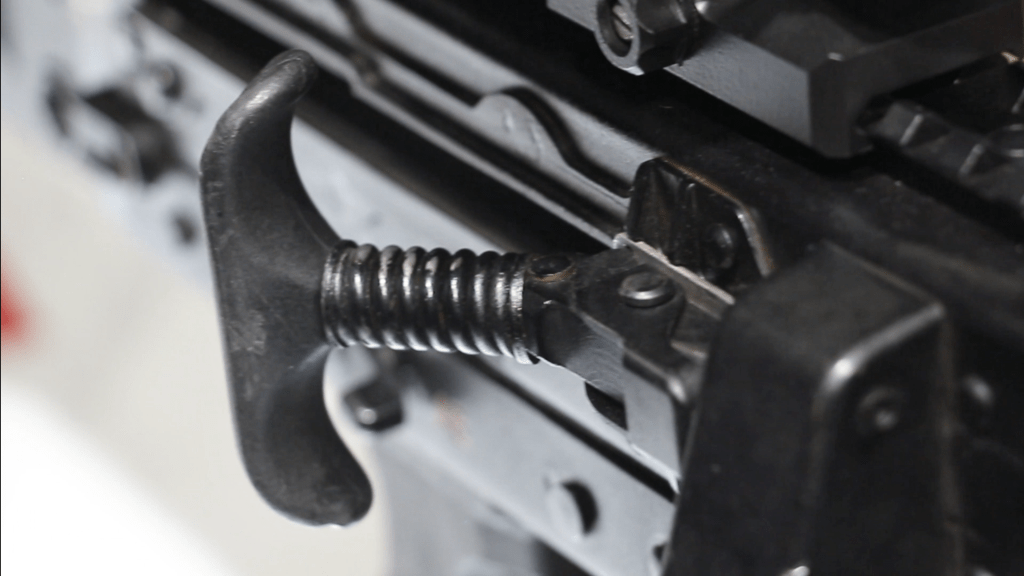
A couple of months ago we took a look at Kalashnikov Concern’s new belt-fed machine gun, the RPL-20. That video was made in collaboration with firearms researcher Deni Almaskhanov, of Just Guns. Deni has also kindly shared some video of Kalashnikov’s new GP-46 grenade launcher.
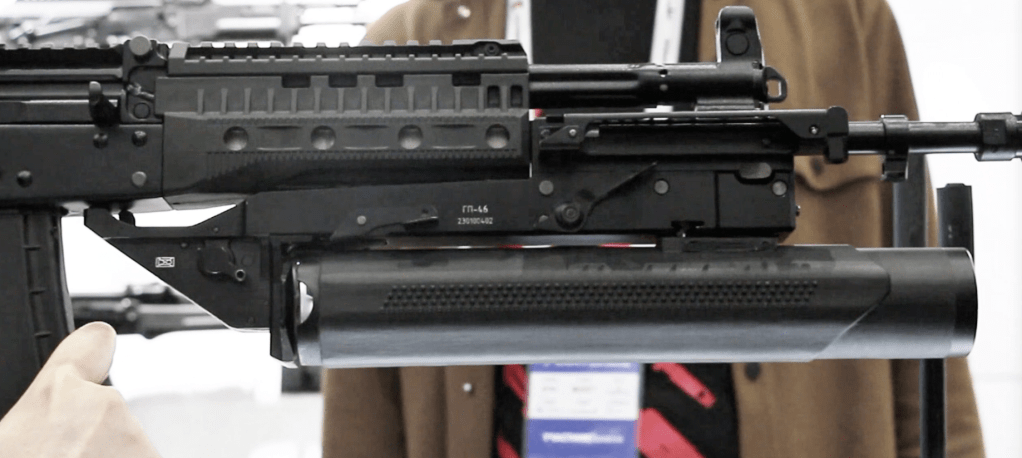
The GP-46 was unveiled by Kalasknikov Concern at the ‘Army-2024’ exposition in August. Unlike other Russian underbarrel grenade launchers the GP-46 is chambered in the Western 40x46mm, the low velocity grenades used in launchers like the M203, and M320. Despite its first public appearance in 2024, the visible serial number indicates that the launcher on display was actually made in 2023. It was reportedly developed in 2023-24 by a design team led by Kalashnikov’s chief small arms designer Sergei Vladimirovich Urzhumtsev.

The GP-46 features ambidextrous controls with mechanical safety selectors, locking mechanism catches and triggers found on both sides of the launcher. The launcher can be mounted on all previous AK-pattern rifles which are able to mount UBGLs.
Kalashnikov Concern list its specs as:
- Length: 380mm
- Caliber: 40mm
- Weight: 1.6kg
- Rate of Fire: 5-6 rounds per minute
It’s currently unclear what range of 40x46mm grenades are available for the GP-46 but Kalashnikov’s promotional video on the launcher featured a grenade tipped with what appears to be a VGM fuze used on VOG-pattern grenades.

Interestingly, Deni noted that the unconventional trigger placement is not entirely new for Kalashnikov. In 2018, Kalashnikov patented another grenade launcher, seemingly one designed around VOG-pattern grenades. That UBGL’s the trigger mechanism was located on the outer cover of the barrel itself. Deni explains that “the latch was to be pressed, unlocking the movement of the cover, the cover was to be pulled backwards. Such design was implemented in order to allow for a double-action trigger action while not requiring lots of strength from the trigger finger”. Deni believes that the GP-46 seems to be following the same philosophy while avoiding overtly complicated design elements.

The GP-46 is aimed using iron sights located on the right side of the launcher. The rear sight allows for shooting at ranges starting at 50 meters, out to 400 meters. The sights also feature a built-in mechanical rangefinder, calibrated for 170 cm (5’7) tall target. Interestingly, the 5.56×45mm AK-19 Type 3 that was used to showcase the grenade launcher at ARMY-2024, also featured what seems to be a new ACOG-style prismatic scope by Dedal-NV, one of Russia’s premium optics manufacturers. Deni notes that the scope featured both rifle and grenade launcher reticles.
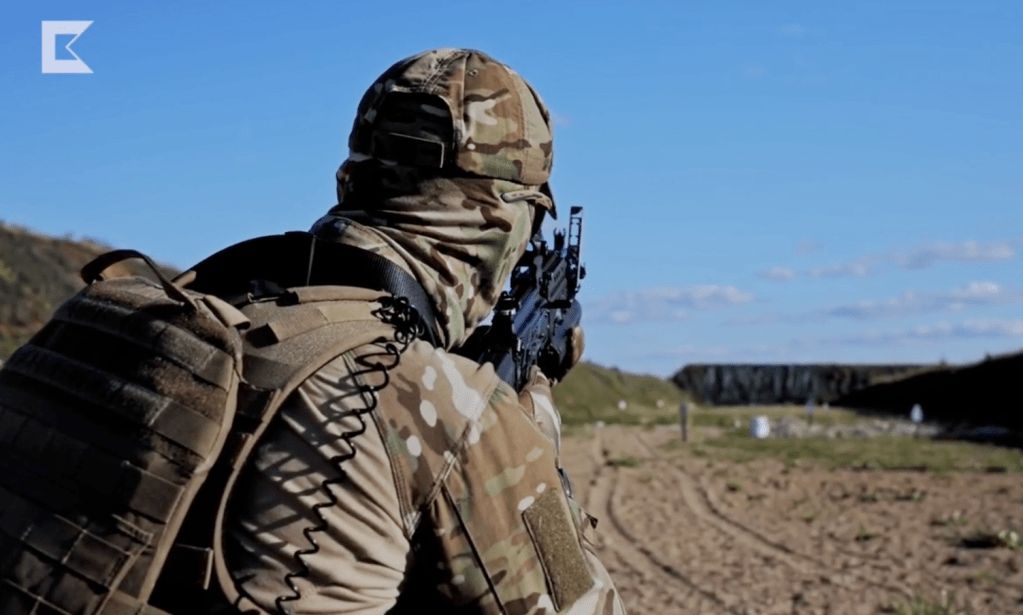

It is unlikely the Russian armed forces will be moving away from their in-service 40mm grenade launchers any time soon and it is worth noting that both the GP-46 and the AK-19 it was mounted on are primarily export models. One potential interesting international customer may be India, which has already contracted with Kalashnikov previously. India recently adopted the AK-203, with plans to produce the rifles under license in India.
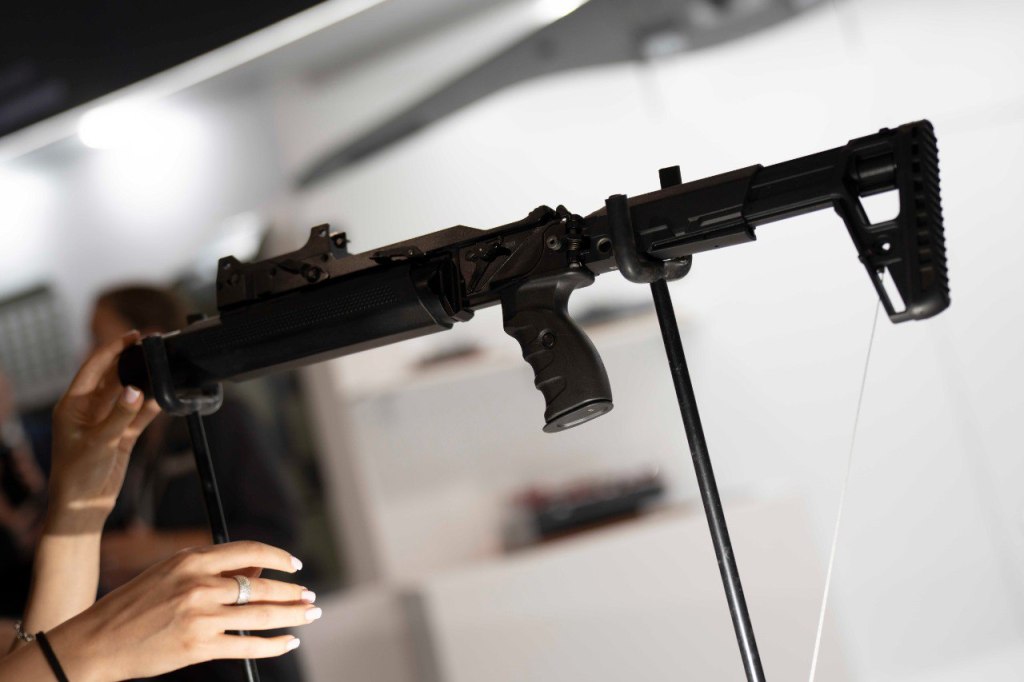

Intriguingly, what sets this this grenade launcher apart from the majority of previous Russian UBGLs is the special module that allows it to be used as a stand-alone launcher. The GP-46 mounts onto a stock chassis which consists of a full-size AK-12 Type 1 pistol grip and an adjustable AK-12 Type 3 buttstock. Given the large number of stand alone stock systems for launchers like the GP-25 which have emerged as a result of the war in Ukraine this development isn’t surprising.
Special thanks to Deni for sharing this footage and information with me so I can bring you guys this video. Please do check out Deni’s pages – Telegram, Instagram, Youtube.
Support Us: If you enjoyed this video and article please consider supporting our work here. We have some great perks available for Patreon Supporters – including early access to custom stickers and early access to videos! You can also find us on the History of Weapons & War app. Thank you for your support!