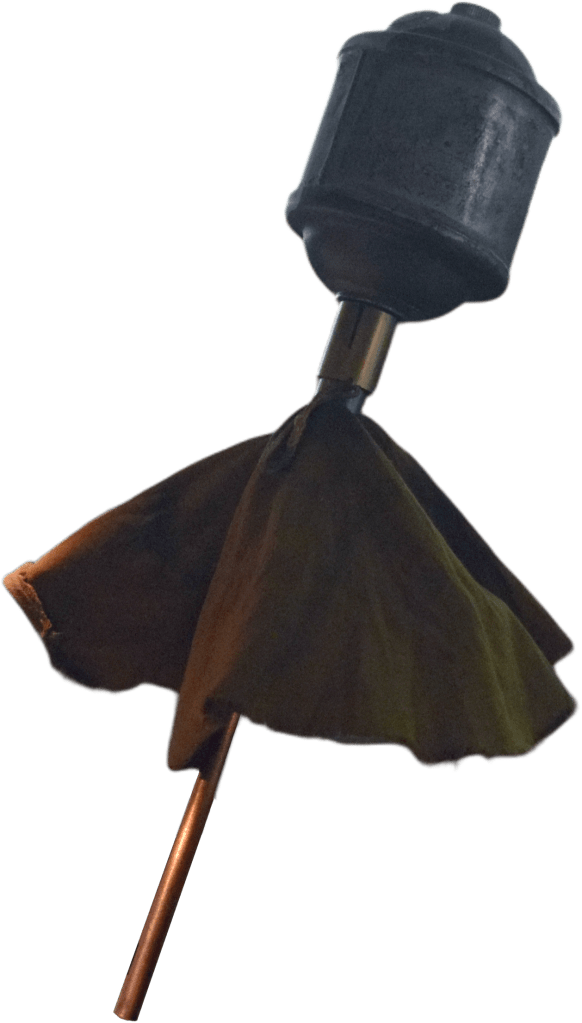
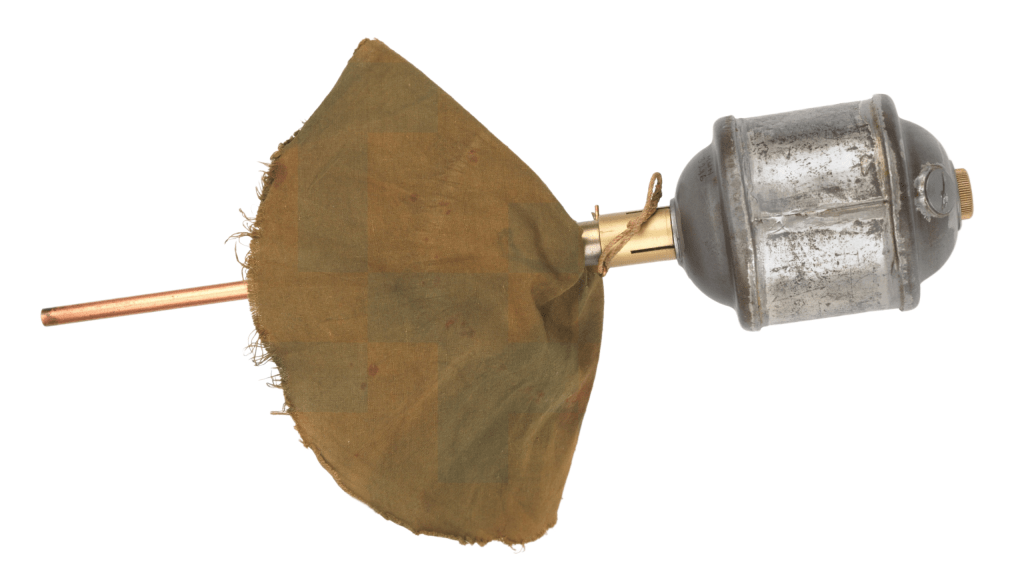
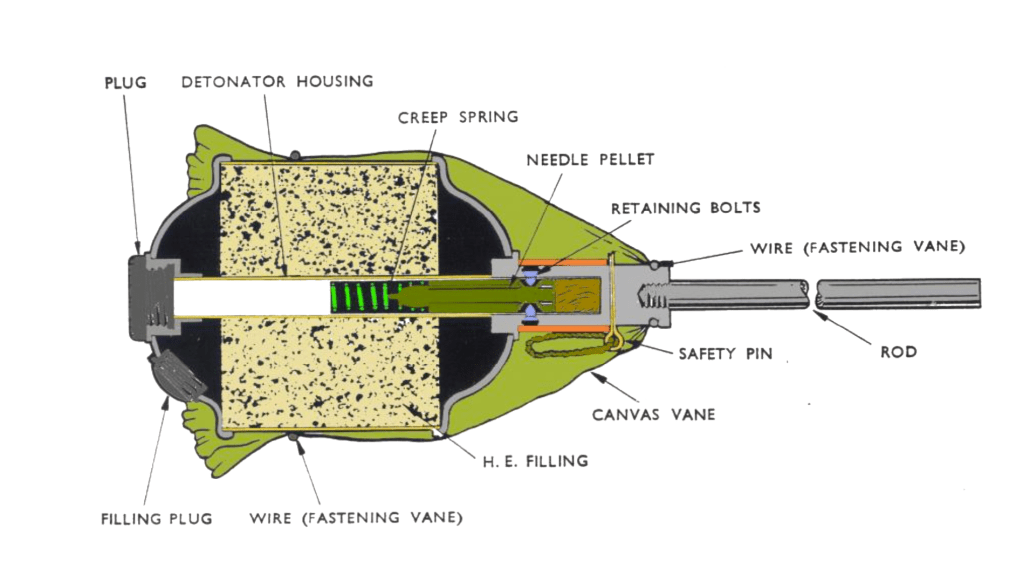
Earlier this summer, Polish PGN-60 rifle grenades began to appear in the hands of various Ukrainian units. These 68mm fin-stabilised, High-Explosive Anti-Tank (HEAT) grenades were developed in the 1950s, to provide Polish infantry with a ranged anti-tank and anti-personnel weapon.
Introduced in the early 1960s they were used in conjunction with the specially adapted Karabinek-granatnik wzór 1960 (Carbine-grenade launcher M1960) which had a spigot onto which the grenade’s tail was slid. The grenade was launched by a blank UNM ‘Universal Propellant Cartridge’. The 7.62×39mm wz.1960 and later wz.1960/72 are long out of Polish service, but it seems that the Polish military decided to retain the rifle grenades in storage. The rifle grenade concept was superseded in Polish service by the issuing of the lightweight RPG-76 Komar anti-armour rocket propelled grenade. These have also appeared in Ukraine.

The stated penetrating power of the PGN-60 varies depending on the source; some say 160mm others suggest up to 200mm of RHA plate. The grenade itself is either Impact or Graze fuze initiated.
While we have seen use of improvised rifle grenades in Ukraine, it is unlikely the PGN-60s have been used for their original purpose, instead they appear to have been either harvested for their explosive content or used as warheads for FPV (First Person View) drones.
One example of the use of the rifle grenades by a drone team was shared by Joe McDonald, a British volunteer serving with the Ukrainian Marines in Kherson. Joe kindly shared some photos of a consignment of Polish rifle grenades his unit received in July. Included in the consignment were not only the PGN-60 HEAT grenades but also Polish KGN anti-personnel grenades. The first sighting of one of the KGN grenades came earlier, back in mid-April 2024. Sources suggest that the KGN grenades contain nearly 250 fragmentation pieces. One of Joe’s photograph shows 10 PGN-60s and five KGNs, along with their detached tail assemblies.
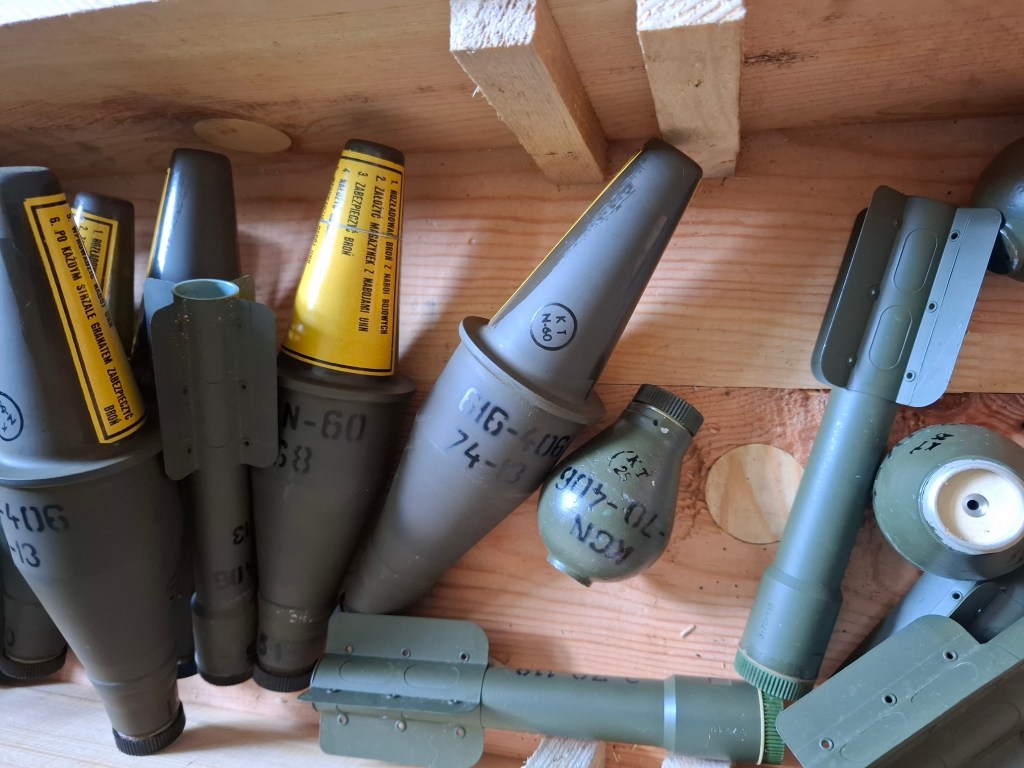

The yellow label markings are instructions on how to use the rifle grenade, they read [machine translated]:
- Unload the rifle
- Load magazine with propellant cartridges
- Put the rifle on safe
- Seat the grenade
- Chamber a propellant cartridge
- After each shot put the weapon on safe
Other markings include various factory, year and lot markings.

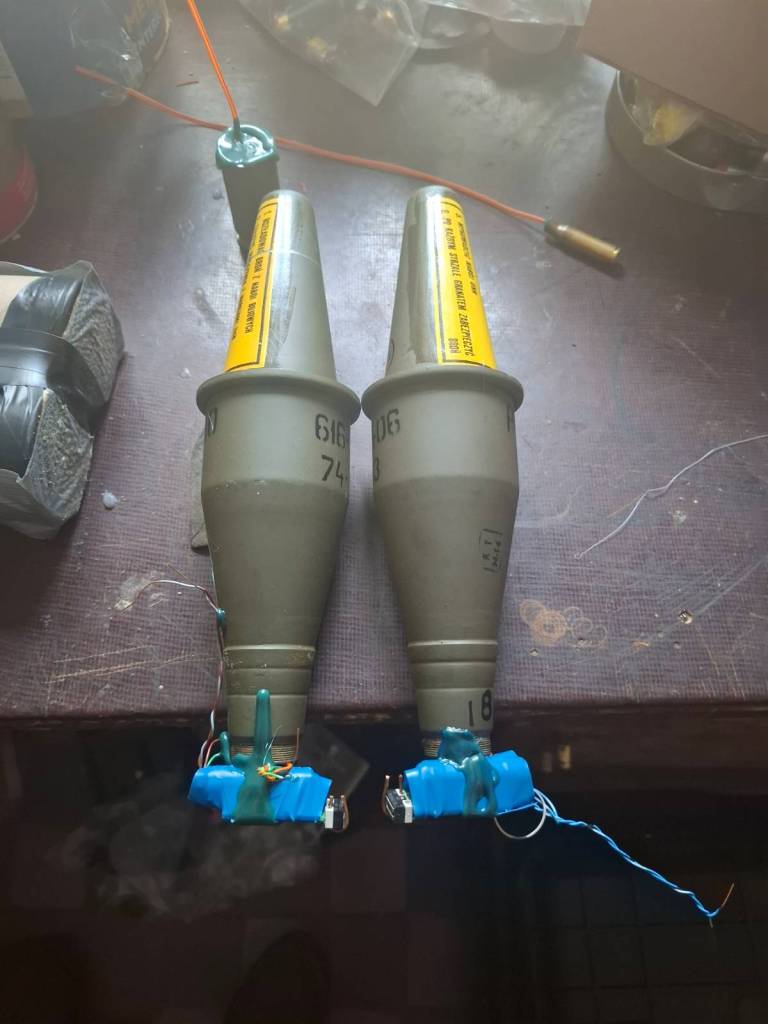
Joe noted that the KGN grenades have either been used as drone-dropped munitions or have been mounted on 7-inch first person view (FPV) drones in addition to a quantity of additional plastic explosive. Joe recently shared some video of five of the PGN-60 warheads electronically wired and ready for mounting on an FPV drone, these are some of the last of the grenades his unit received in July.

The PGN-60s aren’t the only interesting rifle grenades to turn up. In September a photograph of a 1990-dated French 58mm PAB F2 anti-tank rifle grenade was shared. France may have provided them for their explosive content or to accompany the 1,000 FAMAS F1 Valorise rifles which have been transferred to Ukraine. Only one image of this type of rifle grenade has surface so far but from the image it appears it’s tail assembly has been removed and is likely to be utilised as part of an FPV.

It is currently unclear just how many Polish and French rifle grenades have been transferred to Ukraine. The imagery sample featured in this article/video represents all of the imagery I have been able to find. If you have come across any additional sightings of the grenades I’d love to hear from you.
Special thanks to Joe for his help with this video. Check out Joe’s channel here.
Update – 27/10/25:
Another PGN-60 was seen in a short video shared by an officer with Ukraine’s Unmanned Systems Forces in February 2024.

Bibliography:
Karabinek-granatnik wzór 1960/72 Rifle-grenade launcher, AK-Info, (source)
Grenades for rifle-grenade launcher systems kbkg wz.60 and kbkg wz.60/72, AK-Info, (source)
PGN-60, CAT-UXO, (source)
Support Us: If you enjoyed this video and article please consider supporting our work here. We have some great perks available for Patreon Supporters – including early access to custom stickers and early access to videos! You can also find us on the History of Weapons & War app. Thank you for your support!