anti-drone rounds has moved rapidly, with the shift to 3D printing in some areas leading to the potential production of thousands of rounds. While printing may expedite one element of production the loading of the sabots and the seating of them in cartridge cases remains a bottle neck in the manufacturing of the rounds.
Update – 3/4/25
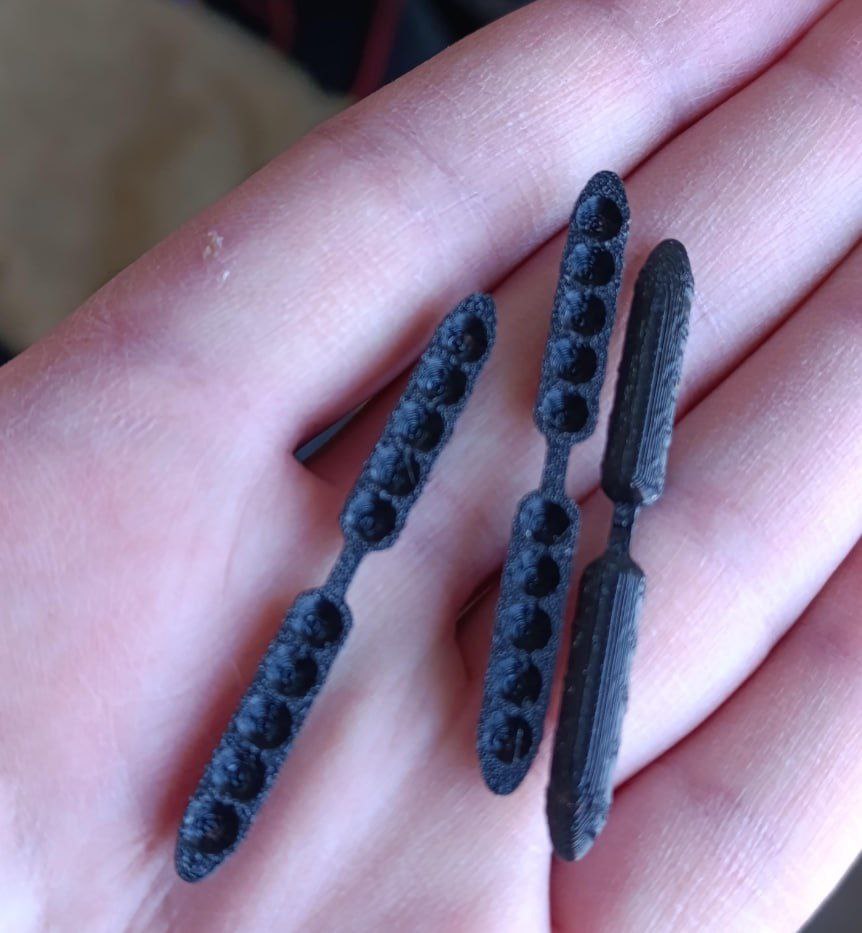
Another version of the 3D printed sabots has appeared on line in a video showing a Ukrainian combatant from the . Printed as once piece the sabot has five recesses for BBs. A video shows the firing of three rounds from an AK-74 pattern rifle. A target is shown approximately 5 metres away with a pattern of impacts from the anti-drone rounds.


Support Us: If you enjoyed this video and article please consider supporting our work here. We have some great perks available for Patreon Supporters – including early access to custom stickers and early access to videos! You can also find us on the History of Weapons & War app. Thank you for your support!